indexable threading mill
Indexable threading mills are revolutionizing thread cutting in various industries, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility compared to traditional methods. This article delves into the core principles of indexable threading mills, exploring their types, applications, benefits, and best practices for optimal performance. Whether you're a seasoned machinist or new to the world of thread milling, this guide provides a comprehensive overview to help you maximize your threading operations and reduce costs.What is an Indexable Threading Mill?An indexable threading mill is a cutting tool used for creating threads (both internal and external) by a helical interpolation process. Unlike taps and dies that cut all threads simultaneously, a threading mill cuts one thread pitch at a time. The 'indexable' aspect refers to the replaceable cutting inserts, which allows for tool longevity and versatility.Key Components of an Indexable Threading MillTool Body: The main structure that holds the cutting inserts. Usually made from hardened steel.Cutting Inserts: Replaceable blades that perform the actual thread cutting. Different inserts can be used for various thread profiles, materials, and applications.Clamping System: Mechanisms (screws, levers, etc.) that securely hold the inserts in place.Types of Indexable Threading MillsSeveral types of indexable threading mills cater to different needs:Solid Carbide Threading Mills: For smaller threads and harder materials. Offer high precision and rigidity.Indexable Threading Mills with Replaceable Inserts: More versatile and cost-effective for larger threads. Allow for quick insert changes.Multi-Tooth Threading Mills: Designed for faster threading operations by cutting multiple threads simultaneously.Coolant-Through Threading Mills: Feature internal coolant channels to improve chip evacuation and tool life.Applications of Indexable Threading MillsIndexable threading mills are widely used across various industries:Aerospace: Manufacturing threaded components for aircraft engines and structures.Automotive: Producing threaded parts for engine blocks, transmissions, and chassis.Oil and Gas: Creating threads for pipes, fittings, and drilling equipment.Medical: Machining threaded implants and surgical instruments.Mold Making: Threading mold components with high precision.Benefits of Using Indexable Threading MillsCompared to traditional threading methods like tapping and single-point threading, indexable threading mills offer several advantages:Versatility: One tool can produce different thread sizes and profiles by simply changing the inserts.Improved Thread Quality: Thread milling produces cleaner, more precise threads with better surface finish.Reduced Tool Breakage: Less likely to break compared to taps, especially in hard materials.Faster Cycle Times: Can often be faster than single-point threading, especially for large threads.Deburring Capabilities: Some threading mills can also deburr the thread in the same operation.Wayleading Tools provides high-quality indexable threading mills that enhance your machining operations. Our tools are designed for durability and precision.Choosing the Right Indexable Threading MillSelecting the appropriate indexable threading mill is crucial for achieving optimal results. Consider the following factors:Thread Size and Profile: Choose inserts that match the required thread dimensions and type (e.g., ISO metric, NPT, UN).Workpiece Material: Select inserts with appropriate grade and coating for the material being machined.Machine Tool: Ensure the threading mill is compatible with the machine's spindle speed, feed rates, and tool holding system.Coolant System: Determine if coolant-through capability is needed for effective chip evacuation and cooling.Application: Choose a mill designed for internal or external threading, depending on the application.Best Practices for Using Indexable Threading MillsFollow these best practices to maximize the performance and lifespan of your indexable threading mills:Use Proper Speeds and Feeds: Consult the manufacturer's recommendations for optimal cutting parameters.Ensure Rigid Tool Holding: Use a high-quality tool holder to minimize vibration and deflection.Apply Coolant Effectively: Flood coolant or coolant-through tools can significantly improve chip evacuation and tool life.Use Sharp Inserts: Replace worn inserts to maintain thread quality and prevent tool damage.Program Correct Toolpaths: Use CAM software to generate accurate and efficient toolpaths.Troubleshooting Common IssuesHere are some common issues and potential solutions when using indexable threading mills:Poor Thread Quality: Check for worn inserts, incorrect cutting parameters, or vibration.Premature Insert Wear: Verify coolant flow, reduce cutting speed, or use a more wear-resistant insert grade.Chip Evacuation Problems: Increase coolant flow, use coolant-through tools, or modify toolpaths.Tool Breakage: Reduce feed rates, ensure rigid tool holding, or select a more robust tool design.Comparing Indexable Threading Mills to Other Threading MethodsThe following table provides a comparative overview of indexable threading mills versus other common threading methods: Method Pros Cons Applications Indexable Threading Mills Versatile, good thread quality, reduced tool breakage Can be more expensive than taps, requires CNC machine Aerospace, automotive, oil & gas, medical Tapping Fast, simple, inexpensive Prone to breakage, limited versatility High-volume production of small to medium threads Single-Point Threading Versatile, can produce complex threads Slow, requires skilled operator Low-volume production, large threads, custom threads The Future of Indexable Threading MillsAdvancements in materials, coatings, and tool designs are continually improving the performance and capabilities of indexable threading mills. Future trends include:Improved Insert Grades: Development of more wear-resistant and heat-resistant insert materials.Advanced Coatings: Application of coatings with higher hardness and lower friction coefficients.Optimized Tool Geometries: Designs that improve chip evacuation and reduce cutting forces.Integration with Smart Manufacturing: Implementation of sensors and data analytics to optimize threading processes.ConclusionIndexable threading mills are powerful tools for producing high-quality threads efficiently and accurately. By understanding the principles, types, applications, and best practices discussed in this article, you can effectively leverage indexable threading mills to improve your threading operations. Consider Wayleading Tools for reliable and innovative threading solutions that can significantly enhance your manufacturing processes. Investing in the right tooling and following proper procedures will ensure that you get the most out of your indexable threading mill.Disclaimer: All product names, logos, and brands are property of their respective owners. All company, product and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, logos, and brands does not imply endorsement.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 Precision V Block And Clamps Set With Customized Type
Precision V Block And Clamps Set With Customized Type -
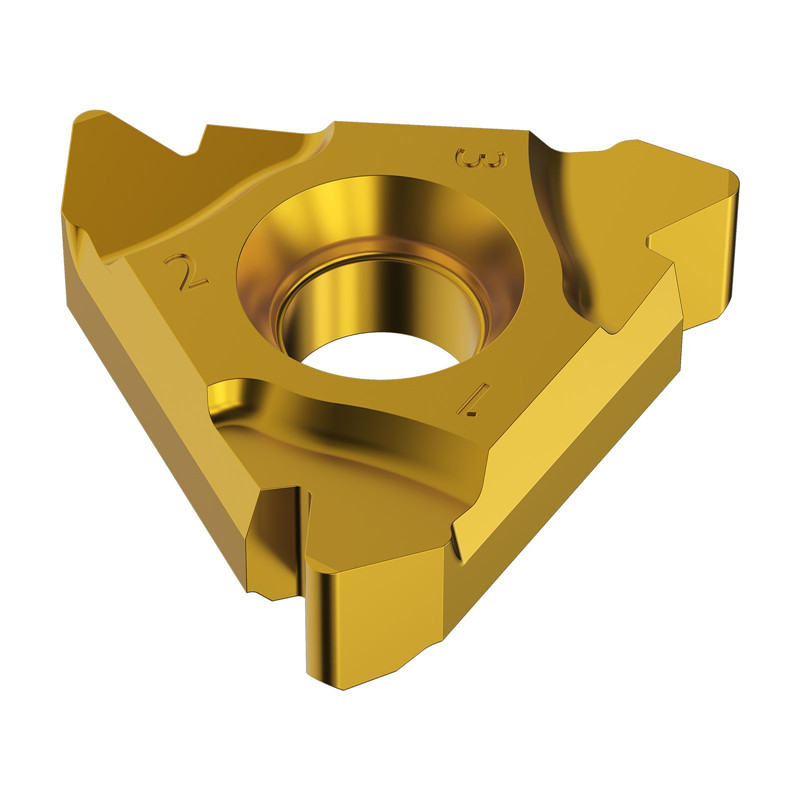 Partial profile 60° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type
Partial profile 60° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type -
 Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank
Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank -
 5C Square Collet With Inch and Metric Size
5C Square Collet With Inch and Metric Size -
 Precision Vernier Caliper With Nib Style Jaws Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Vernier Caliper With Nib Style Jaws Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 Boring Head Shank For Boring Head With Industrial Type
Boring Head Shank For Boring Head With Industrial Type -
 ER Collet Set With Hight Precision Milling
ER Collet Set With Hight Precision Milling -
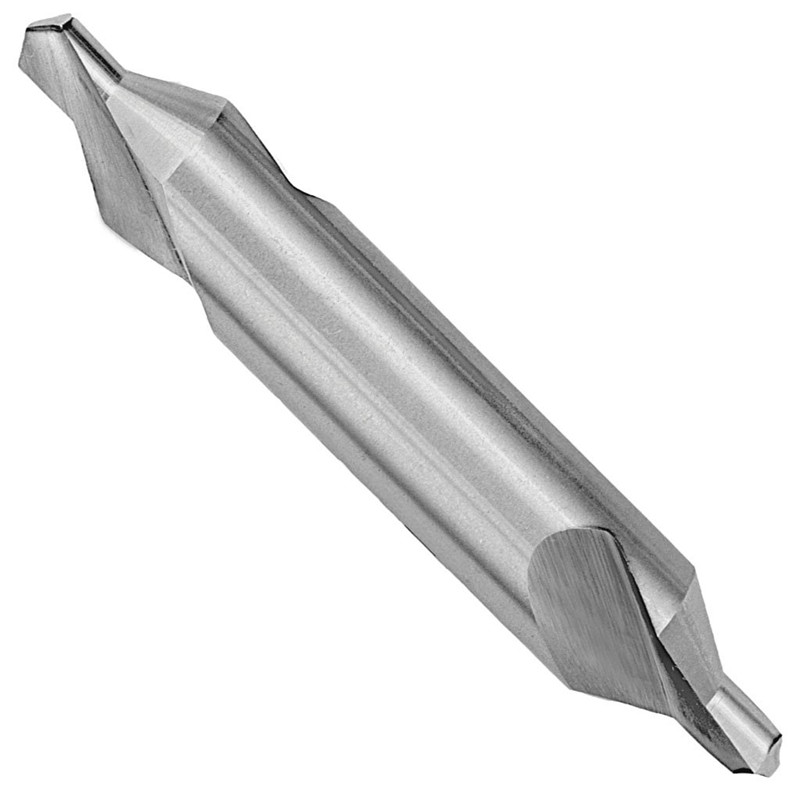 DIN333A HSS Center Drills With Milled & Fully Ground Flute
DIN333A HSS Center Drills With Milled & Fully Ground Flute -
 Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output
Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output -
 HSS Threading Taps – ISO 529, Straight Flute, Spiral Flute & Spiral Point
HSS Threading Taps – ISO 529, Straight Flute, Spiral Flute & Spiral Point -
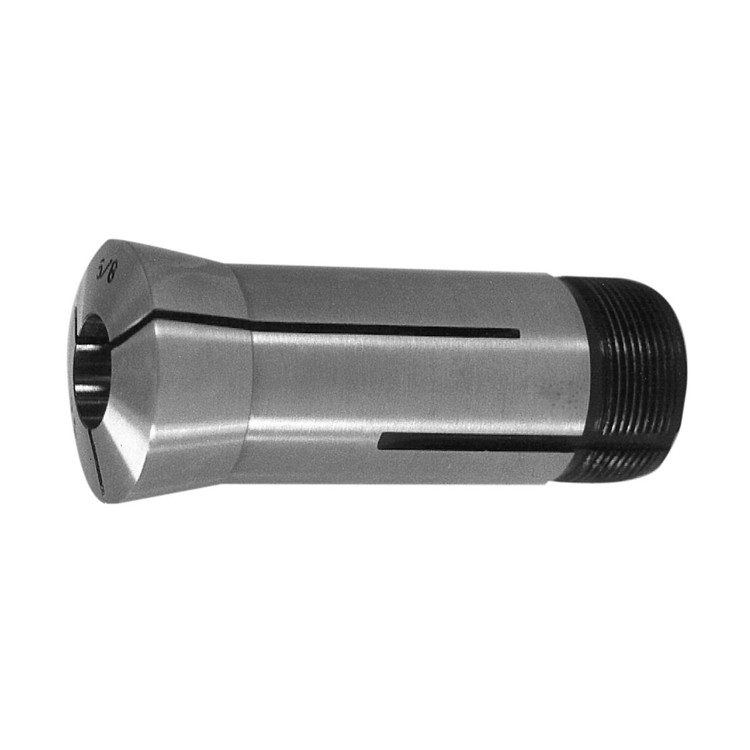 5C Round Collet With Inch and Metric Size
5C Round Collet With Inch and Metric Size -
 Dual Wheel Knurling Tools With Diamond Pattern For Industrial Type
Dual Wheel Knurling Tools With Diamond Pattern For Industrial Type
Related search
Related search- Deburring Tool Factory
- mdjnr tool holder Suppliers
- Wholesale carbide center drill
- morse taper sleeves Manufacturer
- american dryseal taper pipe full profile threading insert Factories
- CCGX insert Manufacturers
- Involute Gear Cutters Manufacturer
- G60 threading insert Manufacturers
- 3pcs boring bar sets Manufacturers
- Live center Supplier










