machine tools
Machine tools are power-driven machines used to shape or form metal or other materials through cutting, boring, grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformation. They are fundamental to manufacturing, enabling the precise creation of components for everything from automobiles to aerospace equipment. This guide explores the different types of machine tools, their applications, and key considerations for selecting the right tool for your needs.What are Machine Tools?Machine tools represent the backbone of modern manufacturing. They are sophisticated machines that manipulate materials to create parts with precise dimensions and finishes. Unlike hand tools, machine tools are power-driven, allowing for greater accuracy, speed, and repeatability in production.Key Components of Machine Tools Spindle: The rotating axis of the machine, holding the cutting tool or workpiece. Cutting Tool: The tool that removes material to shape the workpiece (e.g., drill bits, milling cutters, grinding wheels). Workpiece: The material being shaped or formed. Slides/Ways: Precision guides that allow for controlled movement of the cutting tool and/or workpiece. Control System: The system (often CNC - Computer Numerical Control) that governs the machine's operation, including speed, feed rate, and tool path. Coolant System: Provides lubrication and cooling to the cutting tool and workpiece, extending tool life and improving surface finish.Types of Machine ToolsThere are many different types of machine tools, each designed for specific applications. Here are some of the most common:LathesLathes are used for turning operations, where the workpiece is rotated while a cutting tool is advanced along its length. They are ideal for creating cylindrical or conical shapes. Engine Lathes: General-purpose lathes suitable for a variety of turning operations. Turret Lathes: Equipped with a rotating turret that holds multiple cutting tools, allowing for faster setups and complex operations. CNC Lathes: Computer-controlled lathes offering high precision and automation. These are commonly used in high-volume production environments.Milling MachinesMilling machines use rotating cutters to remove material from a workpiece. They are versatile machines capable of creating a wide range of shapes and features. Vertical Milling Machines: The spindle is oriented vertically, allowing for end milling, face milling, and drilling operations. Horizontal Milling Machines: The spindle is oriented horizontally, suitable for machining large or heavy workpieces. CNC Milling Machines: Computer-controlled milling machines offering precise and automated machining capabilities. Wayleading Tools offers a range of CNC milling accessories; check out our products here.Drilling MachinesDrilling machines are used to create holes in workpieces. They come in various sizes and configurations, from simple benchtop models to large, multi-spindle machines. Bench Drills: Small, portable drills suitable for light-duty applications. Floor Drills: Larger, more powerful drills designed for heavier workloads. Radial Drills: Feature a movable arm that allows the drill head to be positioned over a large workpiece.Grinding MachinesGrinding machines use abrasive wheels to remove material and achieve very fine surface finishes. They are often used for finishing operations or for machining hardened materials. Surface Grinders: Used for grinding flat surfaces. Cylindrical Grinders: Used for grinding cylindrical shapes, both internal and external. Centerless Grinders: Used for grinding cylindrical parts without the need for center holes.Shapers and PlanersShapers and planers are reciprocating machine tools that use a single-point cutting tool to remove material. They are primarily used for creating flat surfaces and are less common in modern manufacturing due to their slower speeds compared to milling machines.Broaching MachinesBroaching machines use a toothed tool called a broach to remove material. Broaching is a highly efficient process for creating internal shapes, such as keyways and splines.Choosing the Right Machine ToolSelecting the right machine tool for your application depends on several factors: Material: The type of material you will be machining (e.g., steel, aluminum, plastic). Part Size: The dimensions of the parts you will be producing. Production Volume: The number of parts you need to manufacture. Accuracy Requirements: The level of precision required for the finished parts. Budget: The amount of money you are willing to spend on the machine.CNC Machine Tools: A Modern RevolutionCNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tools have revolutionized manufacturing by automating the machining process. CNC machines use computer programs to control the movement of the cutting tool and workpiece, resulting in higher accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency.Benefits of CNC Machine Tools Increased Accuracy: CNC machines can hold tolerances of +/- 0.001 inches or better. Improved Repeatability: CNC machines consistently produce parts to the same specifications. Reduced Labor Costs: CNC machines can operate unattended for extended periods, reducing the need for manual labor. Faster Production Speeds: CNC machines can perform complex machining operations much faster than manual machines. Greater Flexibility: CNC machines can be easily reprogrammed to produce different parts.Machine Tool MaintenanceProper maintenance is essential for keeping your machine tools running smoothly and efficiently. Regular maintenance tasks include: Lubrication: Lubricating moving parts to reduce friction and wear. Cleaning: Removing chips and debris from the machine. Inspection: Inspecting the machine for signs of wear or damage. Calibration: Calibrating the machine to ensure accuracy.The Future of Machine ToolsThe future of machine tools is being shaped by several key trends, including: Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Combining additive and subtractive manufacturing processes for hybrid manufacturing solutions. Automation and Robotics: Integrating robots and automated systems for lights-out manufacturing. Smart Manufacturing: Using sensors and data analytics to optimize machine performance and predict maintenance needs. More Efficient and Sustainable Machines: Reducing energy consumption and waste.Machine Tool Comparison Table Machine Tool Primary Use Advantages Disadvantages Lathe Creating cylindrical shapes High precision, good surface finish Limited to cylindrical shapes Milling Machine Creating complex shapes and features Versatile, can machine a wide range of materials Can be slower than other processes Drilling Machine Creating holes Simple, cost-effective Limited to creating holes Grinding Machine Achieving fine surface finishes Very high precision, can machine hardened materials Slow material removal rate Wayleading Tools is your trusted partner for high-quality machine tool accessories. Contact us today to learn more about our products and services.Disclaimer: Information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. Always consult with a qualified expert before making any decisions related to machine tools or manufacturing processes.References: National Association of Manufacturers (NAM) Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME)
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
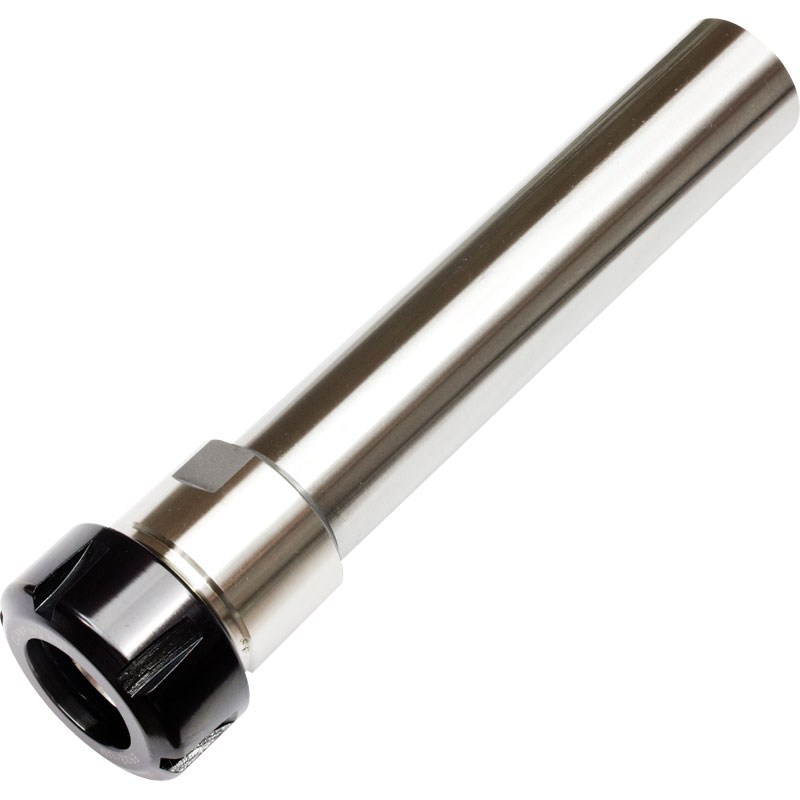 Straight Shank ER Collet Chuck Holders With Extending Rod
Straight Shank ER Collet Chuck Holders With Extending Rod -
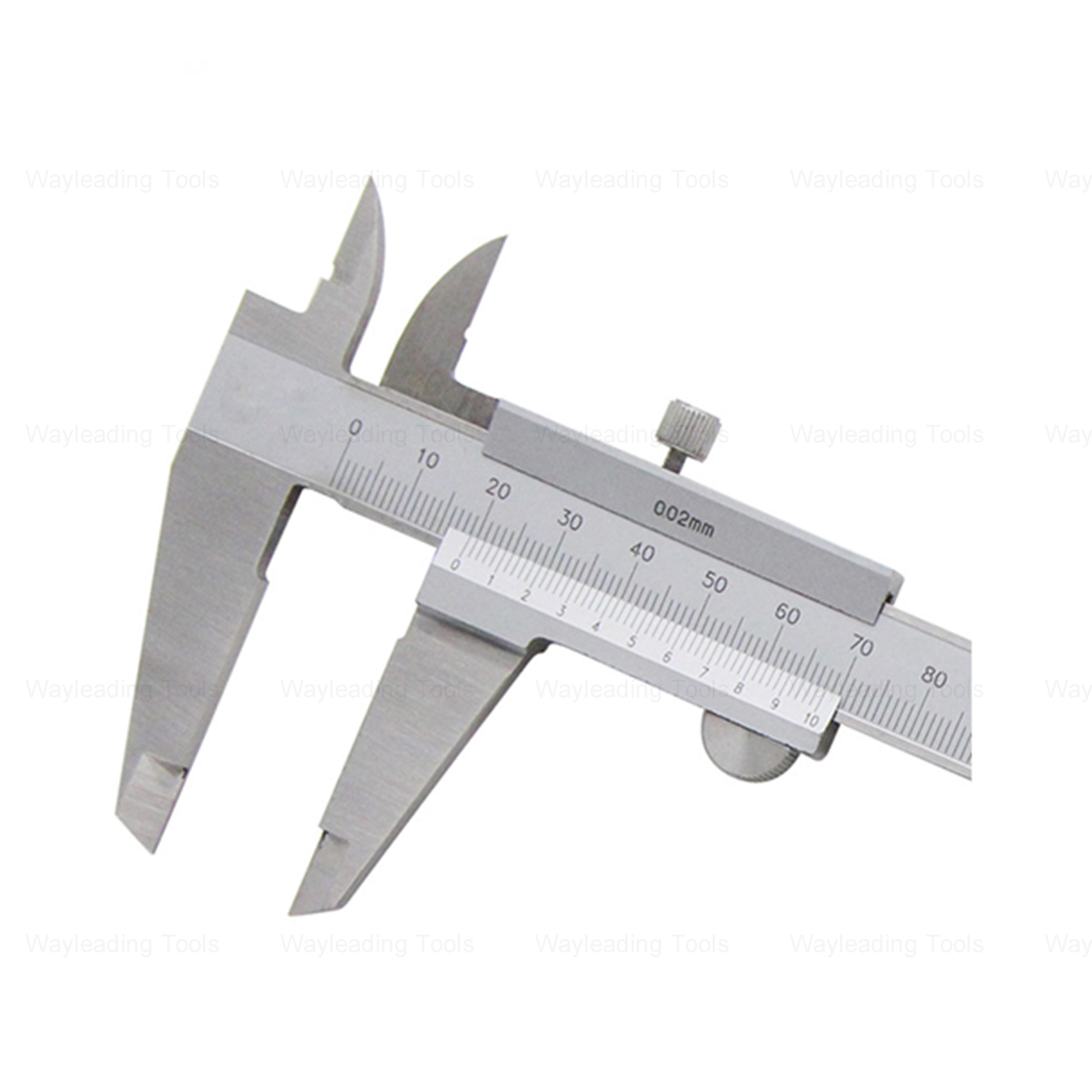
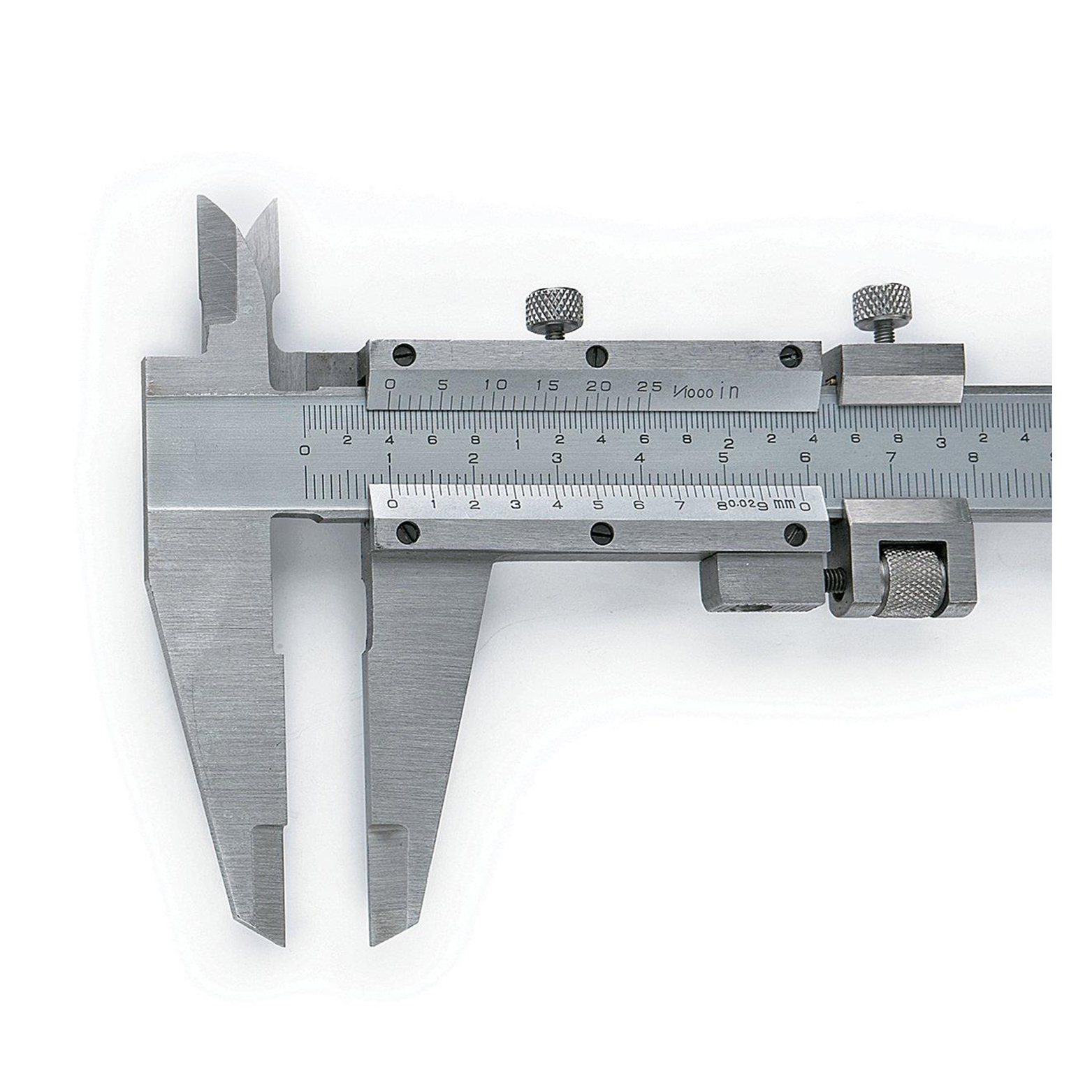 Precision Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 HSS Involute Spline Cutter With PA30
HSS Involute Spline Cutter With PA30 -
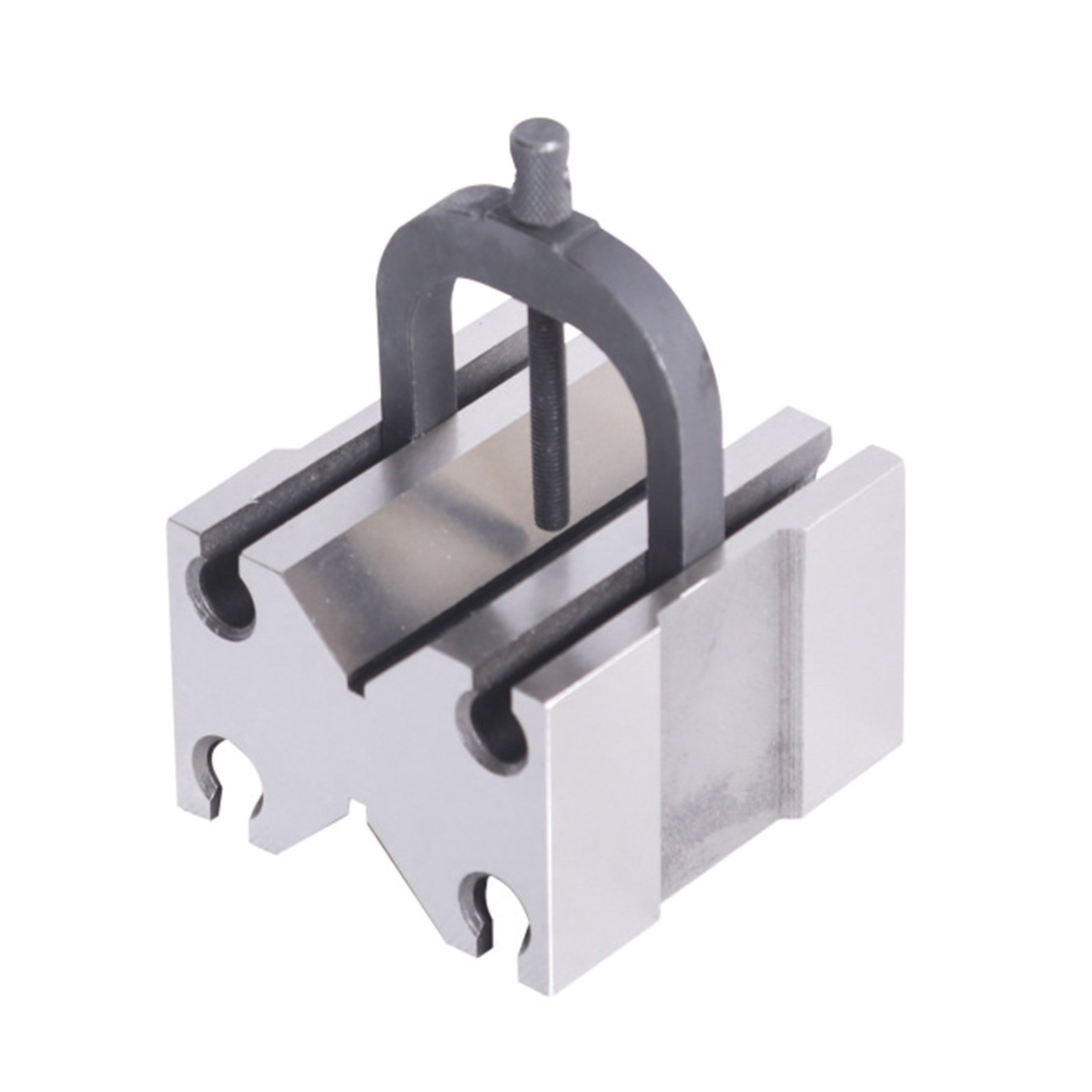 Precision V Block And Clamps Set With Industry Type
Precision V Block And Clamps Set With Industry Type -
 Inch HSS 1/2″ Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision
Inch HSS 1/2″ Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision -
 Precision Dial Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Dial Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank
Dead Center For Morse Taper Shank -
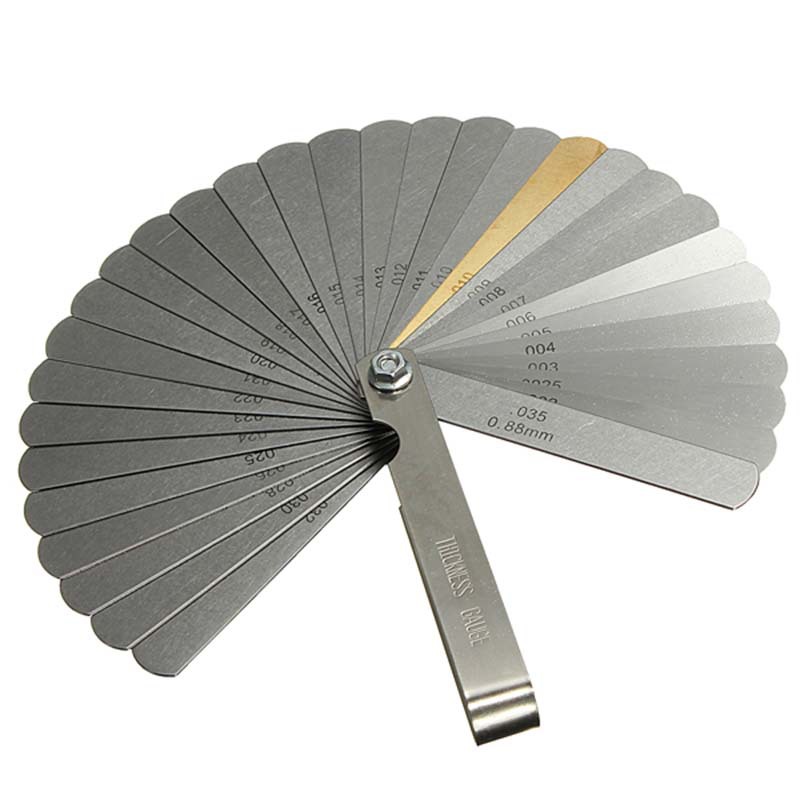 32 Blades Feeler Gauge From 0.04-0.88MM
32 Blades Feeler Gauge From 0.04-0.88MM -
 F1 Precision Boring Head With Metric & Inch
F1 Precision Boring Head With Metric & Inch -
 Precision IP65 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output
Precision IP65 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output -
 Type E Heavy Duty Deburring Tool Set With Deburring Holder And Deburring Blade
Type E Heavy Duty Deburring Tool Set With Deburring Holder And Deburring Blade -
 Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output
Precision IP54 Digital Outside Micrometer Of Inch & Metric With Data Output











