bore gauge
A bore gauge is a precision instrument used to measure the internal diameter of a hole or cylinder. It's essential for ensuring accuracy in manufacturing, engineering, and automotive industries. Choosing the right bore gauge and using it correctly can significantly improve the quality and reliability of your work.Understanding Bore GaugesWhat is a Bore Gauge?A bore gauge, also known as a cylinder gauge, is a measuring tool designed to determine the internal diameter of a hole, cylinder, or pipe. These gauges are vital for ensuring dimensional accuracy and consistency in various applications.Types of Bore GaugesThere are several types of bore gauges available, each suited for different applications and levels of precision: Dial Bore Gauges: These are the most common type, featuring a dial indicator that displays the measurement reading. They are versatile and relatively easy to use. Digital Bore Gauges: These gauges use a digital display for readings, offering improved accuracy and ease of reading. They often have features like data storage and output. Telescoping Bore Gauges (Small Hole Gauges): These gauges consist of a handle with telescoping arms that expand to fit the bore. The size is then measured with an external micrometer. Useful for small bores. Small Hole Gauges: These are similar to telescoping gauges but designed for even smaller bores. Air Bore Gauges: These gauges use air pressure to measure the bore diameter. They offer high precision and are suitable for automated measurement systems.Key Components of a Bore GaugeUnderstanding the key components will help you better utilize your bore gauge: Measuring Head: The part that enters the bore and makes contact with the internal surface. Dial Indicator (or Digital Display): Shows the measurement reading. Centralizing Shoe: Helps align the gauge within the bore for accurate measurement. Extension Rods: Used to extend the gauge's reach for deeper bores.Choosing the Right Bore GaugeSelecting the appropriate bore gauge depends on several factors: Bore Size: Ensure the gauge's measuring range matches the bore size you need to measure. Accuracy Requirements: Choose a gauge with the necessary accuracy for your application. Digital gauges typically offer higher accuracy. Application: Consider the specific application and environment. For example, for very small bores, a small hole gauge set is necessary. Budget: Prices vary widely depending on the type and features.How to Use a Bore GaugeProper usage is crucial for accurate measurements. Here's a step-by-step guide: Calibration: Calibrate the bore gauge using a setting ring or a known standard. Preparation: Clean the bore surface and the measuring head of the gauge. Insertion: Insert the measuring head into the bore. Rocking Motion: Gently rock the gauge back and forth to find the minimum reading on the dial indicator. This indicates the true diameter. Reading: Record the measurement reading. Multiple Measurements: Take multiple measurements at different points within the bore to check for ovality or taper.Applications of Bore GaugesBore gauges are used in a wide range of industries and applications: Automotive: Measuring cylinder bores, valve guides, and bearing bores. Manufacturing: Quality control of machined parts. Engineering: Dimensional inspection of components. Aerospace: Precision measurement of engine parts and hydraulic systems.Troubleshooting Common IssuesHere are some common issues and their solutions: Inaccurate Readings: Ensure the gauge is properly calibrated and the bore surface is clean. Also, verify that the centralizing shoe is correctly positioned. Gauge Not Entering Bore: Check for obstructions in the bore and ensure the measuring head is properly adjusted. Difficulty Reading Dial Indicator: Use a digital bore gauge for easier reading, or ensure adequate lighting.Maintenance and CareProper maintenance will extend the life of your bore gauge: Cleaning: Clean the gauge after each use to remove dirt and debris. Storage: Store the gauge in a protective case to prevent damage. Calibration: Regularly calibrate the gauge to ensure accuracy.Where to Buy Bore GaugesBore gauges can be purchased from various sources: Industrial Supply Stores: Grainger, MSC Industrial Supply, and other industrial suppliers. Online Retailers: Amazon, eBay, and specialized tool websites. Specialty Tool Suppliers: Companies that specialize in measuring tools, like Wayleading Tools, offer a wide selection and expert advice.Examples and TemplatesExample Measurement ScenarioLet's say you're measuring the cylinder bore of an engine. You would first select a bore gauge with a range that includes the expected bore diameter. Then, you would calibrate the gauge using a setting ring. After cleaning the cylinder bore, you would insert the gauge and rock it back and forth to find the minimum reading. This reading would be the cylinder bore diameter. Taking several measurements at different locations along the cylinder wall will indicate if there is any taper or ovality.Table: Common Bore Sizes and Applicable Bore Gauges Bore Size (mm) Recommended Bore Gauge Type Example Model 6 - 10 Small Hole Gauge Starrett S565WB 10 - 150 Dial Bore Gauge Mitutoyo Large Capacity Bore Gauge Fowler ConclusionA bore gauge is an indispensable tool for anyone needing to accurately measure internal diameters. By understanding the different types, choosing the right gauge for your needs, and following proper usage and maintenance procedures, you can ensure precise and reliable measurements. Remember to consider factors like bore size, accuracy requirements, and application when selecting a bore gauge. With the right tool and technique, you can achieve accurate and consistent results in your work.External Resources Mitutoyo Official Website: https://www.mitutoyo.com/ Starrett Official Website: https://www.starrett.com/
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 Inch HSS 1/2″ Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision
Inch HSS 1/2″ Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision -
 GTN Parting & Grooving Insert For NCIH Blade
GTN Parting & Grooving Insert For NCIH Blade -
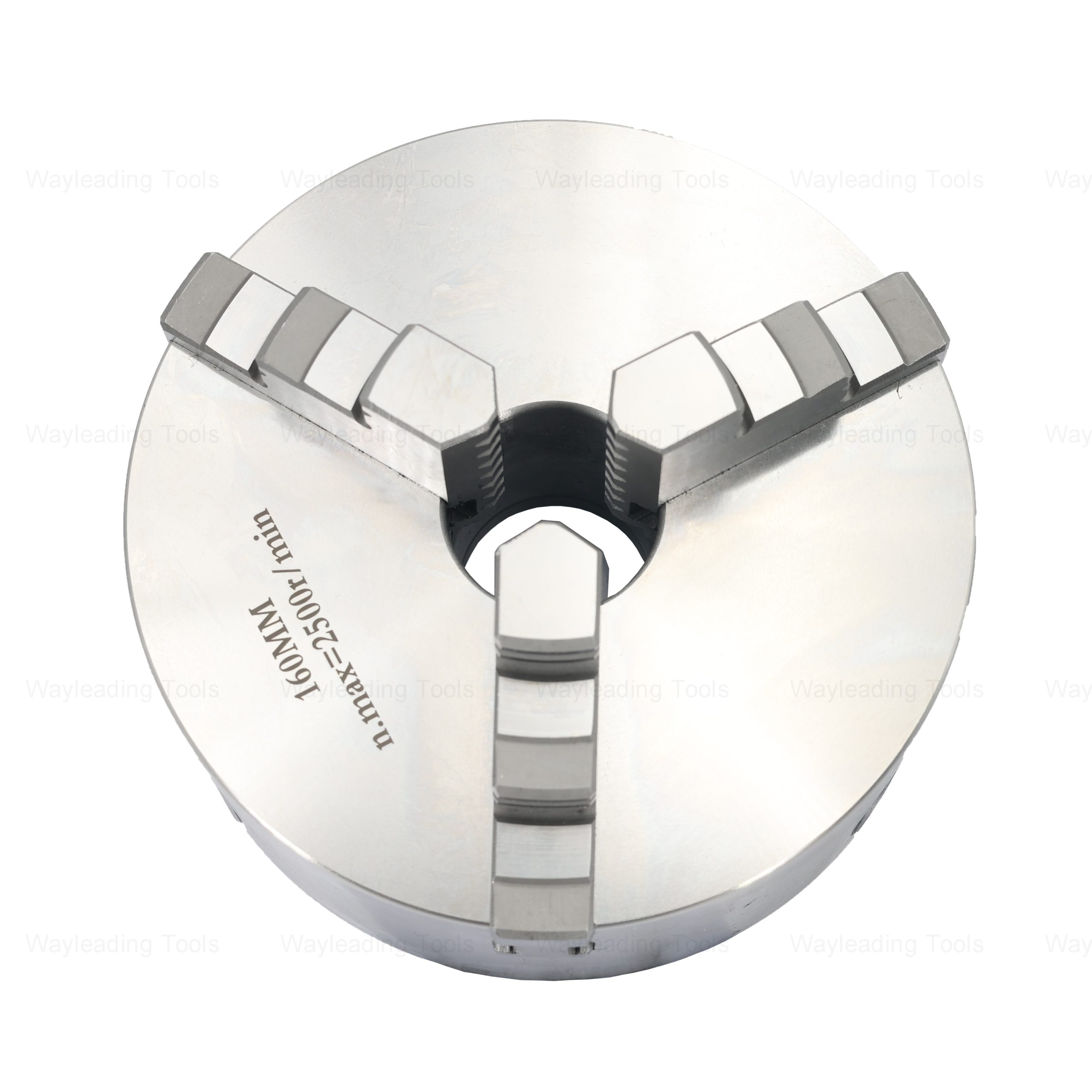 K11 Series 3-Jaw Self-Centering Lathe Chuck – Scroll Type, for Manual Lathes
K11 Series 3-Jaw Self-Centering Lathe Chuck – Scroll Type, for Manual Lathes -
 Precision V Block And Clamps Set With High Quality Type
Precision V Block And Clamps Set With High Quality Type -
 HSS Metric Plain Metal Slitting Saws For Industrial
HSS Metric Plain Metal Slitting Saws For Industrial -
 Electronic Digital Height Gauge From 300 to 2000mm
Electronic Digital Height Gauge From 300 to 2000mm -
 Type D Ball Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type D Ball Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
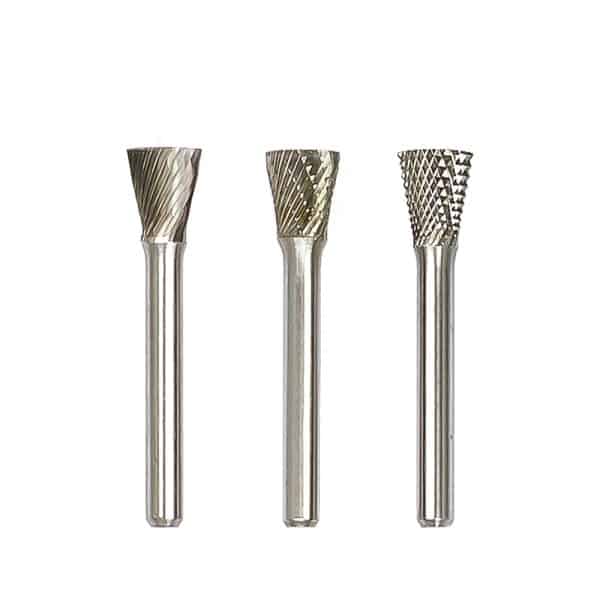 Type N Inverted Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type N Inverted Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
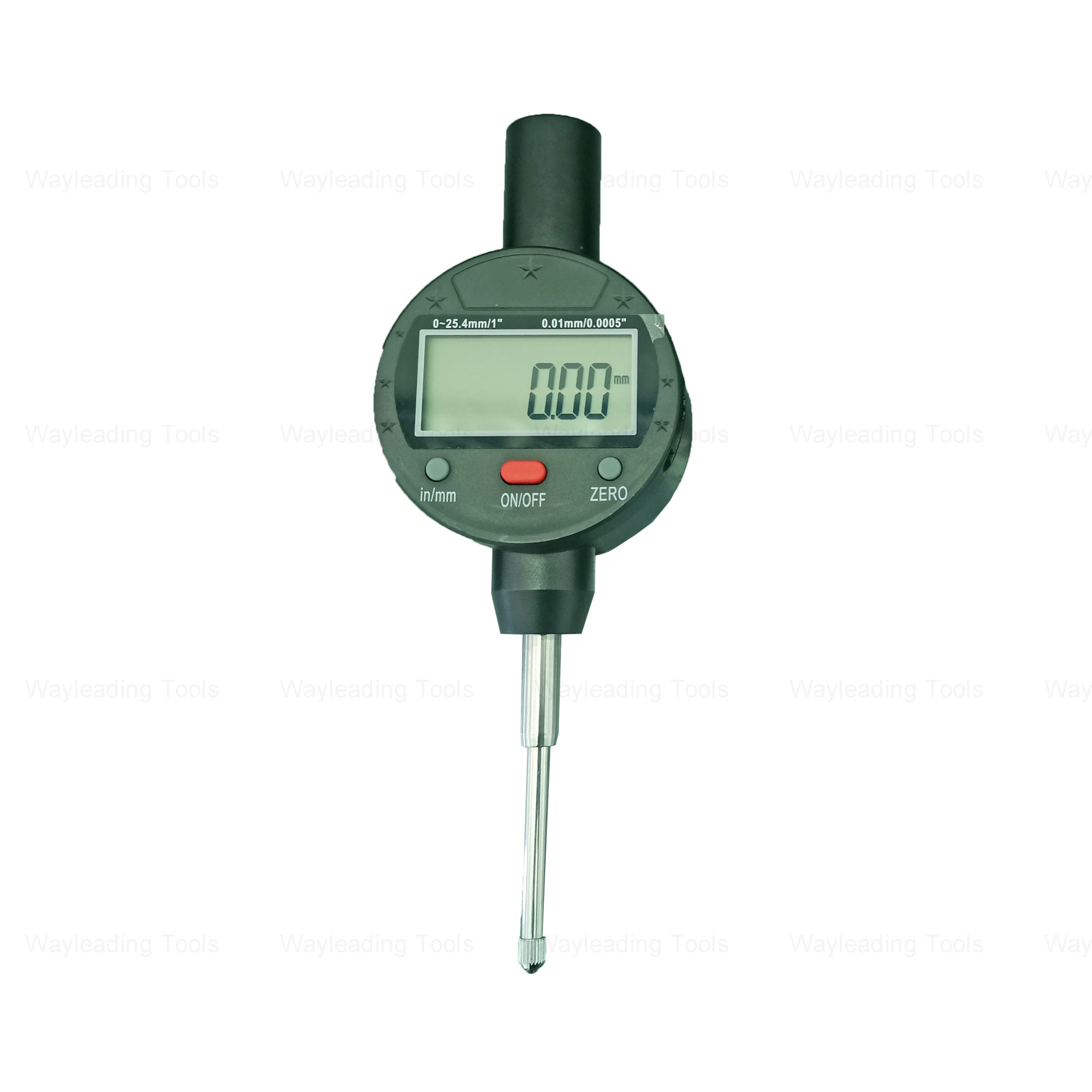 Digital Indicator – Precision Type, Inch/Metric, Industrial Grade
Digital Indicator – Precision Type, Inch/Metric, Industrial Grade -
 Vernier Height Gauge With Magnifier With Adjustable Main Bean
Vernier Height Gauge With Magnifier With Adjustable Main Bean -
 Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank
Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank -
 Precision Dial Caliper Of Double Shock-Proof For Industrial
Precision Dial Caliper Of Double Shock-Proof For Industrial