End Mills
End mills are essential cutting tools used in a variety of machining operations, including milling, profiling, contouring, slotting, and drilling. Selecting the right end mill depends on factors such as the material being machined, the desired finish, and the type of cut required. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of end mills, covering different types, materials, coatings, and usage tips to help you make informed decisions for your machining projects. At Wayleading Tools, we understand the importance of high-quality cutting tools, so read on to learn more and ensure precision in your work.Understanding End Mills: The BasicsEnd mills are rotary cutting tools with cutting edges on the end and sides. They are used in milling machines to remove material and create specific shapes. The design of an end mill significantly impacts its performance, making it crucial to understand the different variations available.What are the Key Features of End Mills? Flutes: The number of flutes affects the chip load and finish. More flutes provide a better finish but can reduce chip clearance. Helix Angle: The angle of the flutes affects the cutting action. High helix angles are better for softer materials, while low helix angles are better for harder materials. Shank: The shank is the part of the end mill that is held by the machine. Common shank types include straight shanks, Weldon shanks, and collet shanks. Cutting Geometry: The geometry of the cutting edges influences the tool's performance and the type of materials it can effectively cut.Types of End Mills and Their ApplicationsChoosing the right type of end mill is crucial for achieving optimal results. Here's an overview of some common types:Square End MillsSquare end mills have square corners and are used for general-purpose milling, slotting, and profiling. They are versatile tools suitable for a wide range of materials.Ball Nose End MillsBall nose end mills have a rounded tip and are ideal for creating contoured surfaces and 3D shapes. They are commonly used in mold making and die sinking.Bull Nose End MillsBull nose end mills have a rounded corner radius and are used for applications where a strong corner is needed, such as roughing and finishing operations.Roughing End MillsRoughing end mills, also known as hog mills, are designed for rapid material removal. They have a serrated cutting edge that breaks up chips and reduces cutting forces.Finishing End MillsFinishing end mills are designed to produce a smooth surface finish. They typically have more flutes and a finer cutting edge than roughing end mills.Corner Radius End MillsCorner radius end mills have a small radius on the corners and are used to reduce stress concentrations and prevent chipping.Materials Used in End MillsThe material of an end mill affects its hardness, wear resistance, and ability to withstand heat. Common materials include:High-Speed Steel (HSS)HSS end mills are relatively inexpensive and suitable for general-purpose machining of softer materials. They have good toughness but lower wear resistance than carbide end mills.Cobalt HSSCobalt HSS end mills contain cobalt, which improves their heat resistance and wear resistance compared to standard HSS end mills. They are suitable for machining harder materials.Carbide End MillsCarbide end mills are made from a hard, wear-resistant material and are ideal for machining abrasive materials and high-speed applications. They offer excellent performance and long tool life.Coatings for End Mills: Enhancing PerformanceCoatings can significantly improve the performance and lifespan of end mills by reducing friction, increasing wear resistance, and preventing heat buildup. Some common coatings include:Titanium Nitride (TiN)TiN coatings are general-purpose coatings that improve wear resistance and cutting speed.Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN)TiCN coatings offer higher hardness and wear resistance than TiN coatings and are suitable for machining abrasive materials.Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN)AlTiN coatings provide excellent heat resistance and are ideal for high-speed machining and dry cutting applications.Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC)DLC coatings reduce friction and prevent chip adhesion, making them suitable for machining non-ferrous materials like aluminum and copper.Selecting the Right End Mill: A Step-by-Step GuideChoosing the right end mill involves considering several factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make the best choice: Material: Determine the material you will be machining. Harder materials require carbide end mills with appropriate coatings. Application: Identify the type of operation you will be performing (e.g., roughing, finishing, slotting, profiling). Size: Choose the appropriate diameter and length of the end mill based on the dimensions of your workpiece and the machine's capabilities. Flute Count: Select the appropriate number of flutes based on the material and desired finish. More flutes provide a better finish but can reduce chip clearance. Coating: Choose a coating that is suitable for the material you will be machining.Tips for Using End Mills EffectivelyTo maximize the performance and lifespan of your end mills, follow these tips: Use the Right Cutting Parameters: Refer to the manufacturer's recommendations for cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. Ensure Proper Coolant: Use an appropriate coolant to dissipate heat and lubricate the cutting edge. Secure the Workpiece: Ensure that the workpiece is securely clamped to prevent vibration and chatter. Inspect the End Mill: Regularly inspect the end mill for wear and damage. Replace worn or damaged end mills promptly. Proper Storage: Store end mills in a dry, clean environment to prevent corrosion and damage.Troubleshooting Common End Mill ProblemsEven with proper selection and usage, problems can sometimes occur. Here are some common issues and their solutions: Problem Possible Causes Solutions Chipping Excessive cutting speed, insufficient coolant, worn end mill Reduce cutting speed, increase coolant flow, replace the end mill Vibration/Chatter Insecure workpiece, excessive cutting depth, machine instability Secure the workpiece, reduce cutting depth, check machine stability Poor Surface Finish Dull end mill, incorrect cutting parameters, insufficient coolant Replace the end mill, adjust cutting parameters, increase coolant flow Where to Buy High-Quality End MillsPurchasing high-quality end mills from a reputable supplier is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Wayleading Tools offers a wide range of high-performance end mills designed to meet the needs of various machining applications. Check out our extensive catalog at www.wayleading.com for all your cutting tool needs.ConclusionUnderstanding the different types, materials, and coatings of end mills is essential for achieving optimal results in machining operations. By following the guidelines and tips outlined in this article, you can select the right end mill for your specific application and maximize its performance and lifespan. Whether you are a professional machinist or a hobbyist, investing in high-quality end mills is a worthwhile investment that will pay off in the long run. And remember, Wayleading Tools is here to provide you with top-notch tools and expert advice to help you succeed in your machining endeavors.Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general guidance only. Always refer to the manufacturer's recommendations for specific tools and materials.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 GTN Parting & Grooving Insert For NCIH Blade
GTN Parting & Grooving Insert For NCIH Blade -
 Precision Digital Caliper Of Metal Case For Industrial
Precision Digital Caliper Of Metal Case For Industrial -
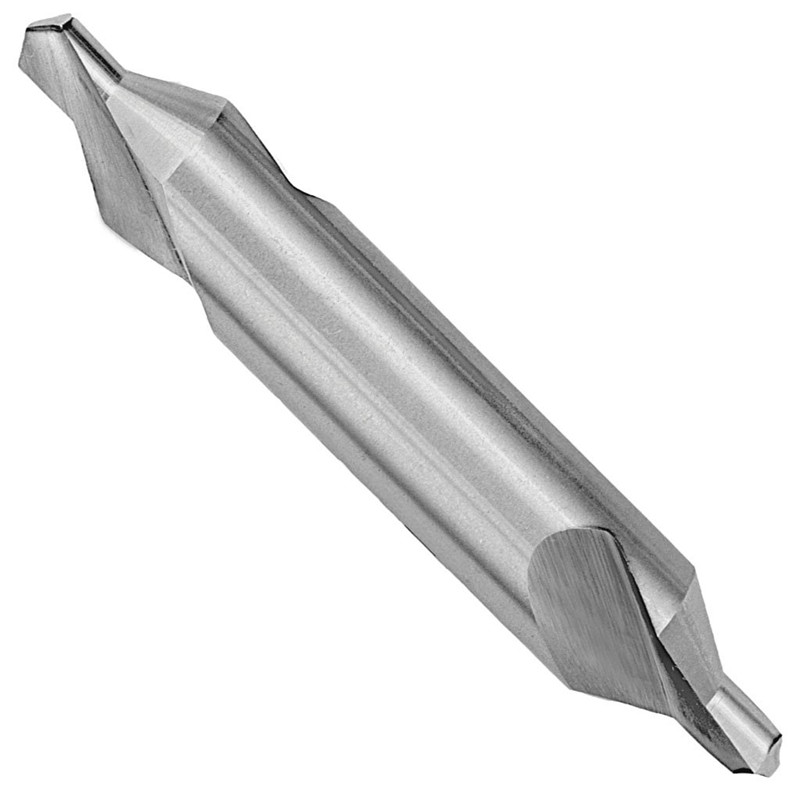
 3 Flutes HSS Chamfering Countersink Drill bitl With 60 And 90 Degree
3 Flutes HSS Chamfering Countersink Drill bitl With 60 And 90 Degree -
 Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank
Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank -
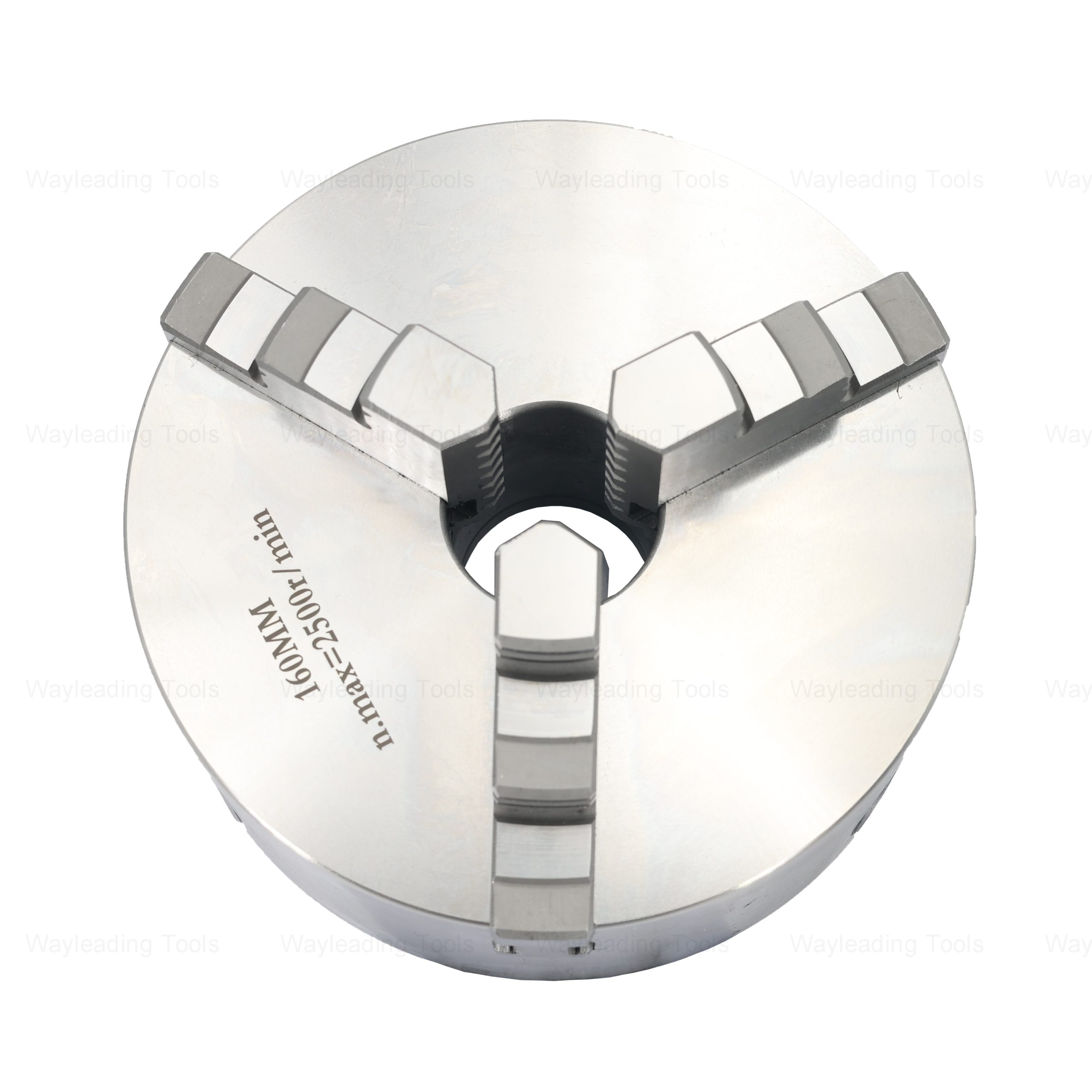 K11 Series 3-Jaw Self-Centering Lathe Chuck – Scroll Type, for Manual Lathes
K11 Series 3-Jaw Self-Centering Lathe Chuck – Scroll Type, for Manual Lathes -
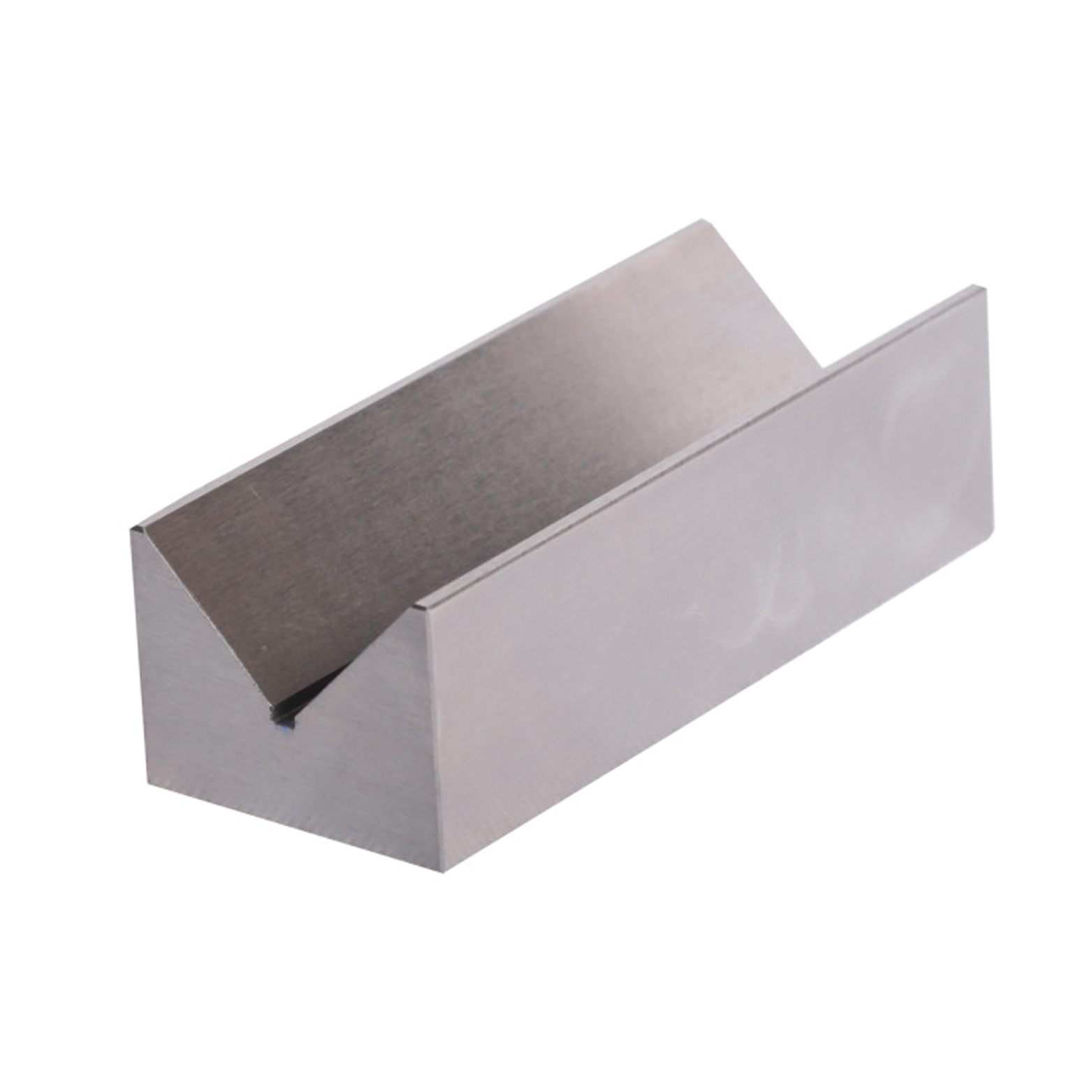
 Precision V Block Set With M Type
Precision V Block Set With M Type -
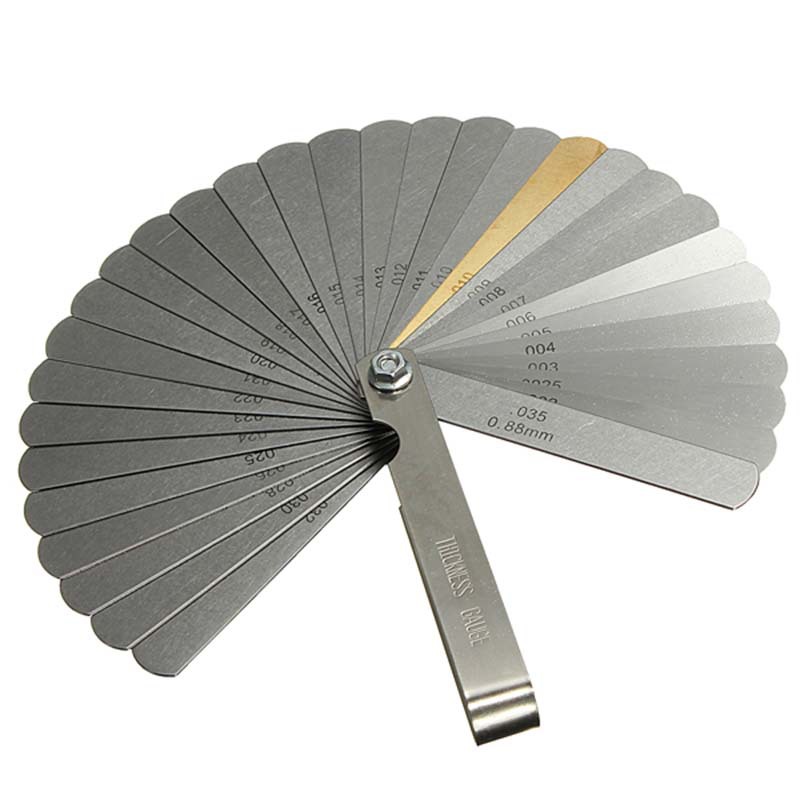 32 Blades Feeler Gauge From 0.04-0.88MM
32 Blades Feeler Gauge From 0.04-0.88MM -
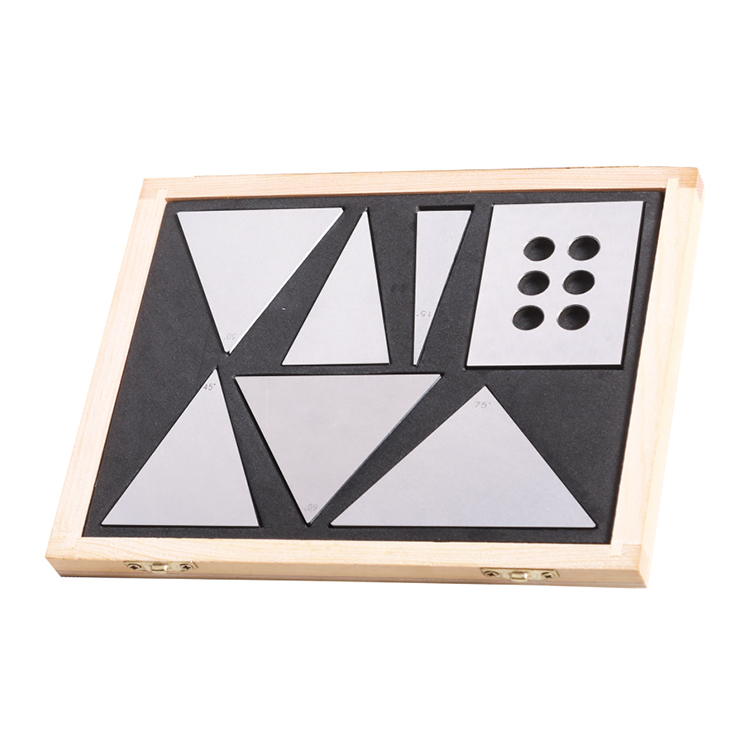 Precision 7pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 7pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
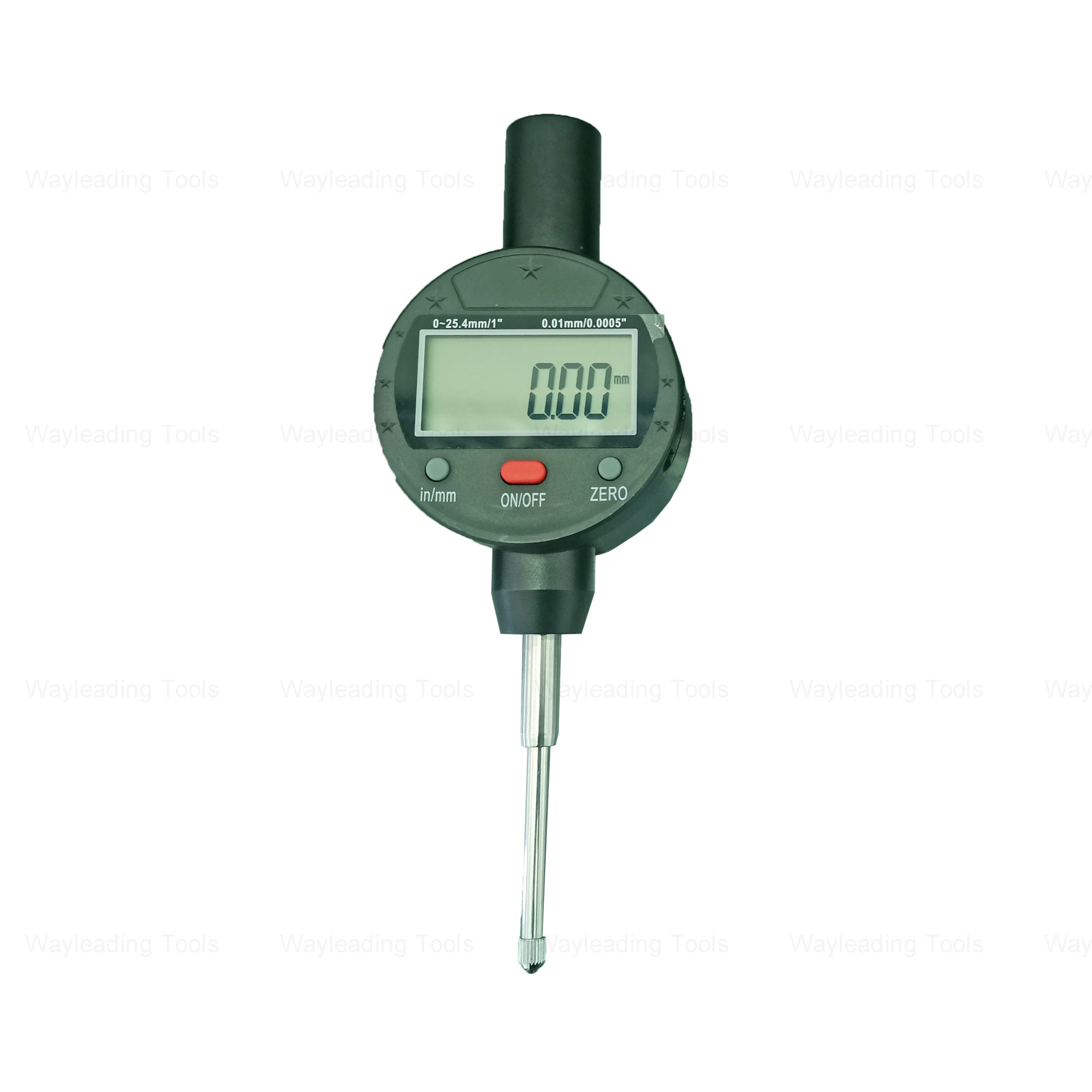
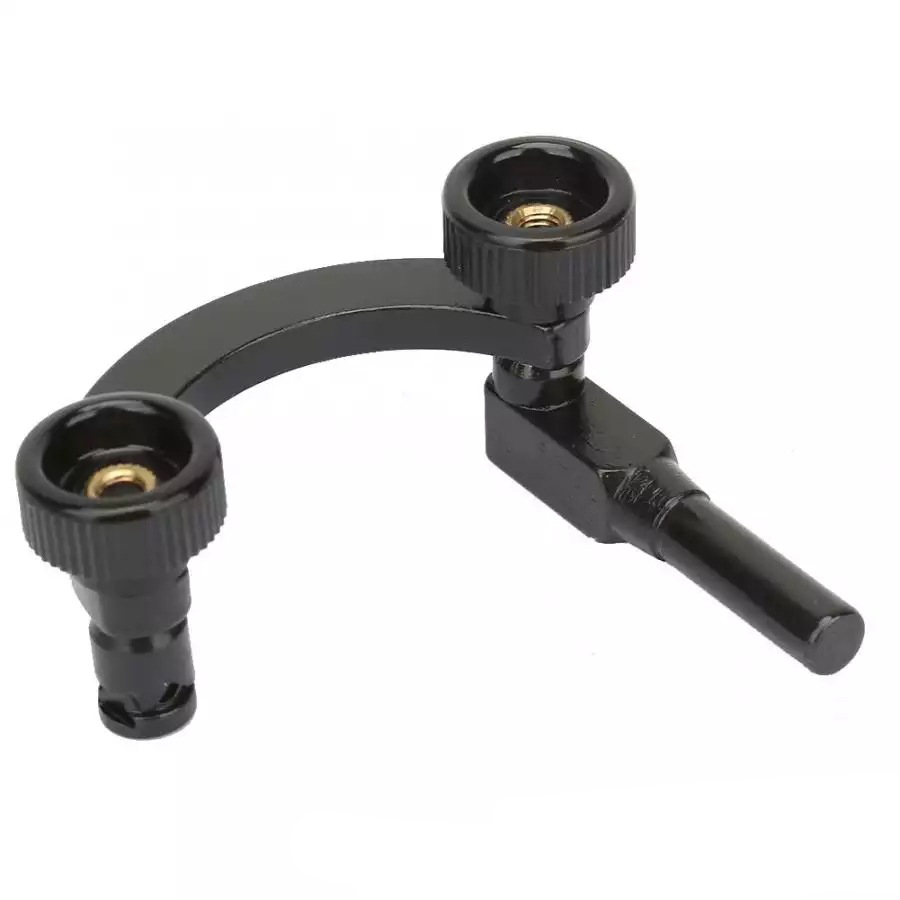 Precision Dial Test Indicator Holder For Industrial
Precision Dial Test Indicator Holder For Industrial -
 Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output
Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output -
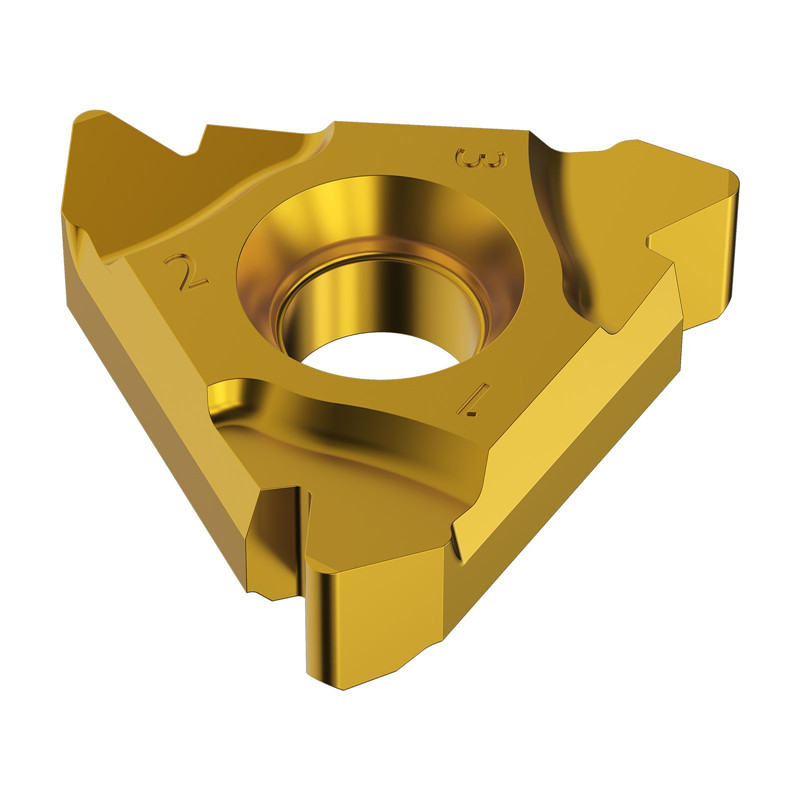 Partial profile 60° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type
Partial profile 60° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type -
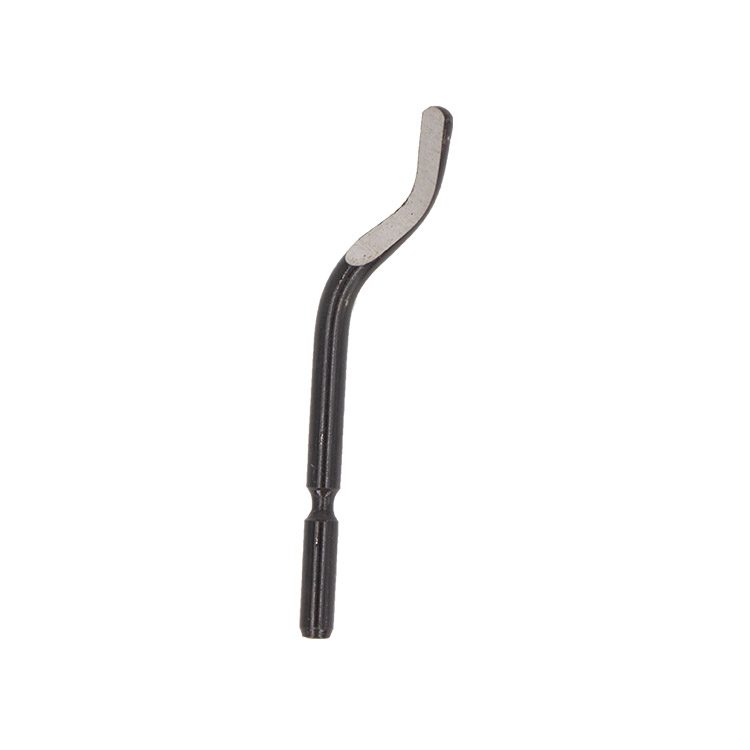 Deburring Tool Blades Using For Deburring
Deburring Tool Blades Using For Deburring











