machining tools
Machining tools are essential for shaping materials into desired forms through cutting, drilling, grinding, and other processes. This guide explores various types of machining tools, their applications, and factors to consider when selecting the right tool for your project, empowering you to make informed decisions for optimal results. Learn about the precision and efficiency these tools bring to manufacturing and fabrication.What are Machining Tools?Machining tools, also known as machine tools, are power-driven machines used to shape or form metal or other materials by cutting, grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformation. These tools are fundamental to manufacturing and fabrication processes across various industries. The precision and control they offer enable the creation of complex parts with tight tolerances.Types of Machining ToolsLathesLathes are machining tools that rotate a workpiece while a cutting tool removes material. They are commonly used for creating cylindrical or conical shapes. Different types of lathes exist, including: Engine Lathes: General-purpose lathes suitable for a wide range of turning operations. Turret Lathes: Equipped with a turret that holds multiple tools, allowing for faster and more complex machining. CNC Lathes: Computer-controlled lathes that offer high precision and repeatability.Milling MachinesMilling machines use rotating cutters to remove material from a workpiece. They are versatile machining tools capable of producing a variety of shapes and features. Types of milling machines include: Vertical Milling Machines: The spindle is oriented vertically, and the cutter moves along multiple axes. Horizontal Milling Machines: The spindle is oriented horizontally, offering better support for heavy workpieces. CNC Milling Machines: Computer-controlled milling machines that offer precise and automated machining. The team at Wayleading Tools highlights the growing popularity of CNC milling in modern manufacturing.Drilling MachinesDrilling machines are machining tools used to create holes in a workpiece. They utilize rotating drill bits to remove material. Types of drilling machines include: Upright Drilling Machines: General-purpose drilling machines for various drilling tasks. Radial Drilling Machines: Equipped with a radial arm that allows the spindle to be positioned over a large work area. CNC Drilling Machines: Computer-controlled drilling machines that offer precise and automated hole creation.Grinding MachinesGrinding machines use abrasive wheels to remove small amounts of material, producing very fine finishes and precise dimensions. They are essential machining tools for achieving high accuracy. Types of grinding machines include: Surface Grinders: Used for grinding flat surfaces. Cylindrical Grinders: Used for grinding cylindrical surfaces. Centerless Grinders: Used for grinding cylindrical parts without requiring centers.Shapers and PlanersShapers and planers are machining tools that use a single-point cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece in a linear motion. Shapers are typically used for smaller workpieces, while planers are used for larger ones.Broaching MachinesBroaching machines use a toothed tool (broach) to remove material in a single pass. They are efficient machining tools for creating internal features, such as keyways and splines.Applications of Machining ToolsMachining tools are used in a wide range of industries, including: Automotive: Manufacturing engine parts, transmission components, and other vehicle parts. Aerospace: Producing aircraft components, such as engine blades, landing gear parts, and structural elements. Medical: Creating medical implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment. Electronics: Manufacturing electronic components, such as circuit boards and connectors. Tool and Die Making: Creating molds, dies, and other tooling for manufacturing processes.Factors to Consider When Choosing Machining ToolsSelecting the right machining tools is crucial for achieving desired results. Here are some factors to consider: Material: The type of material being machined (e.g., steel, aluminum, plastic) will influence the choice of tool and cutting parameters. Part Geometry: The shape and complexity of the part will determine the type of machining tools required. Tolerance Requirements: The required dimensional accuracy and surface finish will affect the choice of machine and tooling. Production Volume: The number of parts to be produced will influence the level of automation and efficiency required. Budget: The cost of the machine, tooling, and maintenance should be considered.Advanced Machining TechnologiesAdvancements in technology have led to the development of sophisticated machining tools and processes, including: CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines offer high precision, repeatability, and automation. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): EDM uses electrical sparks to remove material, allowing for the machining of hard and complex shapes. Laser Cutting: Laser cutting uses a focused laser beam to cut materials with high precision and speed. Waterjet Cutting: Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water to cut materials, offering a versatile and environmentally friendly option.Maintenance and SafetyProper maintenance and safety practices are essential for ensuring the longevity and safe operation of machining tools. Regular maintenance tasks include: Lubrication: Keeping moving parts properly lubricated to reduce friction and wear. Cleaning: Removing chips, debris, and coolant to prevent contamination and damage. Inspection: Regularly inspecting the machine for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Calibration: Calibrating the machine to ensure accuracy and precision.Safety precautions when operating machining tools include: Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection. Following lockout/tagout procedures when performing maintenance or repairs. Ensuring proper ventilation to remove fumes and dust. Never operating a machine without proper training and authorization.Cost Comparison of Different Machining ToolsThe cost of machining tools varies greatly depending on the type, size, and features. Here's a general comparison: Machining Tool Type Approximate Cost Range Key Considerations Engine Lathe $5,000 - $50,000 Versatility, manual operation, suitable for small shops. CNC Lathe $30,000 - $200,000+ High precision, automation, programming skills required. Vertical Milling Machine $8,000 - $60,000 Good for general milling, manual or powered feeds. CNC Milling Machine $40,000 - $300,000+ Complex shapes, high accuracy, CAM software knowledge. Surface Grinder $6,000 - $40,000 Finishing flat surfaces, tight tolerances. EDM Machine $50,000 - $500,000+ Machining hard materials, intricate details. Note: Prices are approximate and can vary based on brand, features, and condition.ConclusionMachining tools are indispensable in modern manufacturing, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility. By understanding the different types of machining tools, their applications, and the factors to consider when selecting them, manufacturers can optimize their processes and achieve desired results. Whether you are a seasoned machinist or new to the field, this guide provides a solid foundation for navigating the world of machining tools. For high-quality tooling solutions and expert advice, visit Wayleading Tools.Data Source: Cost ranges are based on industry averages and estimates from machine tool manufacturers and suppliers. Actual costs may vary.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
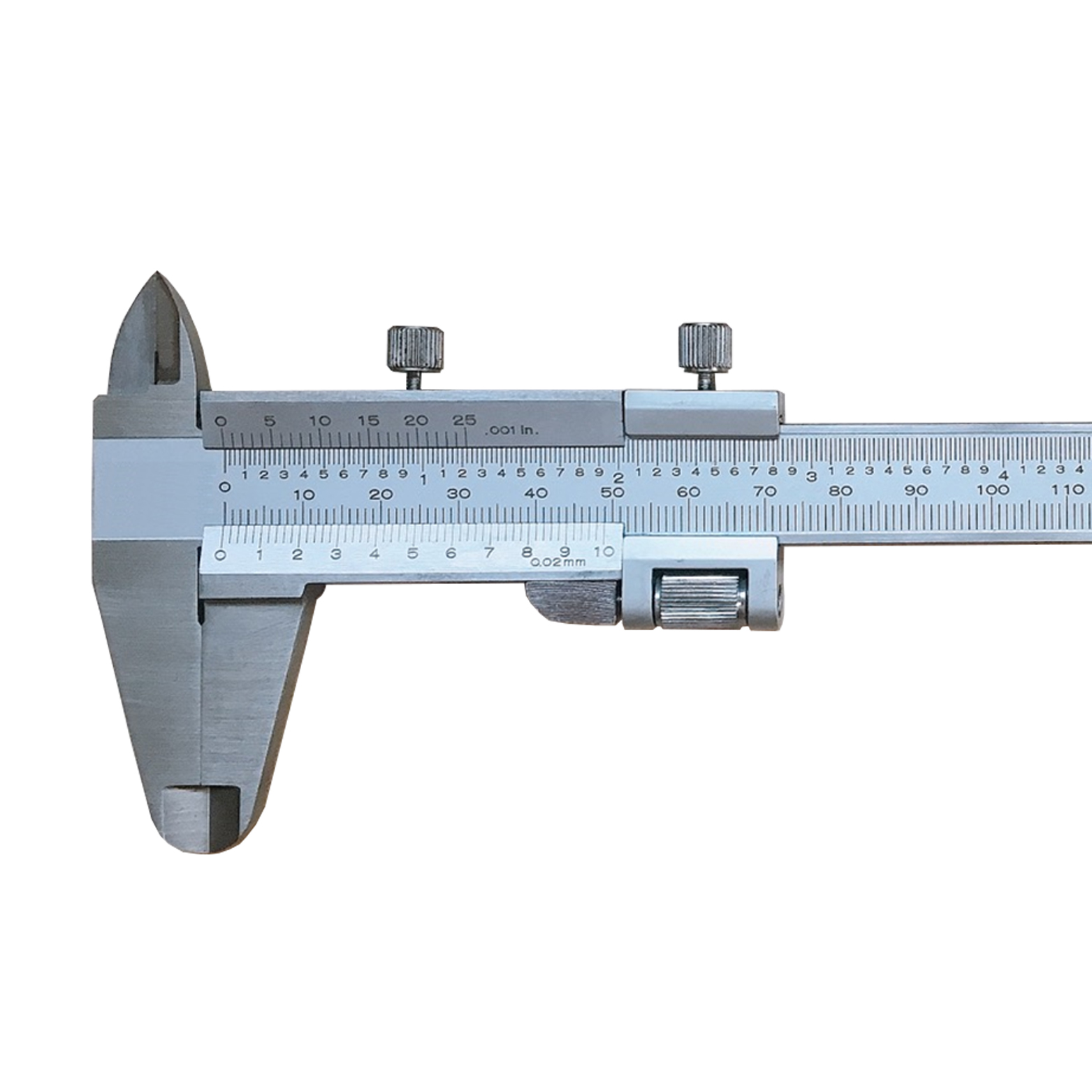
 Precision Dial Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Dial Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 131PCS Thread Repair Set And Helicoil Type Thread Repair Set
131PCS Thread Repair Set And Helicoil Type Thread Repair Set -
 QA Grooving & Cut-Off Tool Holder
QA Grooving & Cut-Off Tool Holder -
 High Precision BT-ER Collet Chuck – CNC Tool Holder, Spring Type, ER16–ER40
High Precision BT-ER Collet Chuck – CNC Tool Holder, Spring Type, ER16–ER40 -
 Digital Indicator – Precision Type, Inch/Metric, Industrial Grade
Digital Indicator – Precision Type, Inch/Metric, Industrial Grade -
 Precision Micrometr Holder For Micrometer
Precision Micrometr Holder For Micrometer -
 Precision V Block Set With High Quality Type
Precision V Block Set With High Quality Type -
 Type K-90 Degree Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type K-90 Degree Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 Metric Thread Ring Gauge 6g Accuracy With Go & NO Go
Metric Thread Ring Gauge 6g Accuracy With Go & NO Go -
 Precision V Block Set With M Type
Precision V Block Set With M Type -
 Stub Milling Machine Arbor With NT, R8 and MT Shank
Stub Milling Machine Arbor With NT, R8 and MT Shank -
 Partial profile 55° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type
Partial profile 55° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type