carbide inserts Factory
Carbide inserts are essential cutting tools in machining, offering superior hardness and wear resistance compared to high-speed steel. This article explores the different types of carbide inserts, their applications, key factors to consider when choosing a carbide insert factory, and provides valuable insights into the world of carbide inserts manufacturing.
Understanding Carbide Inserts
Carbide inserts are small, indexable cutting tools used in machining operations such as turning, milling, and threading. They are made from a composite material consisting of tungsten carbide (WC) as the hard phase, and cobalt (Co) as the binder. The proportion of WC and Co, along with other alloying elements like titanium carbide (TiC), tantalum carbide (TaC), and niobium carbide (NbC), determines the properties of the insert, such as its hardness, toughness, and wear resistance.
Types of Carbide Inserts
Carbide inserts are available in various shapes, sizes, and grades, each designed for specific machining applications. Here are some common types:
- Turning Inserts: Used for turning operations, these inserts come in shapes like square, triangle, rhombus, and round.
- Milling Inserts: Designed for milling applications, these inserts are available in square, round, and trigon shapes.
- Threading Inserts: Used for creating threads on workpieces, these inserts have specific geometries to match different thread forms.
- Grooving Inserts: Designed for creating grooves and cut-offs on workpieces.
- Drilling Inserts: Used in indexable drills, these inserts are designed to remove material efficiently.
Carbide Insert Grades
Carbide insert grades are classified according to ISO standards, which indicate the insert's suitability for different machining conditions and materials. Common grades include:
- P Grades: For machining steel and steel alloys.
- M Grades: For machining stainless steel.
- K Grades: For machining cast iron.
- N Grades: For machining non-ferrous materials like aluminum.
- S Grades: For machining heat-resistant alloys.
- H Grades: For machining hardened materials.
Applications of Carbide Inserts
Carbide inserts are widely used in various industries due to their versatility and performance. Some common applications include:
- Automotive: Machining engine components, transmission parts, and other automotive components.
- Aerospace: Manufacturing aircraft engine parts, structural components, and landing gear.
- Medical: Producing surgical instruments, implants, and other medical devices.
- Oil and Gas: Machining drill bits, valves, and other components used in oil and gas extraction.
- General Manufacturing: Producing a wide range of components for various industries.
Choosing the Right Carbide Insert Factory
Selecting the right carbide insert factory is crucial for ensuring the quality, performance, and cost-effectiveness of your cutting tools. Here are some key factors to consider:
Reputation and Experience
Look for a factory with a proven track record of producing high-quality carbide inserts. Check their customer reviews, testimonials, and industry certifications. A company like Wayleading Tools with years of experience in the tooling industry, can offer valuable expertise and reliable products.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Evaluate the factory's manufacturing capabilities, including their equipment, technology, and quality control processes. Ensure they have the capacity to meet your specific requirements and production volumes.
Material Quality
The quality of the raw materials used in carbide inserts directly affects their performance and lifespan. Ensure the factory uses high-quality tungsten carbide powder and cobalt binder from reputable suppliers.
Customization Options
If you require custom carbide inserts with specific geometries or grades, choose a factory that offers customization services. Consider companies like Wayleading Tools who are committed to delivering bespoke solutions for diverse machining needs.
Pricing and Lead Times
Compare pricing and lead times from different factories to find the best balance between cost and delivery speed. However, don't compromise on quality for the sake of lower prices.
Technical Support
Choose a factory that provides excellent technical support and assistance. They should be able to help you select the right carbide inserts for your specific applications and provide guidance on their proper use and maintenance.
Carbide Insert Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of carbide inserts involves several stages, including:
- Powder Preparation: Mixing tungsten carbide powder, cobalt binder, and other alloying elements.
- Pressing: Compacting the powder mixture into the desired shape using high-pressure presses.
- Sintering: Heating the compacted parts at high temperatures to fuse the powder particles together.
- Grinding: Grinding the sintered parts to achieve the final dimensions and surface finish.
- Coating: Applying a thin layer of coating material (e.g., titanium nitride, titanium carbonitride, aluminum oxide) to improve wear resistance and performance.
- Quality Control: Inspecting the finished inserts for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and other quality parameters.
Factors Affecting Carbide Insert Performance
The performance of carbide inserts is influenced by several factors, including:
- Cutting Speed: Higher cutting speeds can generate more heat and wear on the insert.
- Feed Rate: Higher feed rates can increase the cutting force and lead to insert breakage.
- Depth of Cut: Deeper cuts can put more stress on the insert.
- Workpiece Material: Different workpiece materials have different machinability ratings, which affect the insert's wear rate.
- Coolant: Using coolant can help reduce heat and friction, extending the insert's lifespan.
- Machine Rigidity: A rigid machine can minimize vibrations and improve cutting accuracy.
Troubleshooting Common Carbide Insert Problems
Here are some common problems encountered with carbide inserts and their solutions:
| Problem | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Chipping | Excessive cutting speed, interrupted cuts, incorrect insert grade | Reduce cutting speed, use a tougher insert grade, improve workpiece clamping |
| Wear | High cutting speed, abrasive workpiece material, insufficient coolant | Reduce cutting speed, use a more wear-resistant insert grade, increase coolant flow |
| Breakage | Excessive feed rate, deep cuts, machine vibration | Reduce feed rate, use a more rigid machine, improve machine maintenance |
Conclusion
Carbide inserts are indispensable tools in modern machining, offering high performance and versatility. By understanding the different types of inserts, their applications, and the factors that affect their performance, you can optimize your machining processes and achieve superior results. Choosing the right carbide insert factory is essential for ensuring the quality and cost-effectiveness of your cutting tools. Consider factors such as reputation, manufacturing capabilities, material quality, and technical support when making your selection. Explore what Wayleading Tools can offer for your specific tooling requirements.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 5C Hex Collet With Inch and Metric Size
5C Hex Collet With Inch and Metric Size -
 Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output
Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output -
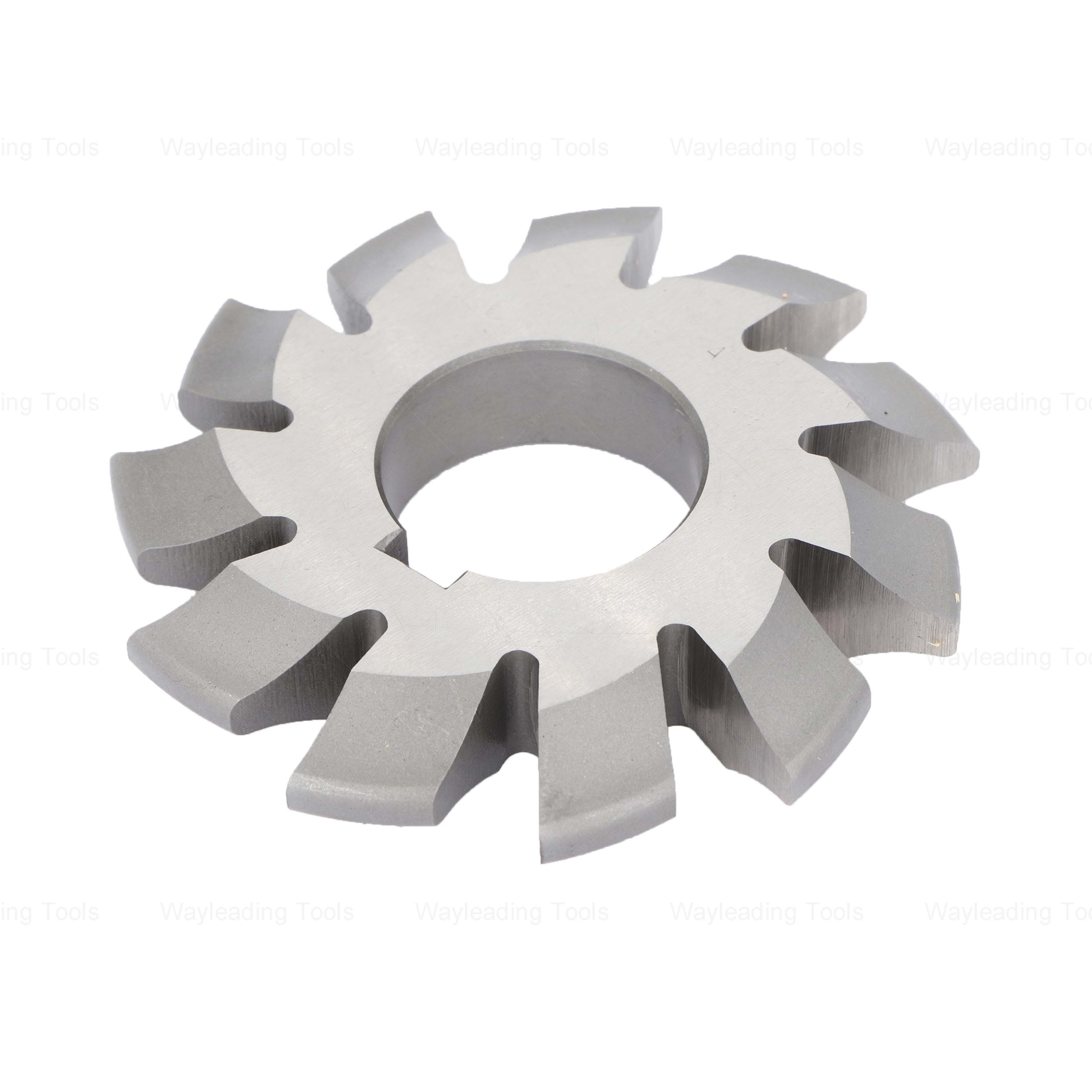 HSS Involute Gear Cutters – Module Type, PA 20° / 14.5°
HSS Involute Gear Cutters – Module Type, PA 20° / 14.5° -
 Vernier Height Gauge With Magnifier With Adjustable Main Bean
Vernier Height Gauge With Magnifier With Adjustable Main Bean -
 7pcs Carbide Turning Tool Set With Metric & Inch Size
7pcs Carbide Turning Tool Set With Metric & Inch Size -
 Precision Expanding Mandrel From 9/16″ to 3-3/4″
Precision Expanding Mandrel From 9/16″ to 3-3/4″ -
 Precision Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 Metric HSS 13mm Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision
Metric HSS 13mm Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision -
 Precision Monoblock Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Monoblock Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 HSS Threading Taps – ISO 529, Straight Flute, Spiral Flute & Spiral Point
HSS Threading Taps – ISO 529, Straight Flute, Spiral Flute & Spiral Point -
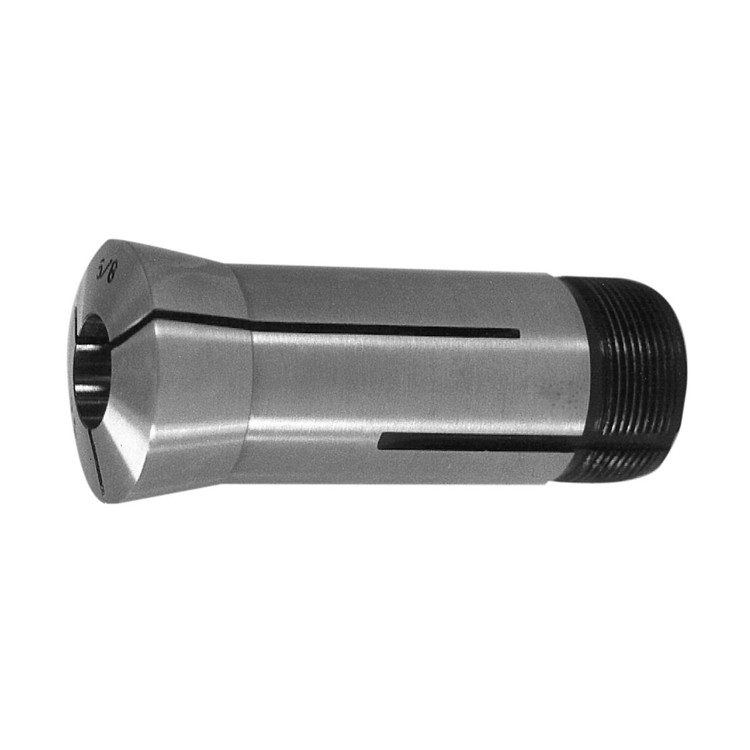 5C Round Collet With Inch and Metric Size
5C Round Collet With Inch and Metric Size -
 Precision IP67 Digital Caliper With Data Output For Industrial
Precision IP67 Digital Caliper With Data Output For Industrial