N60 threading insert
N60 threading inserts are essential cutting tools used in machining for creating precise and reliable threads. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of N60 threading inserts, covering their types, applications, materials, selection criteria, and best practices for optimal performance. Whether you're a seasoned machinist or new to the field, this information will help you understand and effectively utilize N60 threading inserts to achieve high-quality threaded components.Understanding N60 Threading InsertsWhat are N60 Threading Inserts?N60 threading inserts are indexable cutting tools designed specifically for creating internal and external threads on various materials. They are characterized by their 60-degree thread angle, which is a standard for many common thread forms, including metric and unified threads. These inserts are typically made from hard materials like cemented carbide, coated carbide, or cermet to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated during the threading process. The inserts are held in a toolholder, allowing for quick and easy replacement when the cutting edge becomes worn.Key Features of N60 Threading Inserts 60-Degree Thread Angle: The defining characteristic, ensuring compatibility with standard thread forms. Indexable Design: Allows for multiple cutting edges on a single insert, maximizing tool life and reducing downtime. Various Grades and Coatings: Available in different materials and coatings to suit a wide range of workpiece materials and machining conditions. Precise Geometry: Manufactured to tight tolerances to ensure accurate thread profiles and consistent results.Types of N60 Threading InsertsN60 threading inserts are available in various types to cater to different threading applications. The main distinctions are based on the thread type, cutting direction, and insert shape.Based on Thread Type Metric Thread Inserts: Designed for creating metric threads according to ISO standards. Unified Thread Inserts: For creating unified national (UN) threads, including UNC, UNF, and UNEF. Whitworth Thread Inserts: Used for creating Whitworth threads, a British standard. NPT/NPTF Thread Inserts: Designed for creating national pipe threads (tapered and fuel), commonly used in plumbing and fluid power applications. ACME Thread Inserts: For creating ACME threads, often used in lead screws and power transmission applications.Based on Cutting Direction Right-Hand Thread Inserts: Used for creating threads that tighten when rotated clockwise. Left-Hand Thread Inserts: Used for creating threads that tighten when rotated counter-clockwise.Based on Insert Shape Full Profile Inserts: These inserts create the entire thread profile in a single pass, resulting in higher accuracy and surface finish. Partial Profile Inserts: These inserts require multiple passes to create the complete thread profile. They are often used for larger thread sizes or when machining tougher materials.Applications of N60 Threading InsertsN60 threading inserts are used in a wide range of industries for creating threaded components in various applications. Some common examples include: Automotive: Manufacturing threaded fasteners, engine components, and hydraulic fittings. Aerospace: Creating threads on aircraft structural components, engine parts, and landing gear. Oil and Gas: Manufacturing threaded connections for pipelines, valves, and drilling equipment. Medical: Creating threads on surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices. General Machining: Manufacturing threaded parts for various industrial and consumer products.Choosing the Right N60 Threading InsertSelecting the appropriate N60 threading insert is crucial for achieving optimal threading performance and ensuring the quality of the final product. Consider the following factors when making your selection:Workpiece MaterialThe material being machined significantly impacts the choice of insert grade and coating. For example: Steel: Carbide inserts with a TiN or TiAlN coating are generally suitable for machining steel. Stainless Steel: Cermet inserts or carbide inserts with a PVD coating are recommended for stainless steel due to their resistance to built-up edge. Aluminum: Uncoated carbide inserts with a sharp cutting edge are typically used for aluminum. Cast Iron: Carbide inserts with a CVD coating are often used for cast iron.Thread Type and SizeEnsure that the insert is designed for the specific thread type and size required for the application. Use the correct thread pitch.Machining ConditionsConsider the machine tool's capabilities, the desired surface finish, and the required production rate. Higher cutting speeds and feeds may require more wear-resistant insert grades.Insert Grade and CoatingThe insert grade refers to the base material composition, while the coating enhances the insert's performance by providing increased wear resistance, heat resistance, and reduced friction. Consult insert manufacturer recommendations for specific applications.Best Practices for Using N60 Threading InsertsFollowing these best practices will help you maximize the performance and lifespan of your N60 threading inserts: Proper Toolholding: Use a rigid toolholder that provides adequate support and minimizes vibration. Correct Cutting Parameters: Use the recommended cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut for the specific insert grade and workpiece material. Coolant Application: Apply coolant to the cutting zone to reduce heat and flush away chips. Chip Control: Ensure proper chip formation and evacuation to prevent chip jamming and damage to the insert and workpiece. Regular Inspection: Inspect the inserts regularly for wear and replace them when necessary.Troubleshooting Common IssuesEven with careful selection and proper usage, you may encounter some common issues when using N60 threading inserts. Here's how to troubleshoot them: Poor Thread Quality: Could be caused by worn inserts, incorrect cutting parameters, or inadequate toolholding. Insert Breakage: Could be caused by excessive cutting forces, interrupted cuts, or incorrect insert grade. Chipping: Could be caused by hard spots in the workpiece material, excessive cutting speed, or a dull insert. Vibration: Could be caused by inadequate toolholding, excessive overhang, or machine tool instability.Where to Buy N60 Threading InsertsN60 threading inserts are available from various suppliers, including: Online Retailers: Websites like Amazon and AliExpress offer a wide selection of inserts from different manufacturers. Industrial Supply Companies: Companies like MSC Industrial Supply and Grainger carry a variety of cutting tools, including N60 threading inserts. Direct from Manufacturers: Some manufacturers, like Wayleading Tools, sell their products directly to end-users. Local Tool Suppliers: Many local tool suppliers carry a selection of cutting tools and can provide expert advice on choosing the right insert for your application.ConclusionN60 threading inserts are indispensable tools for creating accurate and reliable threads in a wide range of applications. By understanding the different types of inserts, selecting the appropriate grade and coating, and following best practices for usage, you can maximize their performance and ensure the quality of your threaded components. Whether you source from Wayleading Tools or another reputable supplier, investing in quality inserts is a worthwhile investment in your machining operations.Disclaimer: This information is for general guidance only. Always consult the insert manufacturer's recommendations and follow safe machining practices.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
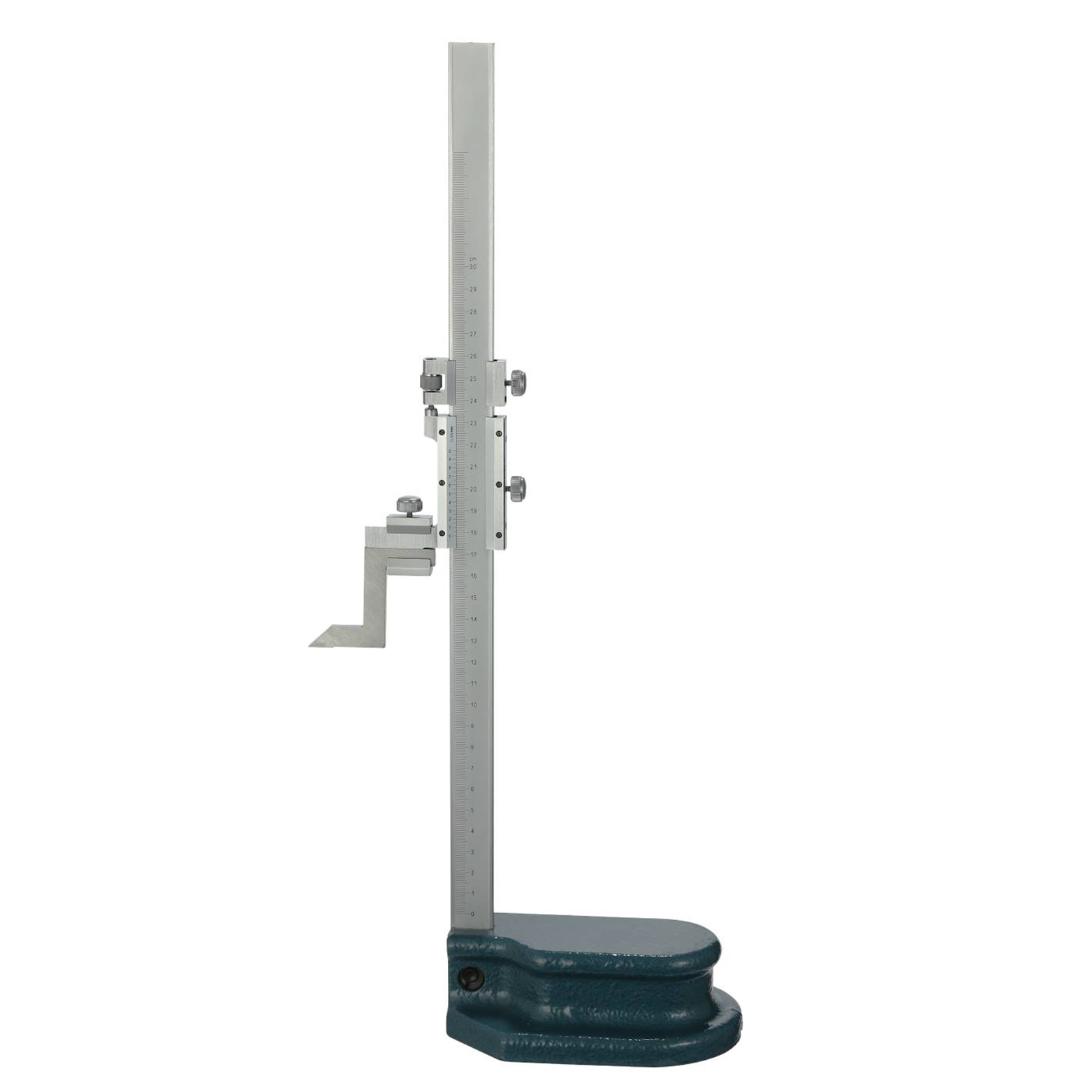 Vernier Height Gauge For Industrial
Vernier Height Gauge For Industrial -
 DIN4971-ISO1 Carbide Tipped Tool Bit With Right And Left Hand
DIN4971-ISO1 Carbide Tipped Tool Bit With Right And Left Hand -
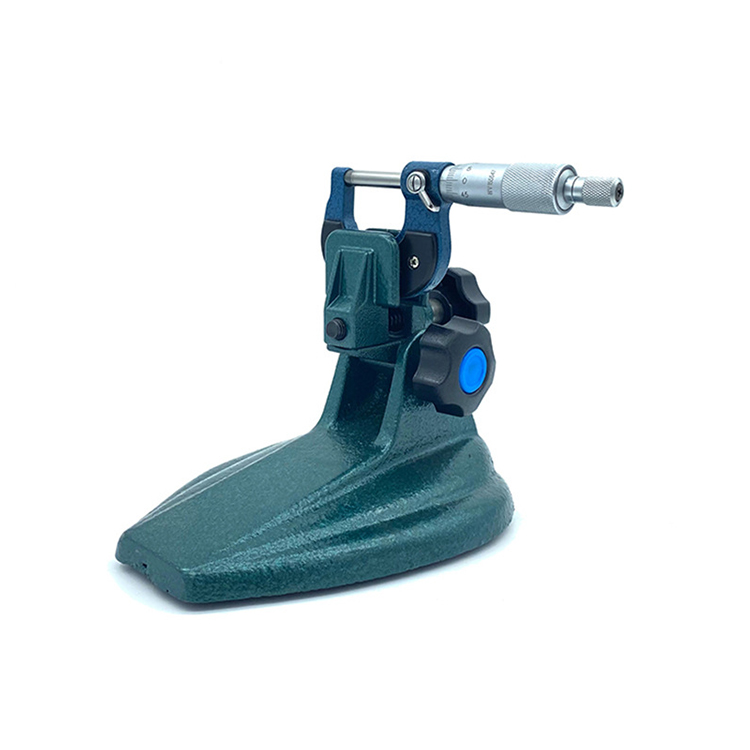 Precision Micrometr Holder For Micrometer
Precision Micrometr Holder For Micrometer -
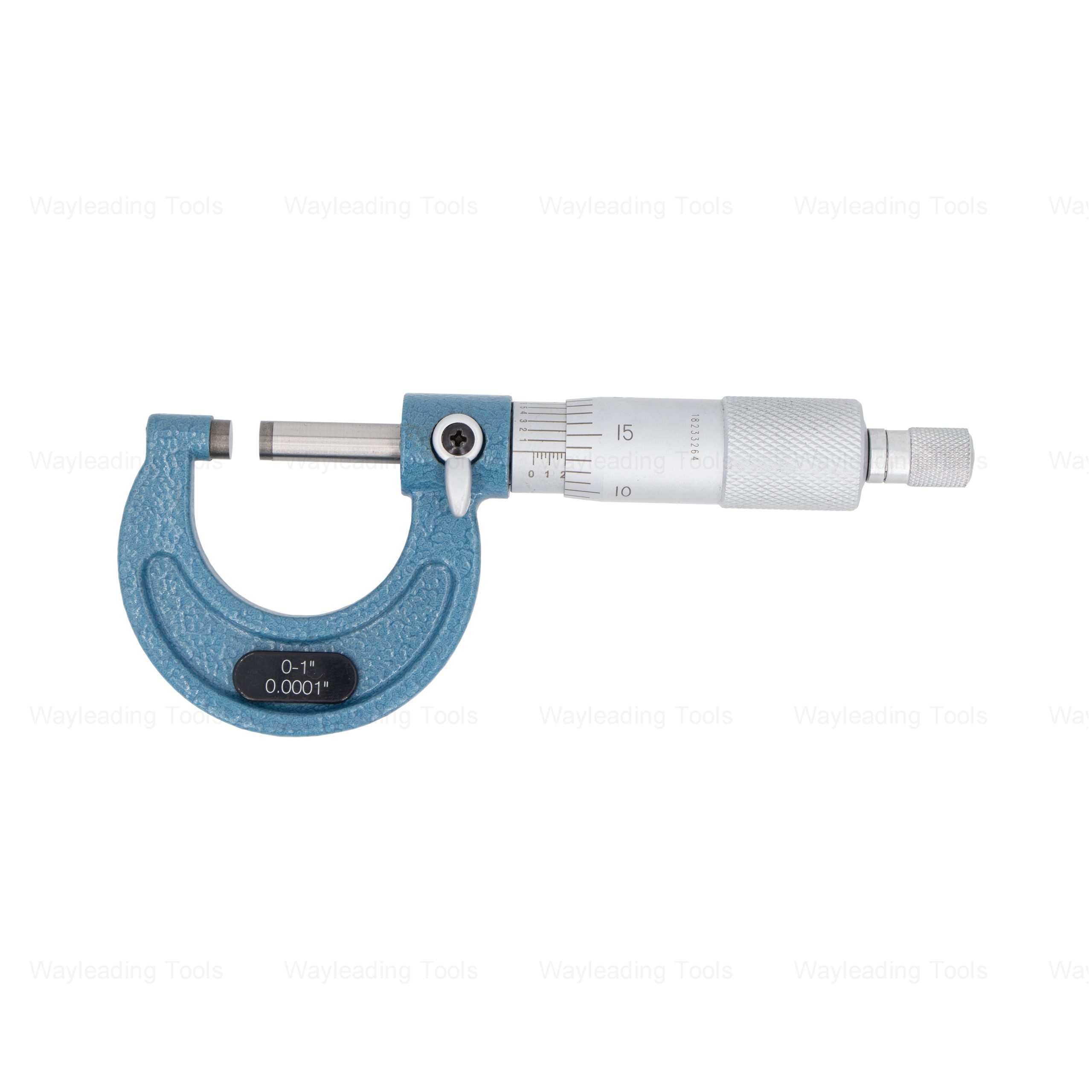 Premium Outside Micrometer – Metric & Inch, Ratchet Stop, Industrial Grade
Premium Outside Micrometer – Metric & Inch, Ratchet Stop, Industrial Grade -
 M42 Bi-Metal Bandsaw Blades For Industrial Type
M42 Bi-Metal Bandsaw Blades For Industrial Type -
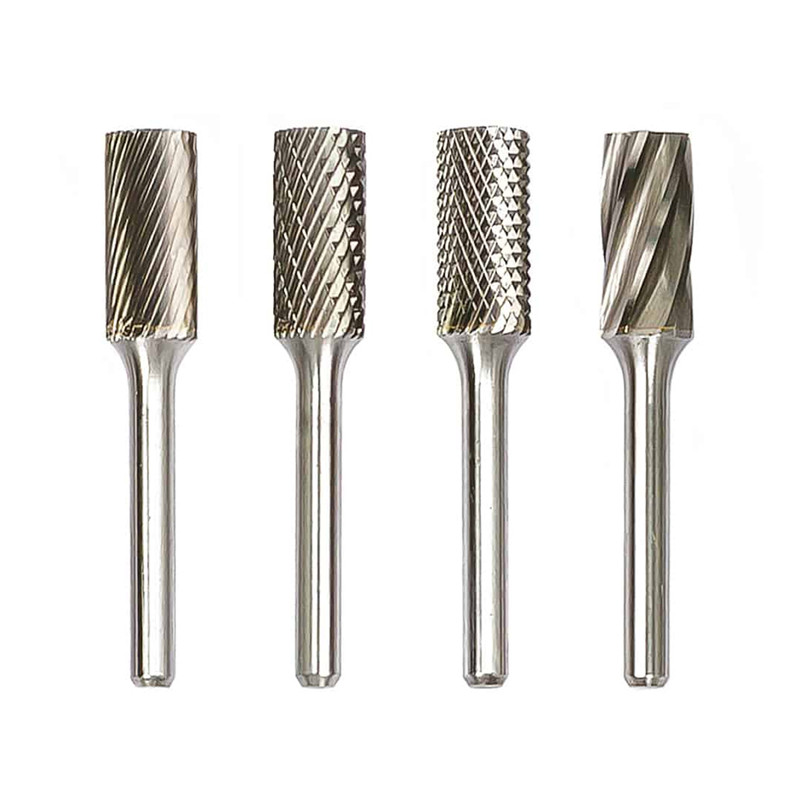 Type A Cylinder Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type A Cylinder Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 Type G Arc Pointed Tree Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type G Arc Pointed Tree Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
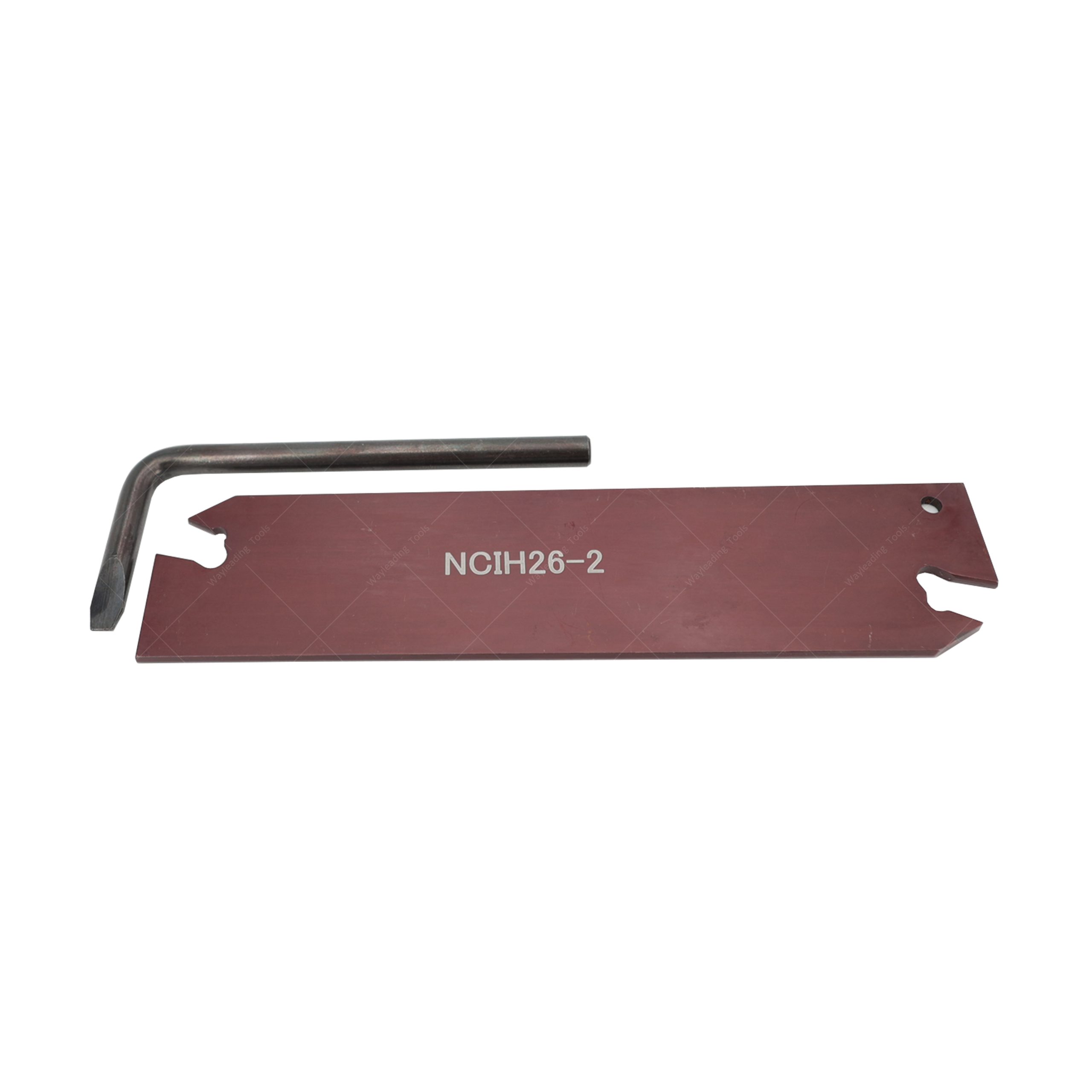 Parting & Grooving Tool Blades For GTN Blades
Parting & Grooving Tool Blades For GTN Blades -
 Precision 5pcs & 6pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 5pcs & 6pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
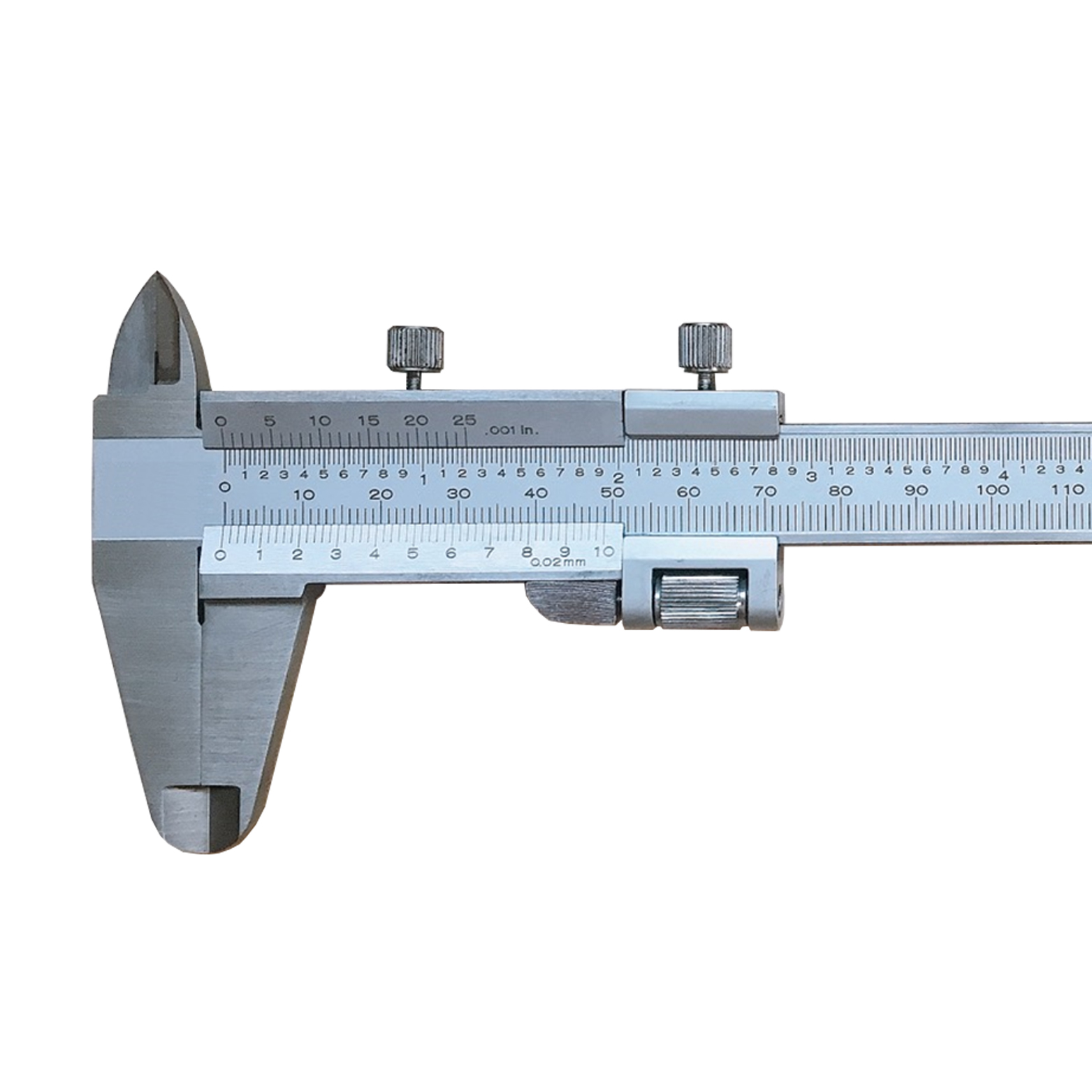 Precision Monoblock Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Monoblock Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 Precision V Block And Clamps Set With High Quality Type
Precision V Block And Clamps Set With High Quality Type -
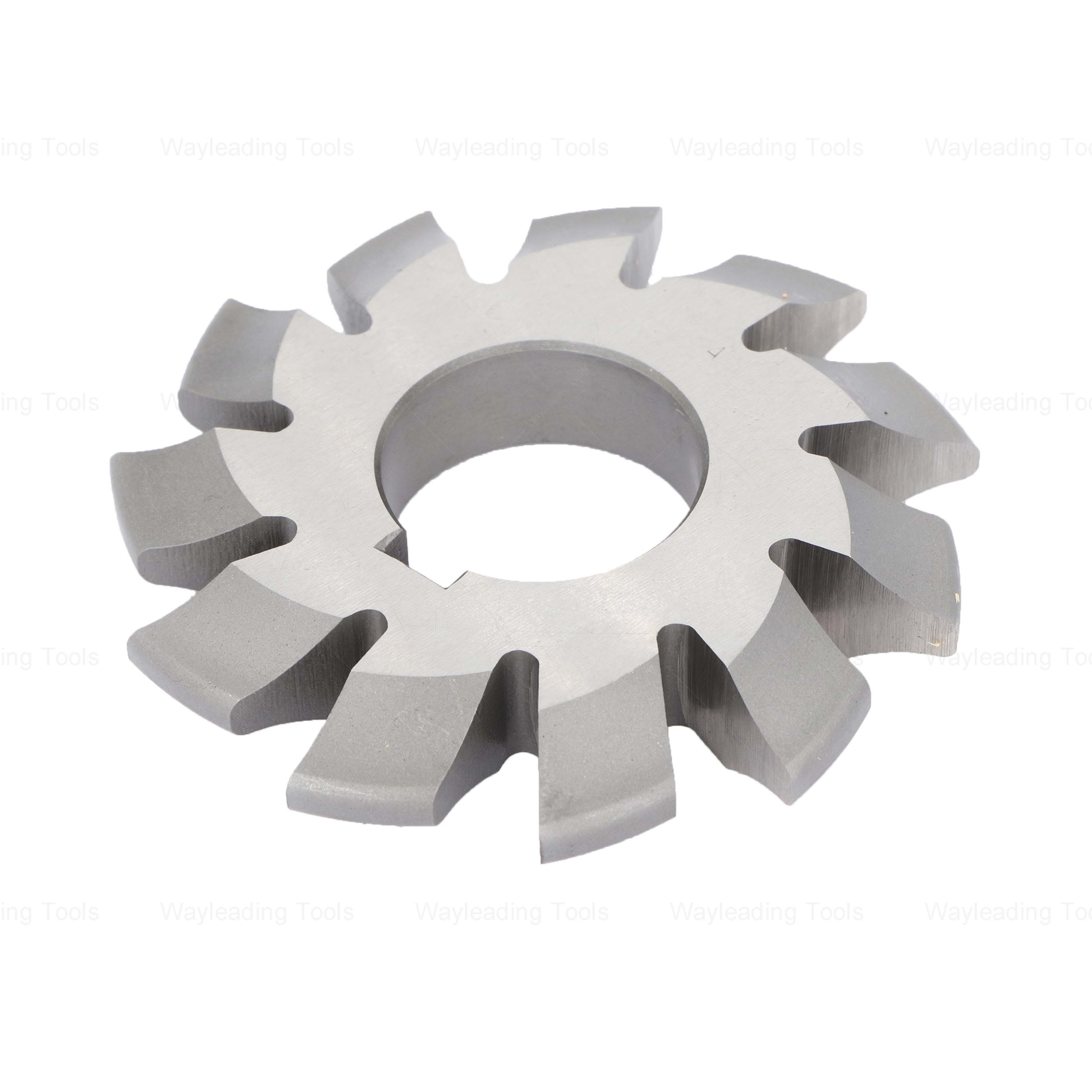 HSS Involute Gear Cutters – Module Type, PA 20° / 14.5°
HSS Involute Gear Cutters – Module Type, PA 20° / 14.5°