dividing head
A dividing head, also known as an index head or dividing headstock, is a precision tool used in machining to accurately rotate a workpiece to specific angles or divisions. It is essential for creating parts with multiple, precisely spaced features such as gears, splines, and flutes. This guide covers the basics, types, operation, and applications of a dividing head, providing a comprehensive understanding for machinists and enthusiasts.What is a Dividing Head?A dividing head is a specialized tool that holds a workpiece and allows it to be rotated accurately through a specific number of degrees or divisions. It's typically used with milling machines, but can also be adapted for use with other machine tools. The primary function of a dividing head is to enable the creation of evenly spaced features on a workpiece, such as the teeth on a gear or the flutes on a cutting tool.Key Components of a Dividing HeadUnderstanding the components of a dividing head is crucial for its effective use. The main parts include: Headstock: The main body of the dividing head that houses the indexing mechanism. Spindle: The rotating shaft that holds the workpiece. It can typically accommodate collets, chucks, or faceplates. Index Plate: A plate with precisely spaced holes used in conjunction with an index pin to achieve accurate divisions. Index Pin/Plunger: A pin that engages with the holes in the index plate to lock the spindle in a specific position. Worm Gear and Worm: A gear system that provides a high gear ratio for precise rotation of the spindle. Crank Handle: Used to rotate the worm, which in turn rotates the spindle.Types of Dividing HeadsSeveral types of dividing heads are available, each offering different capabilities and levels of precision. Here's a look at some common types:Direct Indexing Dividing HeadA direct indexing dividing head has an index plate directly attached to the spindle. This allows for rapid indexing using a limited number of divisions, typically 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, or 24. It's best suited for simple indexing tasks where high precision isn't paramount. Think of dividing a circle into halves, quarters, or thirds.Simple Indexing Dividing HeadThe simple indexing dividing head utilizes a worm gear and worm to rotate the spindle. A crank handle is attached to the worm shaft, and rotating the handle causes the spindle to rotate proportionally. This type uses an index plate with multiple circles of holes, allowing for a wider range of divisions. This is a versatile type often found in machine shops, offering a balance of precision and ease of use. A standard ratio for a simple indexing head is 40:1, meaning 40 turns of the crank handle rotates the spindle one full revolution.Universal Dividing HeadA universal dividing head is the most versatile type, capable of performing simple, direct, angular, and differential indexing. It includes change gears that can be connected to the machine's lead screw, enabling the creation of spirals and helical features. It also features a tilting headstock, allowing for machining at compound angles. They are often equipped with features to handle more complex indexing tasks, like cutting gears and spirals.Optical Dividing HeadAn optical dividing head employs optical encoders to provide extremely accurate angular positioning. It's used in high-precision applications where the tightest tolerances are required. While offering the highest precision, it is also usually the most expensive option.How to Use a Dividing HeadUsing a dividing head effectively requires understanding the indexing process. Here's a general overview: Calculate the Indexing Movement: Determine the number of turns and partial turns of the crank handle needed for each division. For a 40:1 ratio dividing head, the formula is: Turns = 40 / Number of Divisions. Select the Appropriate Index Plate: Choose an index plate with a number of holes that allows for accurate indexing based on the calculated turns. Mount the Workpiece: Securely mount the workpiece in a chuck, collet, or faceplate attached to the spindle. Engage the Index Pin: Position the index pin in the appropriate hole on the index plate. Rotate the Crank Handle: Rotate the crank handle the calculated number of turns and partial turns. Lock the Spindle: Securely lock the spindle in the new position using the spindle lock. Perform Machining Operation: Execute the desired machining operation. Repeat: Repeat steps 5-7 for each division.Dividing Head ApplicationsDividing heads find applications in various machining processes. Here are a few examples: Gear Cutting: Creating gear teeth with precise spacing and profiles. Spline Cutting: Machining splines on shafts for power transmission. Flute Cutting: Cutting flutes on drills, taps, and end mills. Keyway Cutting: Creating keyways in shafts and hubs. Hole Spacing: Drilling precisely spaced holes in circular patterns. Angular Spacing: Machining features at specific angles around a workpiece. Helical Milling: Milling spirals or helical grooves with the use of change gears.Selecting the Right Dividing HeadChoosing the right dividing head depends on your specific needs and applications. Consider the following factors: Accuracy Requirements: For high-precision work, an optical dividing head might be necessary. For general-purpose machining, a simple or universal dividing head may suffice. Frequency of Use: If you frequently perform indexing operations, invest in a robust and reliable dividing head. Workpiece Size and Weight: Ensure the dividing head has the capacity to handle your typical workpiece size and weight. Budget: Dividing heads range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand, depending on their type, features, and accuracy.Maintenance and CareProper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and accuracy of your dividing head. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection will help keep it in good working condition. Always follow the manufacturer's recommendations for maintenance procedures.Wayleading Tools provides a wide range of high-quality machining accessories, including various types of dividing heads. Explore our collection to find the perfect tool for your machining needs. Visit www.wayleading.com to learn more about our products and services.Troubleshooting Common IssuesEven with proper care, issues can arise. Here's a quick look at some potential problems and solutions: Issue Possible Cause Solution Inaccurate Indexing Worn index plate, loose index pin, incorrect calculations. Inspect and replace worn parts. Tighten index pin. Verify calculations. Spindle Hard to Rotate Lack of lubrication, debris in gears, tight bearings. Lubricate moving parts. Clean out any debris. Adjust or replace bearings. Spindle Lock Not Engaging Worn or damaged locking mechanism. Inspect and replace worn parts. ConclusionThe dividing head is an indispensable tool for machinists requiring accurate rotational positioning. By understanding the different types, operation, and maintenance procedures, you can effectively utilize a dividing head to create high-quality, precisely machined parts.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 HSS Inch Taper Shank Twit Drills For Metal Cutting Of High Precision
HSS Inch Taper Shank Twit Drills For Metal Cutting Of High Precision -
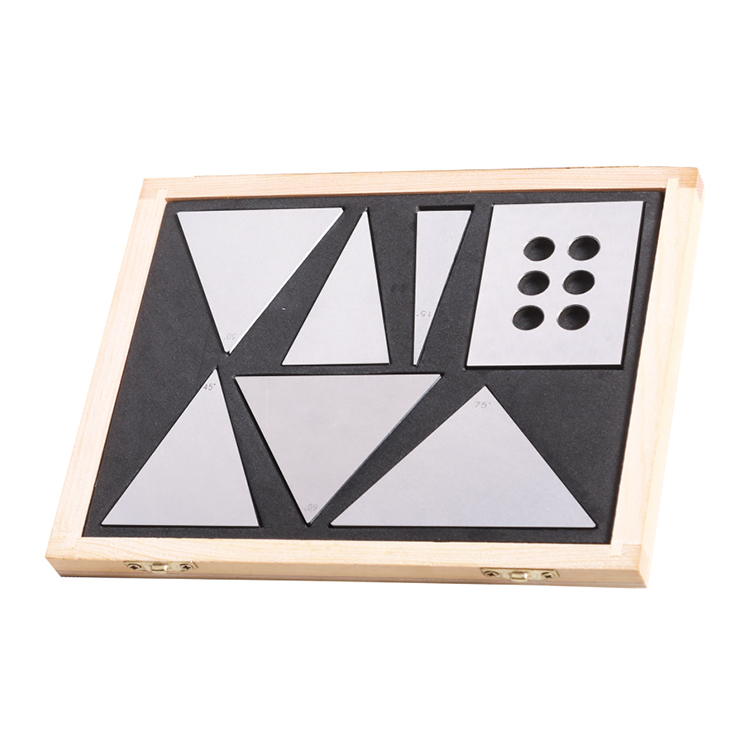 Precision 7pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 7pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
 Parting & Grooving Tool Set With SLTB Blcok, NCIH Blades, GTN Inserts
Parting & Grooving Tool Set With SLTB Blcok, NCIH Blades, GTN Inserts -
 Precision Dial Test Indicator Gage For Industrial
Precision Dial Test Indicator Gage For Industrial -
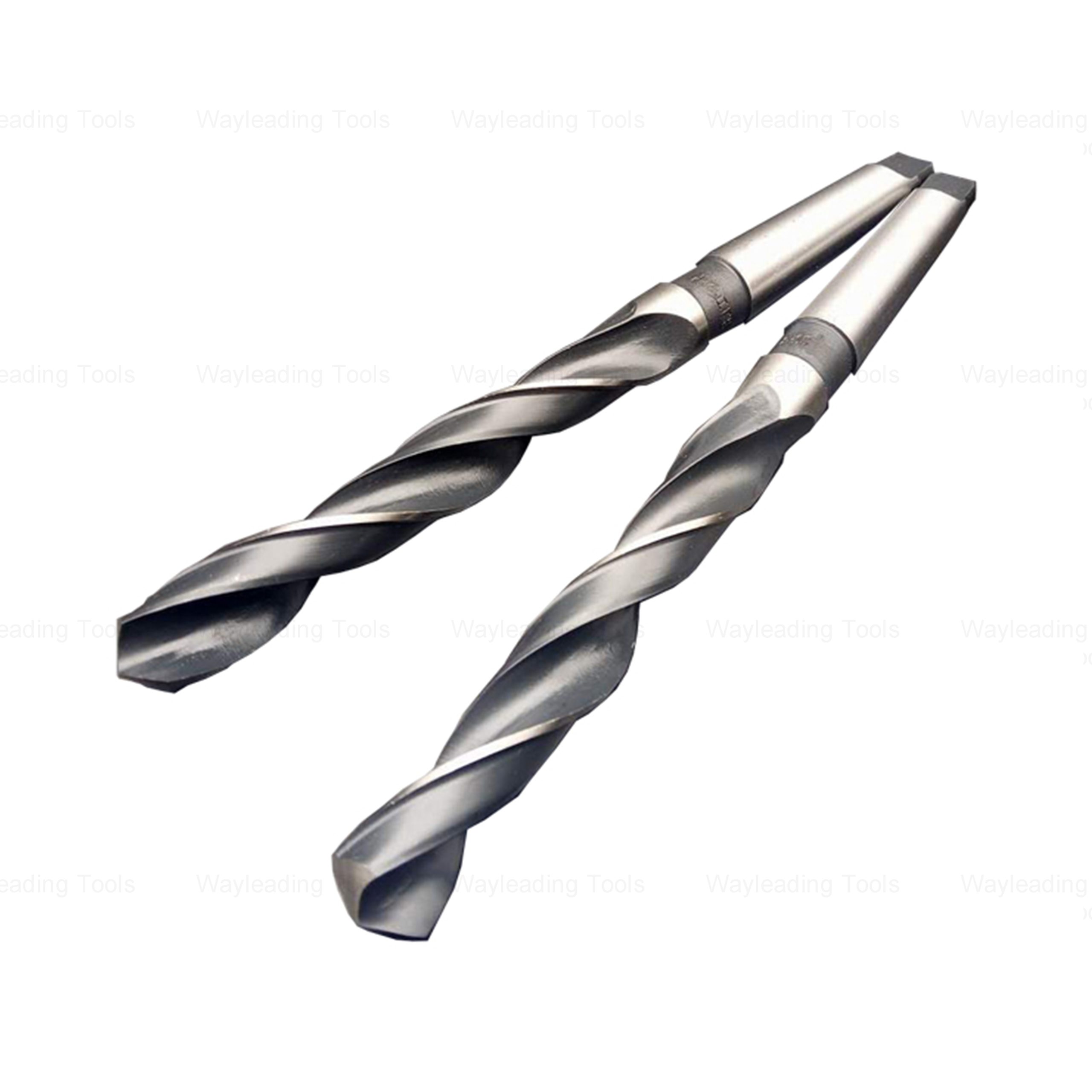 HSS Metric Taper Shank Twist Drills for High-Precision Metal Cutting
HSS Metric Taper Shank Twist Drills for High-Precision Metal Cutting -
 M42 Bi-Metal Bandsaw Blades For Industrial Type
M42 Bi-Metal Bandsaw Blades For Industrial Type -
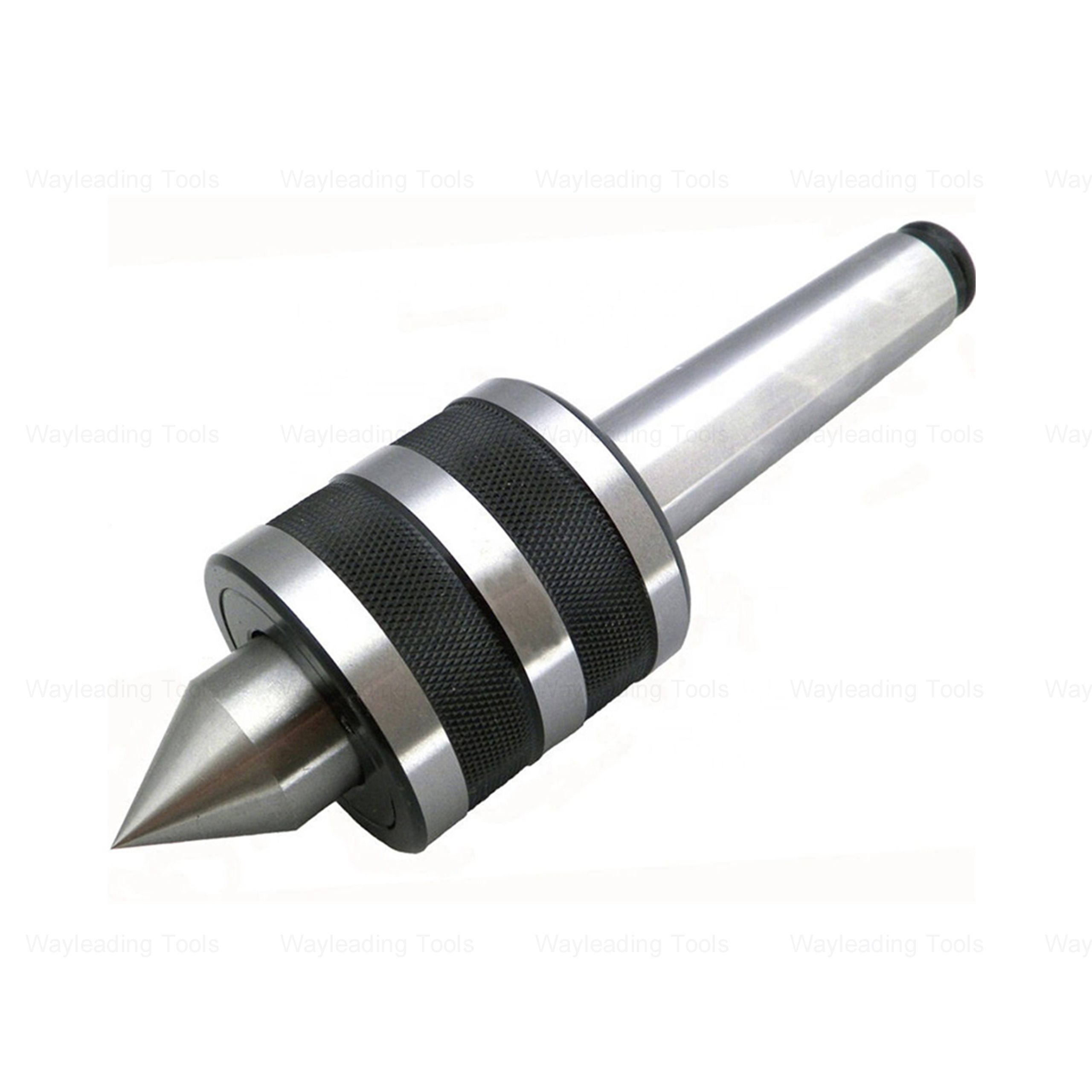 High Precision Medium-Duty Live Center – Hardened Tip, Morse Taper Shank
High Precision Medium-Duty Live Center – Hardened Tip, Morse Taper Shank -
 R8 Round Collet With Inch and Metric Size
R8 Round Collet With Inch and Metric Size -
 HSS Metric & Inch T Slot End Mill For Industrial
HSS Metric & Inch T Slot End Mill For Industrial -
 Deburring Tool Blades Using For Deburring
Deburring Tool Blades Using For Deburring -
 Camlock ER Collet Fixture With Lathe Collet Chuck
Camlock ER Collet Fixture With Lathe Collet Chuck -
 Precision Dustproof Dial Caliper Of Double Shock-Proof For Industrial
Precision Dustproof Dial Caliper Of Double Shock-Proof For Industrial
Related search
Related search- PCBN turning tool holder Supplier
- hss lathe turning tools Suppliers
- BT ER collet chuck Manufacturers
- british standard taper pipe full profile threading insert Supplier
- indexable threading mill Suppliers
- Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr Factory
- angle blocks Suppliers
- turning tool holder Suppliers
- din 338 Factories
- Drill chuck Factory











