Dovetail End Mill
Dovetail end mills are specialized cutting tools used to create precise dovetail joints, essential for woodworking, metalworking, and other applications requiring strong, interlocking connections. This guide explores the different types of dovetail end mills, their applications, key features, and how to choose the right one for your project, ensuring optimal performance and accuracy.Understanding Dovetail End MillsWhat is a Dovetail Joint?A dovetail joint is a robust and visually appealing method of joining two pieces of material. It consists of 'tails' cut into one piece that interlock with 'pins' cut into another. The interlocking shape resists being pulled apart, making it stronger than many other joint types.What is a Dovetail End Mill?A dovetail end mill is a rotary cutting tool specifically designed to create the dovetail shape necessary for this type of joint. Unlike standard end mills, dovetail end mills have a cutting edge angled relative to the shank, allowing them to create the characteristic undercut shape of the dovetail.Types of Dovetail End MillsBy MaterialDovetail end mills are primarily made from two materials: High-Speed Steel (HSS): HSS dovetail end mills are a cost-effective option suitable for softer materials like wood, aluminum, and some plastics. They offer good toughness and can be resharpened. Carbide: Carbide dovetail end mills are significantly harder and more wear-resistant than HSS. They are ideal for machining harder materials like steel, stainless steel, and titanium. Carbide end mills can withstand higher cutting speeds and feeds, resulting in faster material removal and improved surface finish.By Cutting AngleThe cutting angle of a dovetail end mill determines the angle of the dovetail joint it creates. Common angles include: 45-Degree Dovetail End Mills: This is a very common angle for woodworking and general-purpose applications. 60-Degree Dovetail End Mills: Often used in metalworking where stronger joints are needed.The selection of the angle depends on the design of the dovetail joint and the specific application requirements.By Shank TypeThe shank is the part of the end mill that is held by the machine's collet or chuck. Common shank types include: Straight Shank: The most common type, suitable for a wide range of machines. Threaded Shank: Designed for specific machines and toolholders with corresponding threads. Weldon Shank: Features a flat area for secure clamping, preventing slippage during heavy cutting.Applications of Dovetail End MillsDovetail end mills are used in a variety of industries and applications, including: Woodworking: Creating strong and attractive joints for drawers, cabinets, and furniture. Metalworking: Machining dovetail slides, guides, and fixtures. Mold Making: Creating dovetail slots for securing mold components. Aerospace: Manufacturing precision parts with dovetail features.Choosing the Right Dovetail End MillSelecting the appropriate dovetail end mill depends on several factors:Material to be MachinedThe material being cut is the primary factor in determining the end mill material. Carbide is recommended for harder materials, while HSS is suitable for softer materials.Dovetail AngleChoose the end mill angle that matches the desired dovetail joint angle (e.g., 45 degrees or 60 degrees).Cutting DiameterThe cutting diameter determines the size of the dovetail feature. Select a diameter that corresponds to the required dimensions of the joint or feature.Shank DiameterEnsure the shank diameter is compatible with the machine's tool holder.Coating (Optional)Coatings, such as TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride), can improve the end mill's performance and lifespan, especially when machining abrasive materials. Wayleading Tools offers a wide range of coated and uncoated dovetail end mills to suit your specific needs. Contact us at www.wayleading.com for expert advice.Best Practices for Using Dovetail End MillsTo achieve optimal results and extend the life of your dovetail end mill, follow these best practices: Use Proper Cutting Speeds and Feeds: Refer to the manufacturer's recommendations for appropriate speeds and feeds based on the material being machined and the end mill type. Secure Workholding: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped to prevent vibration and movement during cutting. Use Coolant: Applying coolant helps to dissipate heat, reduce friction, and improve surface finish. Inspect Regularly: Regularly inspect the end mill for wear or damage. Replace dull or damaged end mills to maintain accuracy and prevent tool breakage.Troubleshooting Common ProblemsHere are some common issues that might be encountered, along with solutions: Chipping or Breakage: Possible causes include excessive cutting speeds or feeds, inadequate workholding, or a dull end mill. Poor Surface Finish: Possible causes include improper cutting speeds or feeds, a dull end mill, or insufficient coolant. Inaccurate Dovetail Dimensions: Possible causes include a worn end mill, incorrect setup, or machine misalignment.Dovetail End Mill Specifications: A Quick Comparison Feature HSS Dovetail End Mill Carbide Dovetail End Mill Material Hardness Lower Higher Wear Resistance Lower Higher Best Used For Softer materials (wood, aluminum) Harder materials (steel, stainless steel) Cost Lower Higher Resharpening Possible Less Frequent ConclusionDovetail end mills are essential tools for creating strong and precise dovetail joints. By understanding the different types, applications, and best practices, you can select the right end mill for your project and achieve optimal results. Wayleading Tools is a company dedicating to provide high-quality cutting tools, including a comprehensive selection of dovetail end mills to meet your specific machining needs. Visit our Dovetail Cutters page to browse our selection. If you need to discuss your specific requirements with our expert team, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 CCMT Turning Insert For Indexable Turning Tool Holder
CCMT Turning Insert For Indexable Turning Tool Holder -
 Depth Vernier Gauge With Stainless Steel And Monoblock Depth Type
Depth Vernier Gauge With Stainless Steel And Monoblock Depth Type -
 Precision 2pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 2pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
 Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank
Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank -
 Type J-60 Degree Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type J-60 Degree Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 Precision Digital Caliper Of With Metric & Inch Size For Industrial
Precision Digital Caliper Of With Metric & Inch Size For Industrial -
 Straight Shank ER Collet Chuck Holders With Extending Rod
Straight Shank ER Collet Chuck Holders With Extending Rod -
 HSS Metric Side Milling Cutter With Bright Or TiN And TiAlN Coated
HSS Metric Side Milling Cutter With Bright Or TiN And TiAlN Coated -
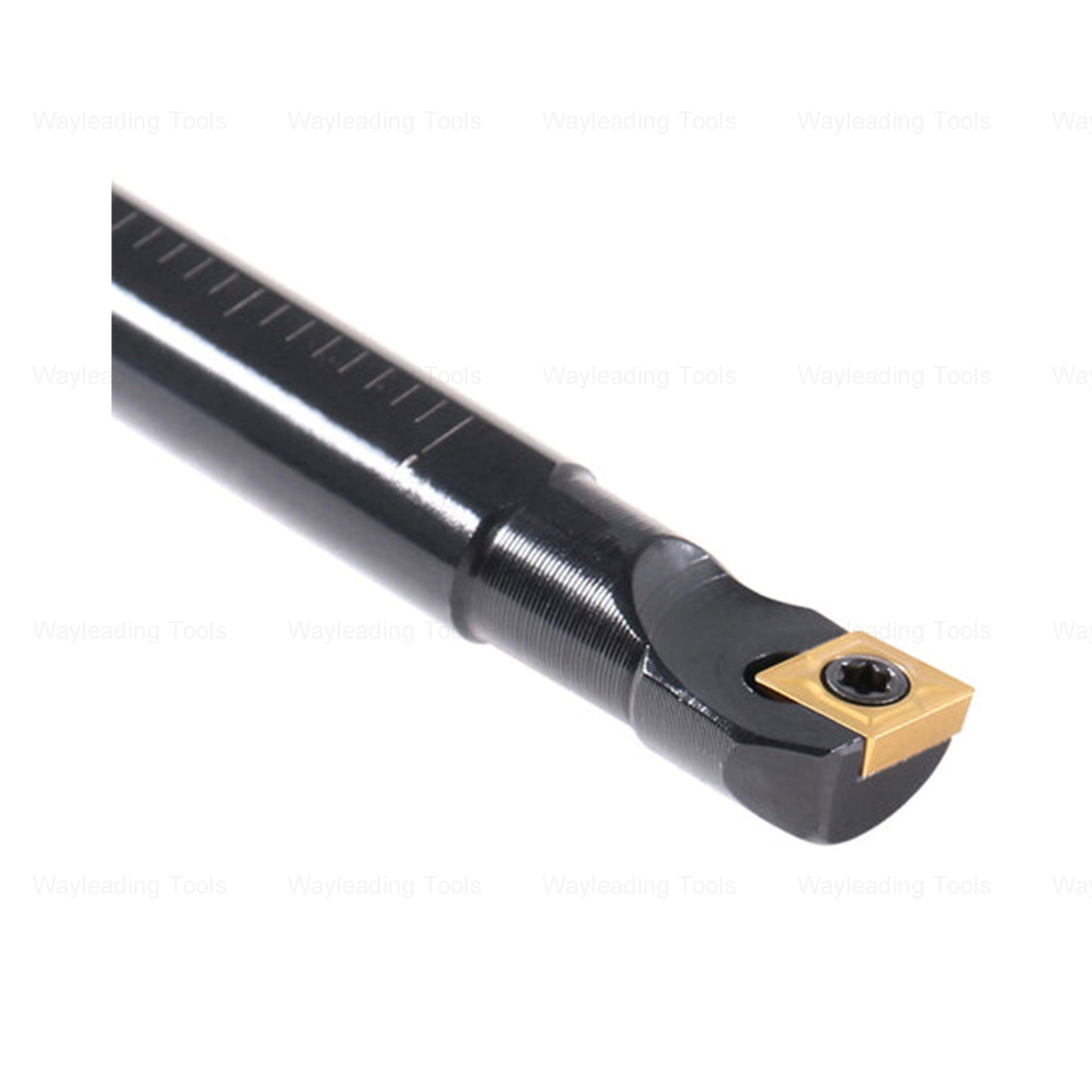 SCFC Indexable Boring Bar – Right- and Left-Hand Types
SCFC Indexable Boring Bar – Right- and Left-Hand Types -
 Deburring Tool Holder For The Deburring Tool Blades
Deburring Tool Holder For The Deburring Tool Blades -
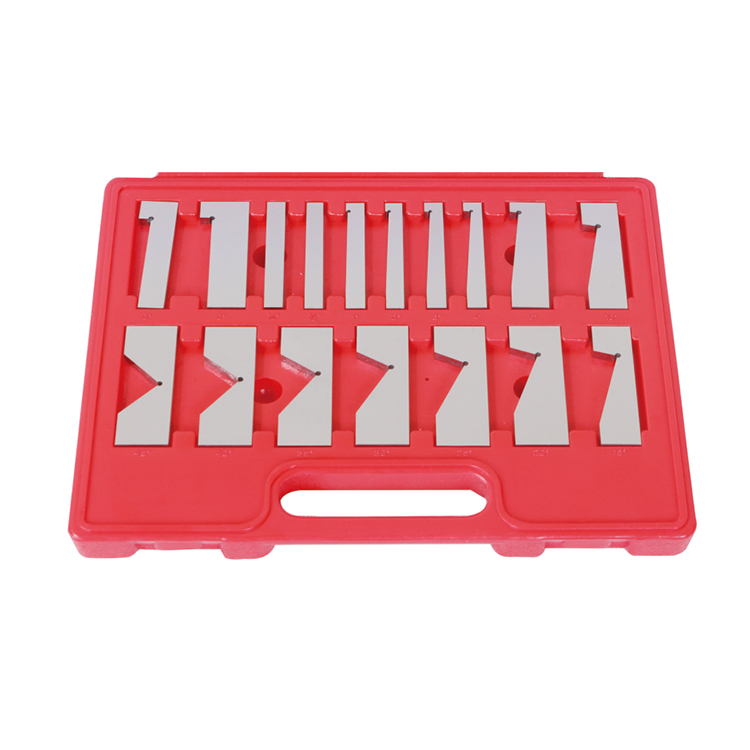 Precision 17pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 17pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
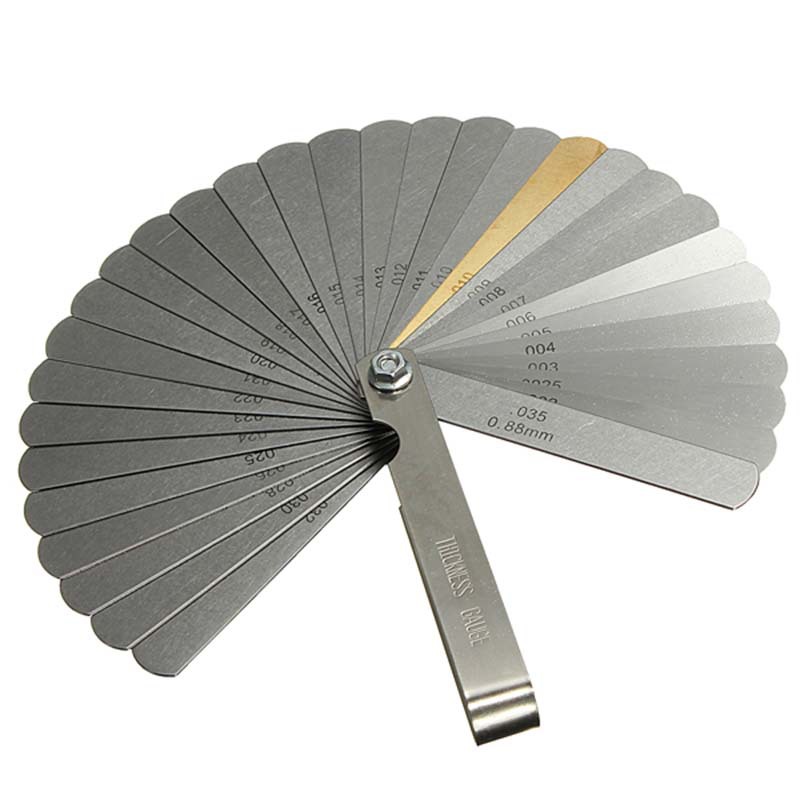 32 Blades Feeler Gauge From 0.04-0.88MM
32 Blades Feeler Gauge From 0.04-0.88MM
Related search
Related search- dial indicator magnetic base Supplier
- thread die Supplier
- depth caliper Manufacturers
- lathe drill chuck Manufacturers
- Indexable tool holders sets Manufacturers
- counter bores Factories
- Indexable tool holders sets Factory
- Wholesale reversible tapping chuck
- SVQC boring bar Manufacturers
- inside micrometer set Manufacturer










