bspt threading insert
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) threading inserts are essential components for creating reliable and leak-proof connections in various fluid and gas systems. This guide explores the nuances of BSPT threading inserts, covering their applications, selection criteria, and best practices for installation, helping you ensure optimal performance and longevity in your projects.What is BSPT Threading?BSPT stands for British Standard Pipe Taper, a technical standard for screw threads that is commonly used worldwide for sealing pipes and fittings by threading them together. Unlike NPT (National Pipe Taper) which is also a tapered thread standard, BSPT threads have a 55-degree thread angle, whereas NPT has a 60-degree angle. The taper on a BSPT thread allows for a tighter seal as the threads are tightened.Key Differences Between BSPT and BSPIt's crucial to distinguish between BSPT and BSP (British Standard Pipe). While both are British standards for pipe threads, BSPT is tapered, and BSP (also known as BSPP - British Standard Pipe Parallel) is parallel. This difference is critical in selecting the correct insert for your application. Using a tapered insert in a parallel threaded hole, or vice versa, will likely result in a leak.Applications of BSPT Threading InsertsBSPT threading inserts find widespread use across diverse industries due to their ability to create secure and leak-resistant connections. Some common applications include: Plumbing: Connecting pipes and fittings in water and gas systems. Hydraulics: Creating sealed connections in hydraulic equipment. Pneumatics: Ensuring airtight seals in pneumatic systems. Manufacturing: Integrating fluid and gas lines in machinery. Automotive: Connecting fuel and coolant lines.Choosing the Right BSPT Threading InsertSelecting the appropriate BSPT threading insert is crucial for ensuring a reliable and long-lasting connection. Consider the following factors:Material CompatibilityEnsure the insert material is compatible with the fluid or gas being conveyed and the materials of the connected components. Common materials for BSPT threading inserts include: Brass: Good corrosion resistance, suitable for water and gas applications. Stainless Steel: Excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for harsh environments and aggressive media. Carbon Steel: High strength, but requires protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Engineered Plastics (e.g., PEEK, PTFE): Chemical resistance and low friction, suitable for specialized applications.Thread Size and DimensionsVerify the thread size matches the mating components. BSPT thread sizes are designated by nominal bore size in inches, such as 1/8', 1/4', 3/8', 1/2', 3/4', 1', etc. Ensure you are using the correct size for your application. Refer to a BSPT thread chart for precise dimensions and tolerances.Insert Type and DesignDifferent insert designs offer varying levels of performance and ease of installation. Common types include: Solid Inserts: Offer maximum strength and durability. Slotted Inserts: Facilitate installation and removal. Self-Tapping Inserts: Create their own threads during installation, simplifying the process. Wire Thread Inserts (Helicoil): Used for thread repair or to strengthen threads in weaker materials.Installation Best Practices for BSPT Threading InsertsProper installation is essential for achieving a leak-proof seal and preventing damage to the threads. Follow these best practices: Prepare the Threads: Clean the threads of both the insert and the mating component. Remove any debris or burrs. Apply Thread Sealant: Use a suitable thread sealant or Teflon tape to ensure a tight seal. Apply the sealant evenly and sparingly. Hand-Tighten: Start by hand-tightening the insert into the fitting or component. Torque to Specification: Use a torque wrench to tighten the insert to the manufacturer's specified torque value. Over-tightening can damage the threads and cause leaks. Inspect for Leaks: After installation, test the connection for leaks using appropriate testing methods.Troubleshooting Common IssuesEven with proper installation, issues can sometimes arise. Here are some common problems and solutions: Leaks: Check for proper thread sealant application, correct torque, and thread damage. Cross-Threading: Ensure the insert is properly aligned before tightening. Do not force the insert if it resists threading. Stripped Threads: Consider using a wire thread insert (Helicoil) to repair the damaged threads.Where to Buy BSPT Threading InsertsYou can purchase BSPT threading inserts from various sources, including: Industrial Supply Companies: Companies like Wayleading Tools offer a wide selection of inserts and related products. Online Retailers: Many online retailers sell threading inserts. Local Hardware Stores: Some hardware stores carry a limited selection of inserts.BSPT Thread Size ChartHere's a simplified chart showcasing common BSPT thread sizes (approximate values). Always consult the manufacturer's specifications for exact dimensions. Nominal Thread Size (inches) Threads Per Inch (TPI) Major Diameter (mm - approximate) 1/8' 28 9./4' 19 13./8' 19 16./2' 14 21./4' 14 26.' 11 33.3 Disclaimer: This table provides approximate values. Consult official standards for precise measurements.ConclusionUnderstanding BSPT threading inserts and their proper application is crucial for creating reliable and leak-proof connections. By carefully considering material compatibility, thread size, insert type, and installation best practices, you can ensure the success of your projects. Always refer to manufacturer specifications and consult with experts when needed to achieve optimal results. For high-quality tooling, consider exploring Wayleading Tools' extensive catalog.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 Precision Digital Caliper Of With Metric & Inch Size For Industrial
Precision Digital Caliper Of With Metric & Inch Size For Industrial -
 Precision V Block And Clamps Set With Customized Type
Precision V Block And Clamps Set With Customized Type -
 DIN6537L Metric Solid Carbide Twist Drill With Internal Coolant & External Coolant
DIN6537L Metric Solid Carbide Twist Drill With Internal Coolant & External Coolant -
 Type B Light Duty Deburring Tool Set With Deburring Holder And Deburring Blade
Type B Light Duty Deburring Tool Set With Deburring Holder And Deburring Blade -
 HSS Metric Plain Metal Slitting Saws For Industrial
HSS Metric Plain Metal Slitting Saws For Industrial -
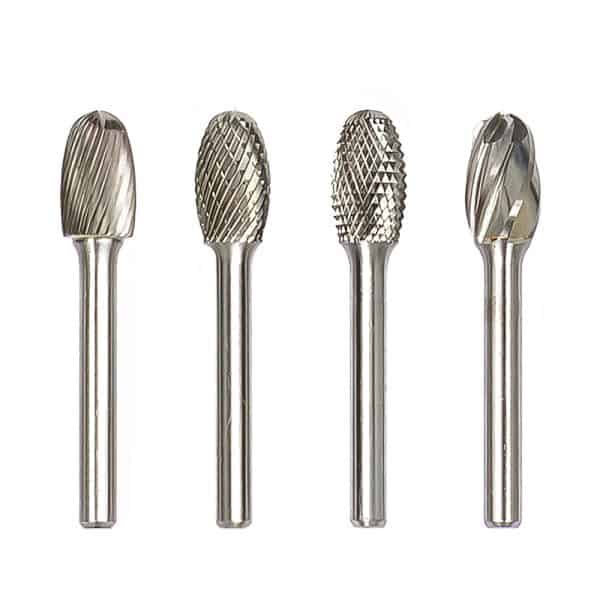 Type E Oval Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type E Oval Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
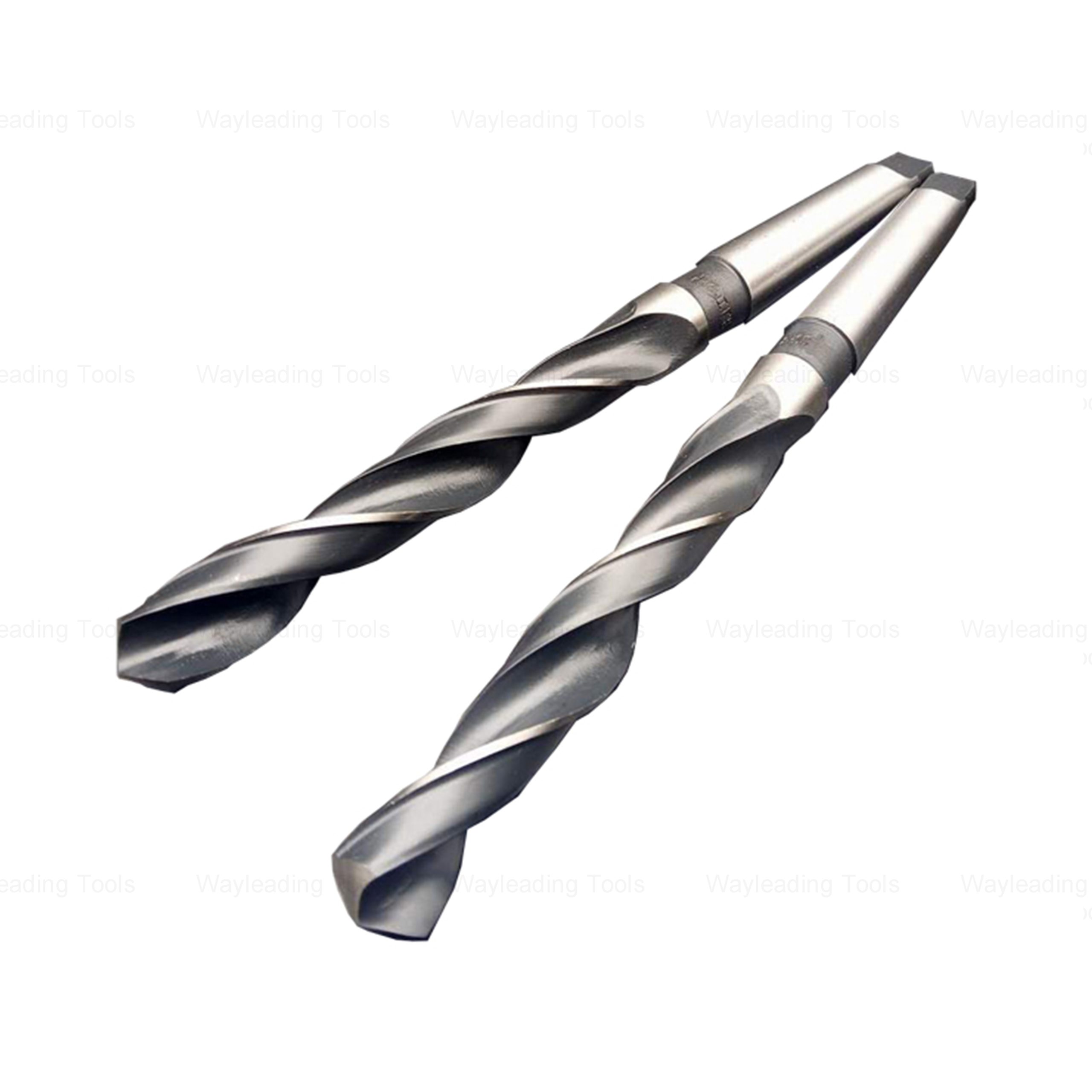 HSS Metric Taper Shank Twist Drills for High-Precision Metal Cutting
HSS Metric Taper Shank Twist Drills for High-Precision Metal Cutting -
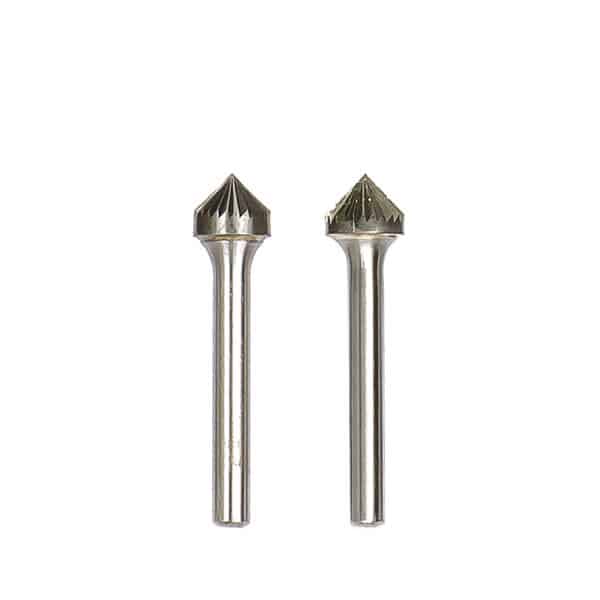 Type K-90 Degree Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type K-90 Degree Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 Precision V Block Set With High Quality Type
Precision V Block Set With High Quality Type -
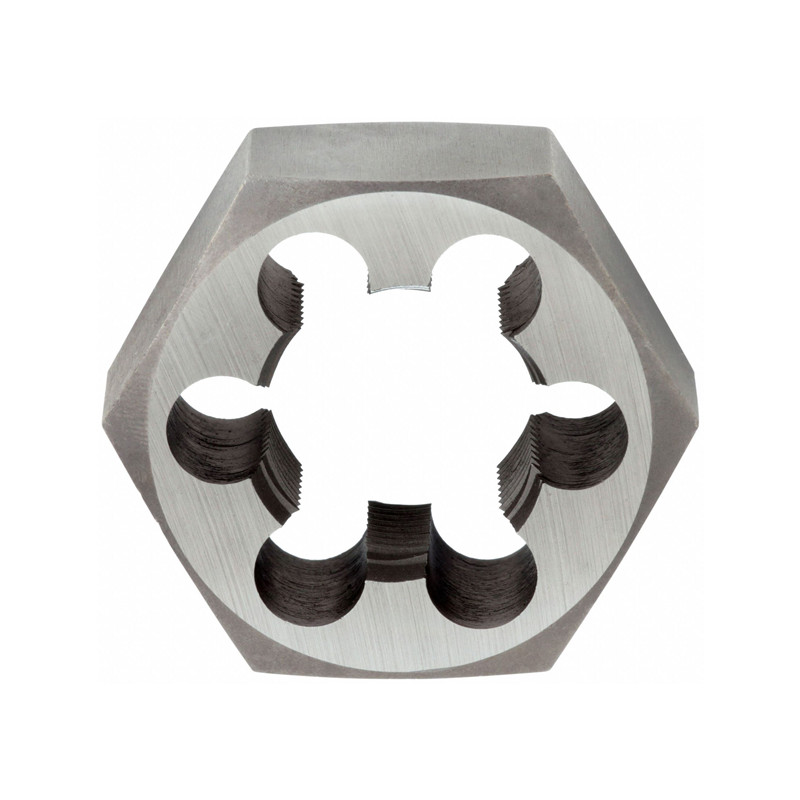 ISO Metric Hexagon Die With Right Hand
ISO Metric Hexagon Die With Right Hand -
 Stub Milling Machine Arbor With NT, R8 and MT Shank
Stub Milling Machine Arbor With NT, R8 and MT Shank -
 Vernier Height Gauge With Magnifier With Adjustable Main Bean
Vernier Height Gauge With Magnifier With Adjustable Main Bean
Related search
Related search- left hand drill bits Manufacturers
- center drill set Factories
- sk collet chuck Factories
- SE indexable thread turning tool Manufacturers
- 90 degree indexable face mills Factories
- Threading Insert Suppliers
- Wholesale thread pitch gauges
- semt insert Factories
- indexable threading mill Suppliers
- AG55 threading insert