thread gauge
A thread gauge, also known as a screw pitch gauge, is a precision tool used to measure the pitch or lead of a screw thread. It assists in identifying the thread size and type on screws, bolts, and tapped holes, crucial for ensuring compatibility and proper fit. This guide explores various types, usage, and selection criteria of thread gauges.Understanding Thread GaugesThread gauges are essential tools in various industries, including machining, manufacturing, and quality control. They provide a quick and accurate way to determine the specifications of a thread, preventing mismatches and ensuring the integrity of threaded connections. These gauges are designed to conform to specific thread standards, such as metric (ISO), Unified National (UN), and British Standard Whitworth (BSW).Types of Thread GaugesThere are several types of thread gauges, each designed for specific applications: Pitch Gauges (Screw Pitch Gauges): These are the most common type, consisting of a set of blades with different thread pitches. The user tries different blades until one fits snugly into the thread. Thread Plug Gauges: These are used to check the internal threads of nuts and tapped holes. They have a 'go' end that should screw in easily and a 'no-go' end that should not. Thread Ring Gauges: These are used to check the external threads of screws and bolts. They function similarly to plug gauges, with 'go' and 'no-go' ends. Taper Thread Gauges: Specifically designed for tapered threads, commonly used in pipe fittings. Digital Thread Gauges: Electronic gauges that provide a digital readout of the thread parameters, offering higher precision and ease of use.How to Use a Thread GaugeUsing a thread gauge is a straightforward process: Identify the Thread Type (if known): Determine whether the thread is metric, UN, or another standard. This will narrow down the appropriate blades on a pitch gauge. Select a Blade: Start with a blade that seems close to the thread pitch. Align and Test: Place the blade's teeth against the thread. Hold it up to a light source to see how well the blade's teeth match the thread on the fastener. Check for Fit: If the blade fits snugly without any light visible between the blade and the thread, you've found the correct pitch. If the blade doesn't fit, try another blade. Read the Marking: Once you find the correct fit, read the marking on the blade to determine the thread pitch (e.g., 1.5mm, 1/4-20 UNC).Selecting the Right Thread GaugeChoosing the appropriate thread gauge depends on your specific needs and the types of threads you'll be measuring: Thread Standard: Ensure the gauge is compatible with the thread standards you'll be working with (e.g., metric, UN, BSW). Measurement Range: Consider the range of thread pitches you need to measure. Some gauges cover a wider range than others. Accuracy: Choose a gauge with the appropriate accuracy for your application. Digital gauges typically offer higher accuracy. Durability: Look for a gauge made from high-quality materials that can withstand frequent use. Ease of Use: Consider the ergonomics and ease of use, especially if you'll be using the gauge frequently.Thread Gauge Standards and SpecificationsThread gauges adhere to various industry standards to ensure accuracy and interchangeability. Key standards include: ISO Standards: International Organization for Standardization, defines metric thread standards. ANSI/ASME Standards: American National Standards Institute/American Society of Mechanical Engineers, defines Unified National thread standards. BS Standards: British Standards, defines British Standard Whitworth and other thread standards.Examples of Thread Gauges and Their ApplicationsHere are a few examples of commercially available thread gauges: Gauge Type Description Typical Application Screw Pitch Gauge Set A set of blades for measuring various metric and inch thread pitches. Identifying thread sizes on fasteners. Thread Plug Gauge 'Go/No-Go' gauge for verifying internal threads. Checking the accuracy of tapped holes. Thread Ring Gauge 'Go/No-Go' gauge for verifying external threads. Checking the accuracy of manufactured bolts and screws. Maintenance and Care of Thread GaugesProper maintenance ensures the accuracy and longevity of your thread gauges: Cleaning: Regularly clean the gauge with a soft cloth to remove dirt and debris. Storage: Store the gauge in a protective case to prevent damage. Calibration: Periodically calibrate the gauge to ensure accuracy, especially for critical applications. Handling: Avoid dropping or subjecting the gauge to excessive force.Where to Buy Thread GaugesThread gauges can be purchased from various sources, including: Industrial Supply Stores: These stores offer a wide selection of gauges and other measuring tools. Online Retailers: Websites like Amazon, and specialized tool vendors such as Wayleading Tools, offer a convenient way to purchase gauges. Machinery Dealers: Dealers who sell machine tools often carry measuring instruments like thread gauges.ConclusionA thread gauge is an indispensable tool for anyone working with threaded fasteners. Understanding the different types of gauges, how to use them, and how to select the right one for your needs is crucial for ensuring accurate and reliable results. Whether you're a professional machinist or a DIY enthusiast, a thread gauge is a valuable addition to your toolbox.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 Type M Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type M Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 Camlock ER Collet Fixture With Lathe Collet Chuck
Camlock ER Collet Fixture With Lathe Collet Chuck -
 Precision 5pcs & 6pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 5pcs & 6pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
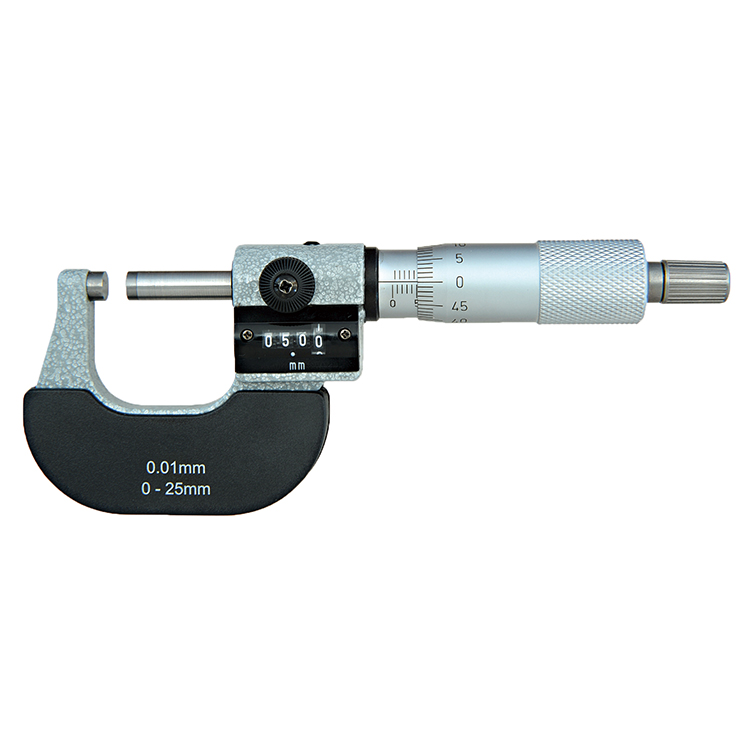 Precision Outside Micrometer With digit Counter Of Inch & Metric With Rachet Stop
Precision Outside Micrometer With digit Counter Of Inch & Metric With Rachet Stop -
 ER Collet Set With Hight Precision Milling
ER Collet Set With Hight Precision Milling -
 Precision Digital Bore Guage From 6-450mm Range
Precision Digital Bore Guage From 6-450mm Range -
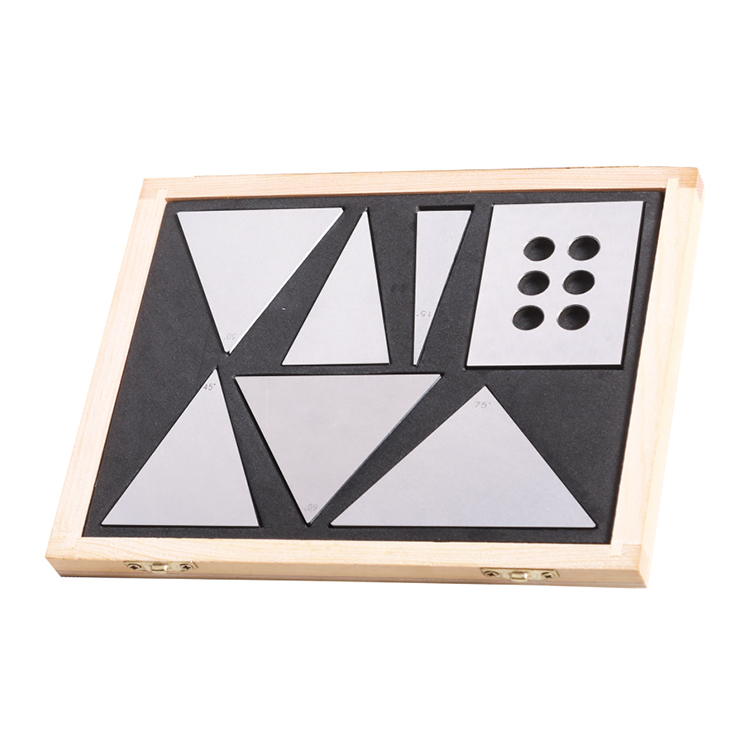 Precision 7pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 7pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
 Precision V Block Set With High Quality Type
Precision V Block Set With High Quality Type -
 ANSI B94 HSS Jobber Length Drill Bits Fully Ground
ANSI B94 HSS Jobber Length Drill Bits Fully Ground -
 HSS Metric Taper Shank Twist Drills for High-Precision Metal Cutting
HSS Metric Taper Shank Twist Drills for High-Precision Metal Cutting -
 DIN6537L Metric Solid Carbide Twist Drill With Internal Coolant & External Coolant
DIN6537L Metric Solid Carbide Twist Drill With Internal Coolant & External Coolant -
 HSS Inch Plain Metal Slitting Saws For Industrial
HSS Inch Plain Metal Slitting Saws For Industrial











