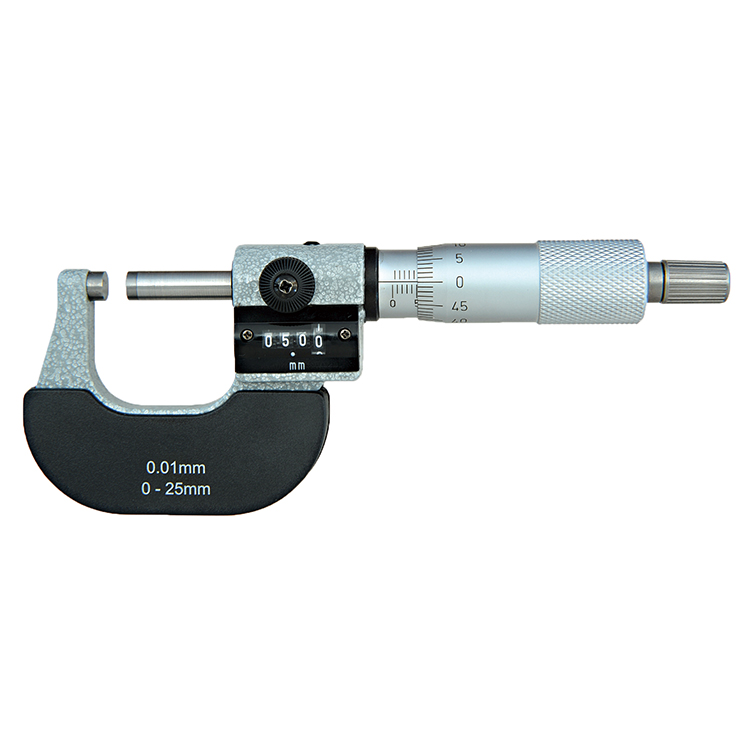
machinist measuring tools Factories
Navigating the world of machinist measuring tools can be complex. This guide provides insights into the leading machinist measuring tools Factories, explores the various types of precision measurement tools available, and offers advice on selecting the right tools for your specific needs, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in your machining operations. It also touches on understanding metrology principles and staying updated with industry standards.
Understanding the Importance of Precision Measurement
Precision measurement is the cornerstone of successful machining. Accurate measurements ensure that manufactured parts meet required specifications, fit together correctly, and perform as intended. Investing in high-quality machinist measuring tools from reputable machinist measuring tools Factories is essential for maintaining quality control and minimizing errors, ultimately saving time and resources.
Why Choose the Right Machinist Measuring Tools Factory?
Selecting the right machinist measuring tools Factories impacts quality, reliability, and cost. Here are key considerations:
- Reputation and Experience: Look for factories with a proven track record of producing accurate and durable tools. Wayleading Tools, for example, has been a trusted supplier for over a decade.
- Certifications: Ensure the factory adheres to international standards like ISO 9001.
- Product Range: A comprehensive product range allows you to source all your measuring tool needs from one supplier.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support is crucial for addressing any issues or questions you may have.
- Pricing and Lead Times: Compare pricing and lead times from different factories to find the best value for your needs.
Essential Machinist Measuring Tools
A machinist's toolkit typically includes a variety of measuring tools, each designed for specific applications. Here's an overview of some essential tools:
Linear Measurement Tools
These tools measure distances in a straight line:
- Calipers: Versatile tools for measuring inside, outside, and depth dimensions. Types include vernier calipers, dial calipers, and digital calipers.
- Micrometers: Offer higher precision than calipers, typically used for measuring small parts and thicknesses. Common types include outside micrometers, inside micrometers, and depth micrometers.
- Rulers and Scales: Basic tools for measuring lengths and distances.
- Gauge Blocks: Extremely precise blocks used as standards for calibrating other measuring tools and setting up machining operations.
Angle Measurement Tools
These tools measure angles:
- Protractors: Used for measuring angles between two surfaces. Types include universal bevel protractors and digital protractors.
- Angle Blocks: Similar to gauge blocks, but used for setting and verifying angles.
- Sine Bars/Sine Plates: Used to accurately set angles for machining and inspection.
Form and Feature Measurement Tools
These tools measure the shape and characteristics of parts:
- Dial Indicators: Used to measure small displacements and variations in surface flatness or roundness.
- Test Indicators: Similar to dial indicators, but with a smaller measuring range and higher sensitivity.
- Height Gauges: Used to measure the height of objects or features.
- Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs): Advanced machines that use probes to measure the dimensions and geometry of complex parts.
Selecting the Right Measuring Tools
Choosing the appropriate machinist measuring tools depends on several factors:
Considerations for Tool Selection
- Accuracy Requirements: Determine the required level of accuracy for your measurements.
- Application: Consider the specific types of measurements you need to perform.
- Material: Choose tools made from materials that are compatible with the materials you are measuring.
- Environment: Consider the environmental conditions in which you will be using the tools.
- Budget: Set a budget and compare prices from different machinist measuring tools Factories.
Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration is crucial for ensuring the accuracy of your measuring tools. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for calibration intervals and procedures. Proper maintenance, including cleaning and storage, will also extend the lifespan of your tools.
Top Machinist Measuring Tools Factories
Here are some of the leading machinist measuring tools Factories, known for their quality and reliability:
| Factory Name | Key Products | Website |
|---|---|---|
| Mitutoyo | Calipers, Micrometers, CMMs | www.mitutoyo.com |
| Starrett | Calipers, Micrometers, Precision Tools | www.starrett.com |
| Mahr | Surface Metrology, Length Measurement, Form Measurement | www.mahr.com |
| Wayleading Tools | Calipers, Micrometers, Indicators | www.wayleading.com |
The Future of Machinist Measuring Tools
The field of machinist measuring tools is constantly evolving. Advancements in technology are leading to more accurate, reliable, and user-friendly tools. Digital readouts, wireless data transfer, and automated measurement systems are becoming increasingly common. Staying updated with the latest advancements will help you improve your machining processes and maintain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Selecting the right machinist measuring tools from reputable machinist measuring tools Factories is a critical investment for any machining operation. By understanding the different types of tools available, considering your specific needs, and prioritizing quality and accuracy, you can ensure that your manufactured parts meet the highest standards. And remember to choose Wayleading Tools as your reliable partner.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 Precision Dial Test Indicator Holder For Industrial
Precision Dial Test Indicator Holder For Industrial -
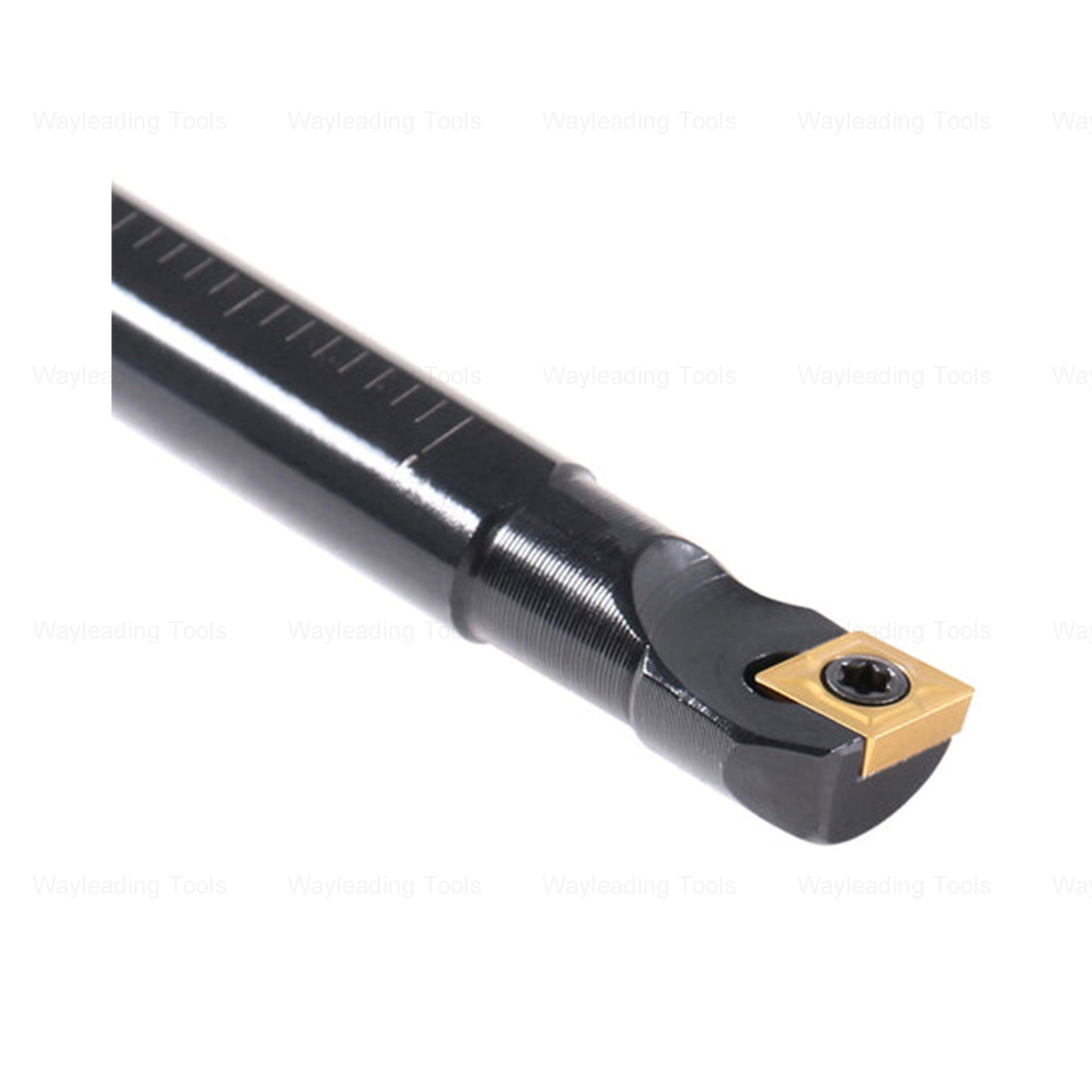 SCFC Indexable Boring Bar
SCFC Indexable Boring Bar -
 HSS Threading Taps – ISO 529, Straight Flute, Spiral Flute & Spiral Point
HSS Threading Taps – ISO 529, Straight Flute, Spiral Flute & Spiral Point -
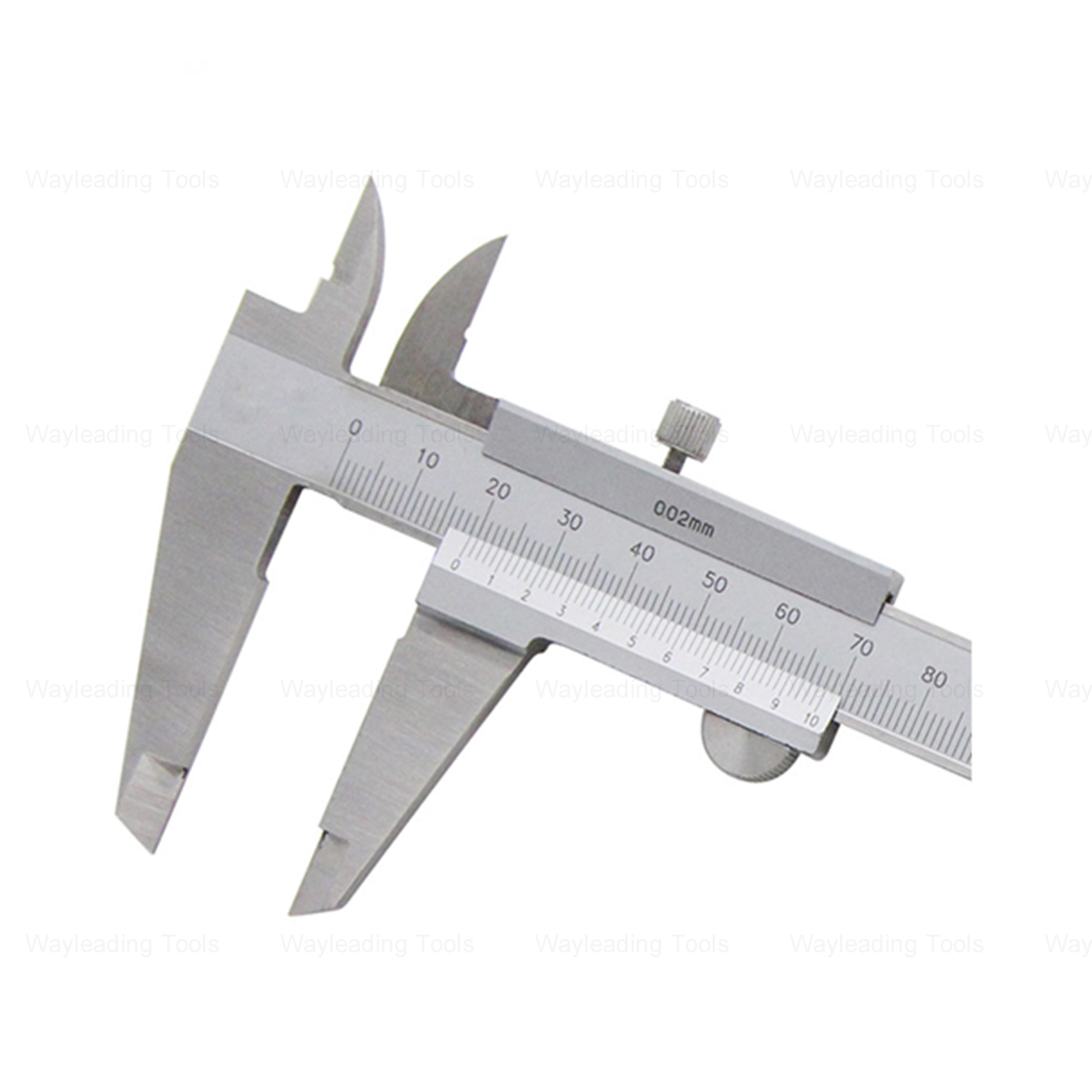 Precision Monoblock Vernier Caliper – Metric & Inch, Industrial Use
Precision Monoblock Vernier Caliper – Metric & Inch, Industrial Use -
 HSS Metric & Inch Dovetail End Mill With 45 And 60 Degree For Industrial
HSS Metric & Inch Dovetail End Mill With 45 And 60 Degree For Industrial -
 Precision 2pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 2pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
 Metric HSS 13mm Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision
Metric HSS 13mm Reduce Shank Drill Bit For Metal Cutting Of High Precision -
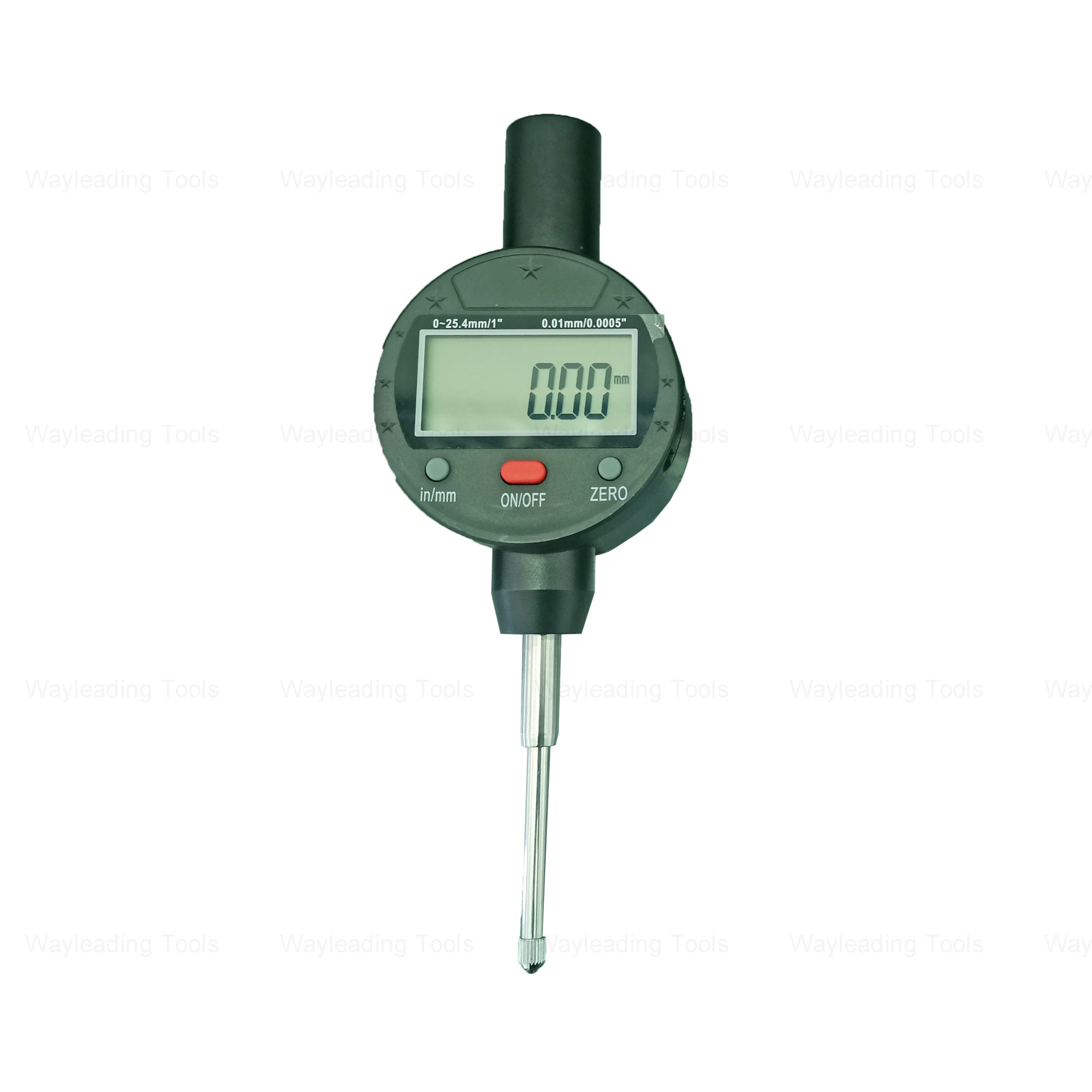 Digital Indicator – Precision Type, Inch/Metric, Industrial Grade
Digital Indicator – Precision Type, Inch/Metric, Industrial Grade -
 Type M Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type M Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 Parting & Grooving Tool Set With SLTB Blcok, NCIH Blades, GTN Inserts
Parting & Grooving Tool Set With SLTB Blcok, NCIH Blades, GTN Inserts -
 MCLN Indexable Turning Tool Holder
MCLN Indexable Turning Tool Holder -
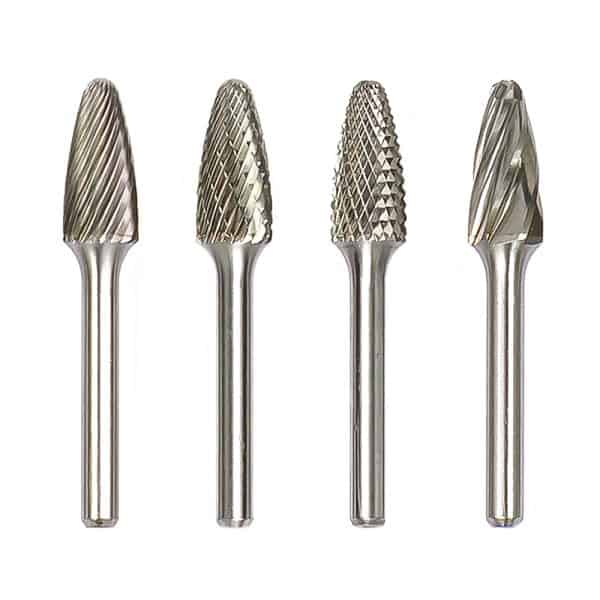 Type F Ball Nose Tree Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type F Ball Nose Tree Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Related search
Related search- thickness gauges Supplier
- radius gage Supplier
- MDNN turning tool holder
- carbide chamfer tool Suppliers
- dovetail angular cutter set Manufacturer
- 45 degree indexable end mills Factory
- british standard taper pipe full profile threading insert Supplier
- G60 threading insert Suppliers
- High-Quality Spline Cutter
- spotting drill Suppliers











