lathe cutting tools
Lathe cutting tools are essential for shaping materials with precision in turning operations. This guide covers various types, materials, applications, and selection criteria, offering practical insights for achieving optimal results in machining.Understanding Lathe Cutting ToolsLathe cutting tools are specialized tools used in lathes to remove material from a rotating workpiece, creating specific shapes and dimensions. They are crucial for precision machining and come in various types, each designed for a specific cutting operation.Types of Lathe Cutting ToolsThere are numerous types of lathe cutting tools, each suited for different machining operations. Understanding these types is key to selecting the right tool for your project. Turning Tools: Used for general material removal and shaping. Facing Tools: Used to create a flat surface on the end of the workpiece. Boring Tools: Used to enlarge or finish existing holes. Threading Tools: Used to create threads on the workpiece. Parting Tools: Used to cut off a finished part from the stock material. Grooving Tools: Used to create grooves on the workpiece.Materials Used in Lathe Cutting ToolsThe material of a lathe cutting tool significantly impacts its performance and lifespan. Common materials include: High-Speed Steel (HSS): Relatively inexpensive and suitable for general-purpose machining. HSS tools offer good toughness but lower hardness and wear resistance compared to other materials. Carbide: Offers excellent hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance. Carbide tools are ideal for high-speed machining and harder materials. Ceramic: Provides superior wear resistance and high-temperature performance, suitable for machining hardened steels and cast iron. Diamond: The hardest material, used for machining non-ferrous materials and achieving extremely fine finishes.Choosing the right material depends on the workpiece material, cutting speed, and desired finish.Selecting the Right Lathe Cutting ToolSelecting the right lathe cutting tool involves several considerations to ensure optimal performance and accuracy. Wayleading Tools provides a wide selection of high-quality lathe cutting tools to meet your specific needs.Factors to Consider Workpiece Material: The material being machined dictates the tool material and geometry. Cutting Speed and Feed Rate: Higher speeds and feeds require tools with better heat resistance and wear resistance. Desired Finish: Achieving a fine finish requires tools with sharp cutting edges and appropriate geometry. Machine Rigidity: Less rigid machines may require tools with lower cutting forces. Tool Geometry: Includes rake angle, clearance angle, and cutting edge angle, all of which affect cutting performance.Lathe Cutting Tool GeometryUnderstanding lathe cutting tool geometry is crucial for optimizing cutting performance. Key angles include: Rake Angle: Affects the chip formation and cutting force. Positive rake angles are suitable for softer materials, while negative rake angles are better for harder materials. Clearance Angle: Prevents the tool from rubbing against the workpiece. Cutting Edge Angle: Affects the strength of the cutting edge and the direction of the cutting force.Applications of Lathe Cutting ToolsLathe cutting tools are used in a wide range of applications, including: Manufacturing: Producing components for automotive, aerospace, and other industries. Prototyping: Creating prototypes and models for design validation. Repair and Maintenance: Repairing and refurbishing parts in various industries. Metalworking: Shaping metal into various forms and sizes.Lathe Cutting Tool MaintenanceProper maintenance of lathe cutting tools is essential for extending their lifespan and maintaining their performance. Key maintenance practices include: Regular Sharpening: Keeping the cutting edges sharp ensures clean cuts and reduces cutting forces. Proper Storage: Storing tools in a clean and dry environment prevents corrosion and damage. Careful Handling: Avoid dropping or bumping tools, as this can damage the cutting edges. Cleaning: Clean tools after each use to remove chips and debris.Troubleshooting Common IssuesEven with the best tools and techniques, you may encounter issues during turning operations. Here are some common problems and their solutions: Chatter: Can be caused by machine vibration, loose tooling, or incorrect cutting parameters. Solutions include increasing machine rigidity, tightening tooling, and adjusting cutting speeds and feeds. Poor Surface Finish: Can be caused by dull tooling, incorrect cutting parameters, or workpiece material inconsistencies. Solutions include sharpening or replacing tooling, adjusting cutting parameters, and using a coolant. Tool Wear: Is inevitable but can be minimized by using the right tool material, cutting parameters, and coolant. Regular inspection and replacement of worn tools are essential.Coolants and LubricantsUsing appropriate coolants and lubricants is crucial for reducing heat, improving surface finish, and extending tool life. Common coolants and lubricants include: Water-Soluble Coolants: Effective for cooling and chip removal. Oil-Based Coolants: Provide better lubrication and are suitable for high-speed machining. Synthetic Coolants: Offer a balance of cooling and lubrication and are suitable for a wide range of materials.Safety ConsiderationsSafety is paramount when working with lathe cutting tools. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses and gloves. Ensure the machine is properly guarded and follow all safety guidelines.Lathe Cutting Tool CoatingsCoatings enhance the performance and lifespan of lathe cutting tools. Common coatings include: Titanium Nitride (TiN): Provides good wear resistance and is suitable for general-purpose machining. Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN): Offers higher hardness and wear resistance than TiN. Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN): Provides excellent heat resistance and is suitable for high-speed machining of hard materials.Advanced Lathe Cutting Tool TechnologiesAdvancements in lathe cutting tool technology are continuously improving machining efficiency and accuracy. Examples include: Indexable Inserts: Allow for quick and easy replacement of cutting edges. Modular Tooling Systems: Provide flexibility and versatility in tool selection and setup. Vibration Damping Tools: Reduce chatter and improve surface finish.Choosing the Right SupplierSelecting a reliable supplier like Wayleading Tools is essential for obtaining high-quality lathe cutting tools that meet your specific requirements. Consider factors such as product quality, pricing, availability, and customer support.Cost AnalysisUnderstanding the cost implications of different lathe cutting tools is crucial for making informed decisions. Consider the initial cost, lifespan, and maintenance costs when evaluating different options. Tool Material Initial Cost Lifespan Maintenance Cost HSS Low Medium Low Carbide Medium High Medium Ceramic High High High ConclusionSelecting the right lathe cutting tools and implementing proper machining techniques is crucial for achieving optimal results. By understanding the different types of tools, materials, and geometries, you can improve your machining efficiency, accuracy, and overall productivity. Explore the selection of lathe cutting tools at Wayleading Tools today.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
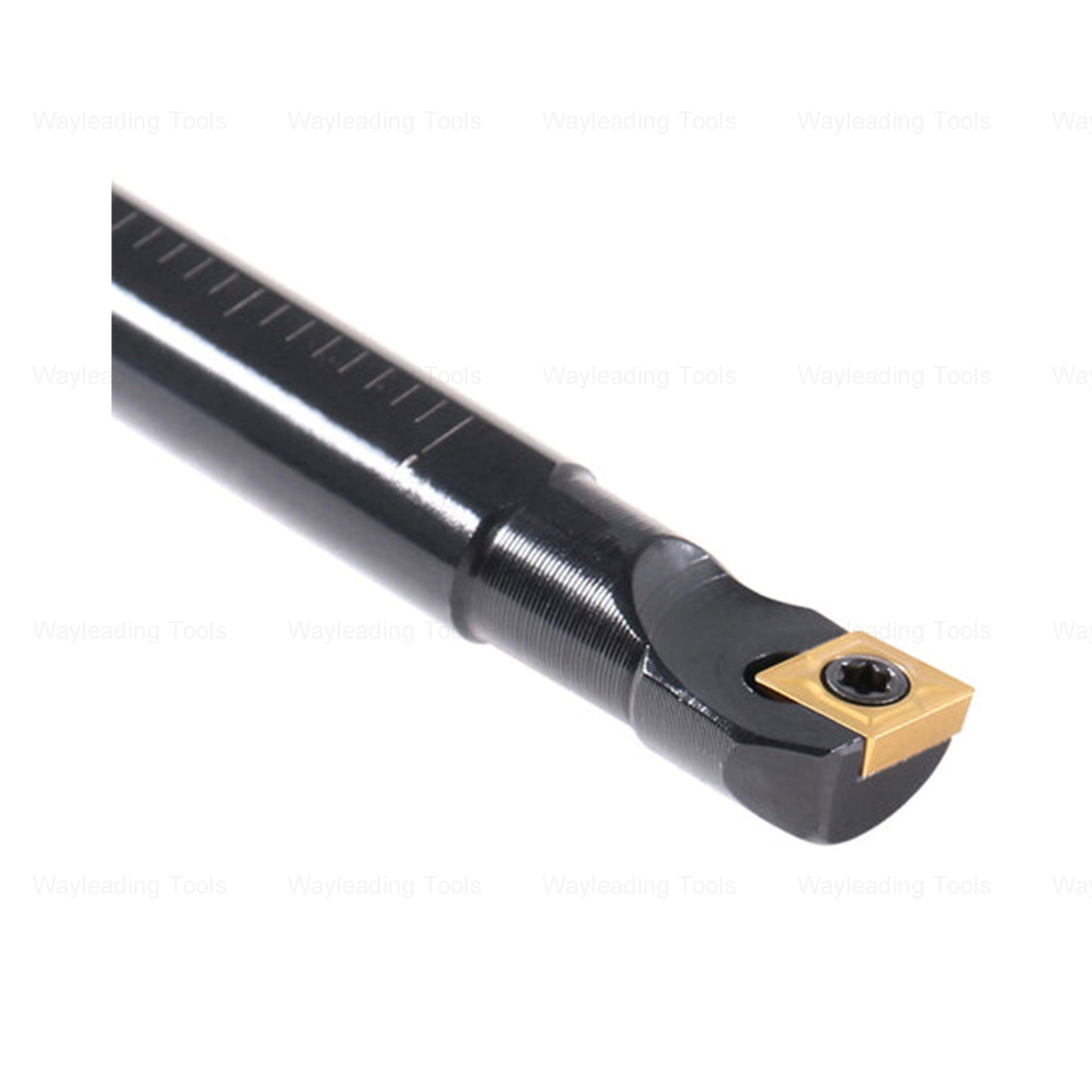 SCFC Indexable Boring Bar – Right- and Left-Hand Types
SCFC Indexable Boring Bar – Right- and Left-Hand Types -
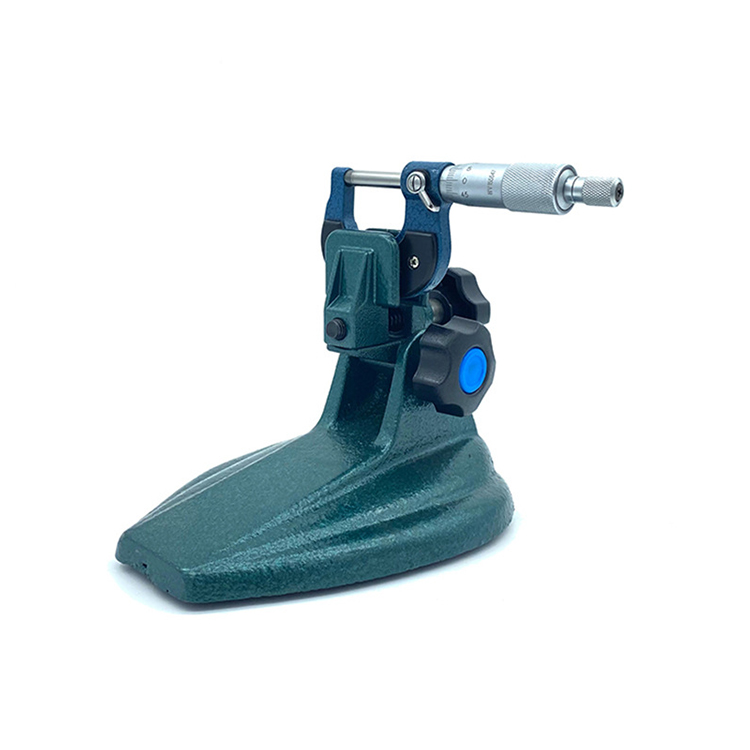 Precision Micrometr Holder For Micrometer
Precision Micrometr Holder For Micrometer -
 MT/R8 Shank Quick Change Tapping Chuck With MT & R8 Shank
MT/R8 Shank Quick Change Tapping Chuck With MT & R8 Shank -
 HSS Inch Screw Slotting Saws For Industrial With Bright Or TiN Coated
HSS Inch Screw Slotting Saws For Industrial With Bright Or TiN Coated -
 58pcs Clamping Kit With Metric & Inch Size
58pcs Clamping Kit With Metric & Inch Size -
 Metric HSS 13mm Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision
Metric HSS 13mm Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision -
 5C Hex Collet With Inch and Metric Size
5C Hex Collet With Inch and Metric Size -
 HSS Inch 4 Flute End Mills With Bright Or TiN And TiAlN Coated
HSS Inch 4 Flute End Mills With Bright Or TiN And TiAlN Coated -
 ER Collet Set With Hight Precision Milling
ER Collet Set With Hight Precision Milling -
 Precision Dustproof Dial Caliper Of Double Shock-Proof For Industrial
Precision Dustproof Dial Caliper Of Double Shock-Proof For Industrial -
 25PCS DIN338 HSS Twist Drill Bit Set From 1-13mm
25PCS DIN338 HSS Twist Drill Bit Set From 1-13mm -
 Precision Vernier Caliper With Nib Style & Standard Style Jaws Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Vernier Caliper With Nib Style & Standard Style Jaws Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial