carbide center
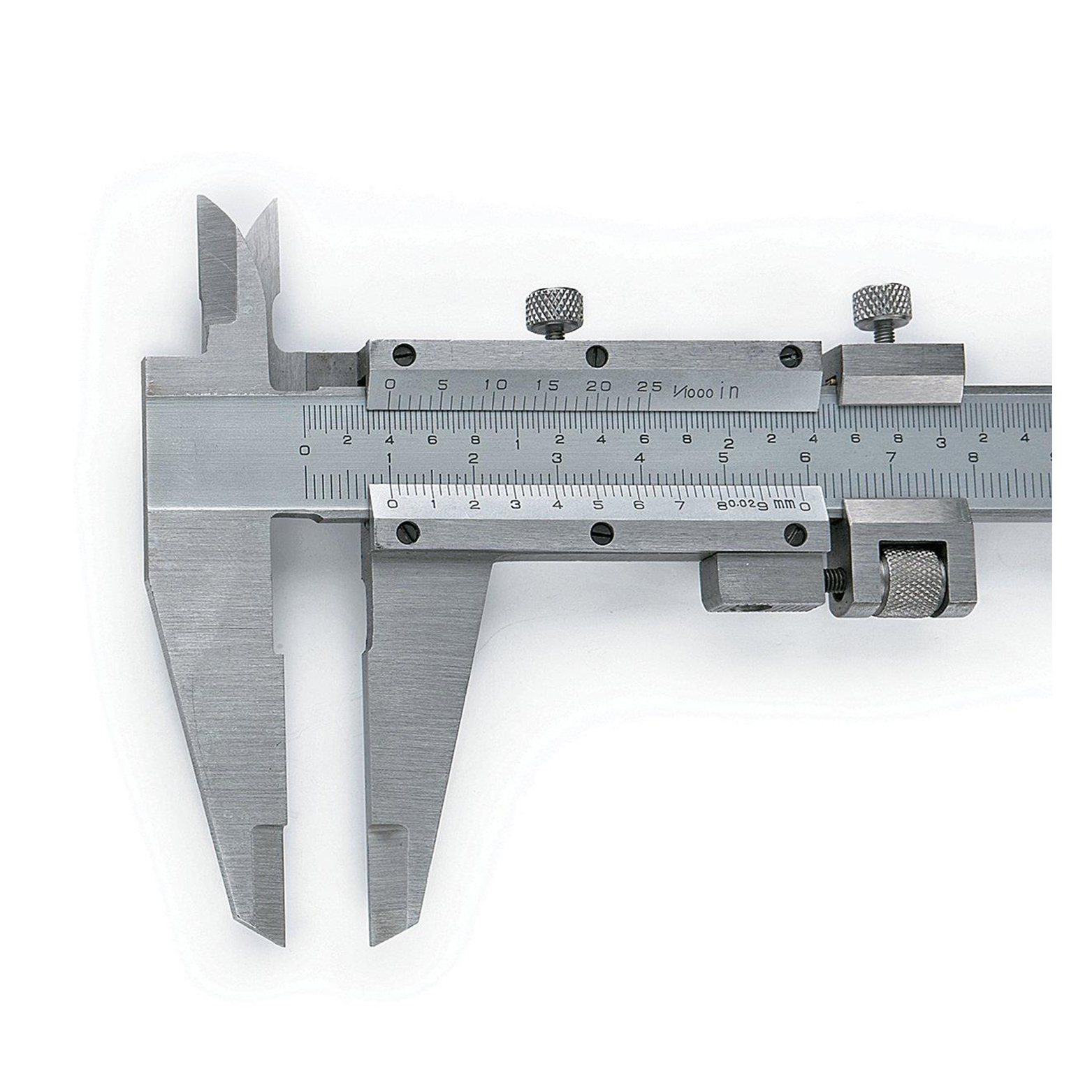
Carbide centers are essential tools used in metalworking lathes to provide stable and accurate support for workpieces during machining. They feature a hard carbide tip that resists wear and deformation, ensuring precise turning, grinding, and other operations. This guide explores the different types, applications, and maintenance of carbide centers, helping you select the right one for your specific needs.Understanding Carbide CentersCarbide centers are a critical component in lathe operations. They are designed to be mounted in the tailstock of a lathe, providing a precise and stable pivot point for the workpiece. The 'center' of the name refers to their primary function: centering the workpiece so it rotates true to the lathe's axis.What is Carbide?Carbide is a compound composed of carbon and a less electronegative element. In the context of cutting tools, including carbide centers, the term usually refers to tungsten carbide (WC). Tungsten carbide is an exceptionally hard and wear-resistant material, making it ideal for applications involving high speeds, heavy loads, and abrasive materials. It is usually combined with a binder metal, typically cobalt, to improve its toughness and resistance to fracture. The percentage of cobalt affects the properties of the carbide; higher cobalt content generally increases toughness but reduces hardness.Why Use Carbide Centers?The primary benefits of using carbide centers compared to other materials like hardened steel centers include: Increased Wear Resistance: Carbide's superior hardness significantly extends the life of the center, especially when working with abrasive materials. Improved Accuracy: The resistance to wear helps maintain the center's shape and point accuracy, leading to more precise machining. Reduced Downtime: Longer lifespan means less frequent replacements, minimizing downtime for tool changes. Higher Cutting Speeds: Carbide centers can withstand higher temperatures generated by faster cutting speeds, boosting productivity.Types of Carbide CentersCarbide centers are available in several different designs, each suited for specific applications.Live Centers (Revolving Centers)Live centers, also known as revolving centers, contain bearings that allow the center point to rotate with the workpiece. This reduces friction and heat buildup, enabling higher cutting speeds and heavier cuts. They are ideal for general turning operations and are offered by suppliers like Wayleading Tools. Live centers are especially beneficial for machining longer workpieces that require support at the tailstock.Features of Live Centers: Precision bearings for smooth rotation. Sealed designs to protect bearings from contaminants. Interchangeable points for different workpiece geometries.Dead Centers (Solid Centers)Dead centers, or solid centers, are stationary and do not rotate. The workpiece rotates against the dead center. While simpler in design, they require proper lubrication to prevent excessive friction and wear. Dead centers are generally used for light-duty applications or for finishing cuts where high precision is required.Features of Dead Centers: Simple and robust construction. High rigidity for accurate centering. Requires frequent lubrication.Bull Nose CentersBull nose centers have a larger diameter, blunt end that provides greater support and stability for large or irregularly shaped workpieces. They are often used when the workpiece has a pre-drilled hole or a machined feature that can accommodate the larger contact area.Combined Drill & CentersThese are specialized tools combining a center drill and a countersink. They are used to create a precise center hole in the workpiece, which then serves as a starting point for the carbide center. Using a combined drill & center ensures accurate alignment and prevents the drill from wandering.Selecting the Right Carbide CenterChoosing the appropriate carbide center is crucial for achieving optimal machining results. Consider the following factors:Workpiece MaterialThe material being machined significantly impacts the choice of carbide center. For abrasive materials like cast iron or hardened steel, a carbide center with a higher carbide content is recommended. Softer materials like aluminum or brass may not require the same level of wear resistance, and a standard carbide center or even a hardened steel center might suffice.Workpiece Size and WeightLarger and heavier workpieces require more robust centers with higher load capacities. Ensure that the selected center can handle the weight of the workpiece without deformation or failure. Bull nose centers are particularly well-suited for supporting large workpieces.Machining OperationsThe type of machining operation also influences the selection. For high-speed turning or heavy cuts, a live center with precision bearings is essential. For finishing cuts or light-duty work, a dead center may be adequate.Taper SizeCarbide centers are available with various taper sizes, such as Morse taper (MT) and Jacobs taper. Ensure that the taper size of the center matches the taper size of the tailstock spindle. Common taper sizes include MT2, MT3, MT4, and MT5. Measure the tailstock and refer to manufacturer specifications to get the correct fit. Common options from Wayleading Tools can be found in their catalogs.Maintenance and Care of Carbide CentersProper maintenance is essential for prolonging the life and accuracy of carbide centers.CleaningRegularly clean carbide centers to remove chips, dirt, and other contaminants. Use a clean cloth and a mild solvent if necessary. Avoid using abrasive cleaners that could damage the carbide tip.LubricationFor dead centers, frequent lubrication is critical to minimize friction and wear. Use a high-quality lathe center lubricant specifically designed for this purpose. Live centers typically have sealed bearings that do not require external lubrication, but inspect them periodically for damage or leakage.InspectionInspect carbide centers regularly for signs of wear, damage, or runout. Check the carbide tip for chips, cracks, or excessive wear. Use a dial indicator to measure runout and ensure that the center is running true. If any issues are detected, replace or repair the center as needed.StorageStore carbide centers in a clean, dry place to prevent corrosion and damage. Use protective covers or cases to shield the carbide tip from impact. Avoid storing carbide centers in direct contact with other tools that could cause damage.Troubleshooting Common IssuesEven with proper maintenance, carbide centers may encounter issues that affect their performance. Here are some common problems and their solutions:Excessive WearCause: Machining abrasive materials, insufficient lubrication (for dead centers), or excessive cutting forces.Solution: Use a carbide center with a higher carbide content, increase lubrication frequency, reduce cutting forces, or consider using a live center.RunoutCause: Damaged bearings (for live centers), bent center point, or loose tailstock.Solution: Replace damaged bearings, replace the center point, tighten the tailstock, or realign the lathe.ChatterCause: Insufficient support, excessive cutting forces, or worn carbide tip.Solution: Use a bull nose center for greater support, reduce cutting forces, replace the worn carbide tip, or increase workpiece rigidity.Carbide Center Data Table Feature Live Center Dead Center Rotation Rotates with workpiece Stationary Friction Low (due to bearings) High Lubrication Minimal (sealed bearings) Frequent Wear Resistance High High Application High-speed turning, heavy cuts Finishing cuts, light-duty work Data compiled from various machining resources.ConclusionCarbide centers are indispensable tools for lathe operations, providing the accuracy and stability required for precise machining. By understanding the different types of carbide centers, selecting the right one for your specific needs, and implementing proper maintenance practices, you can optimize your machining processes and achieve superior results. Whether you need a live center for high-speed turning or a dead center for finishing cuts, investing in quality carbide centers will contribute to the efficiency and accuracy of your machining operations. Remember to source your tooling, including quality carbide centers, from reputable suppliers like Wayleading Tools for best results.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 Type K-90 Degree Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type K-90 Degree Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 3 Flutes HSS Counterbore Drill Bit With Metric And Inch Size
3 Flutes HSS Counterbore Drill Bit With Metric And Inch Size -
 Precision Dial Test Indicator Gage For Industrial
Precision Dial Test Indicator Gage For Industrial -
 Precision Digital Bore Guage From 6-450mm Range
Precision Digital Bore Guage From 6-450mm Range -
 HSS Hand Reamers – Metric & Inch Sizes, Straight or Spiral Flutes
HSS Hand Reamers – Metric & Inch Sizes, Straight or Spiral Flutes -
 Indexable Square Shoulder End Mill For Industrial
Indexable Square Shoulder End Mill For Industrial -
 Single Wheel Knurling Tools With Straight Pattern For Industrial Type
Single Wheel Knurling Tools With Straight Pattern For Industrial Type -
 DIN338 HSS Twist Drill Bit Fully Ground Or TiN Coated
DIN338 HSS Twist Drill Bit Fully Ground Or TiN Coated -
 Type B Cylinder Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type B Cylinder Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 DIN6537L Metric Solid Carbide Twist Drill With Internal Coolant & External Coolant
DIN6537L Metric Solid Carbide Twist Drill With Internal Coolant & External Coolant -
 HSS Metric Side Milling Cutter With Bright Or TiN And TiAlN Coated
HSS Metric Side Milling Cutter With Bright Or TiN And TiAlN Coated -
 30PCS HSS Metric And Inch Size MINI Tap & Die Set
30PCS HSS Metric And Inch Size MINI Tap & Die Set