thread milling insert
Thread milling inserts are essential cutting tools used in thread milling operations to create internal and external threads on various materials. This guide provides a detailed overview of thread milling inserts, covering their types, materials, applications, selection criteria, and best practices for optimal performance. Understanding Thread Milling InsertsThread milling is a machining process that uses a rotating milling cutter to produce threads. It offers advantages over tapping, especially for large diameter threads, blind holes, and difficult-to-machine materials. Thread milling inserts are the replaceable cutting elements of the thread milling cutter.Types of Thread Milling InsertsThread milling inserts are categorized based on several factors, including their shape, thread profile, and coating.By Shape Full Profile Inserts: These inserts machine the entire thread profile in a single pass, offering high productivity. Single Point Inserts: These inserts machine one thread at a time, providing greater flexibility and the ability to create custom thread profiles.By Thread Profile ISO Metric Inserts: Designed for machining ISO metric threads, the most common thread standard globally. UN Inserts: Used for machining Unified National threads (UN, UNC, UNF, UNEF). NPT/NPTF Inserts: Specifically for National Pipe Taper (NPT) and National Pipe Taper Fuel (NPTF) threads, commonly used in plumbing and fluid power applications. ACME Inserts: Used for ACME threads, which are trapezoidal threads used in power transmission applications. BSPT/BSPP Inserts: Designed for British Standard Pipe Taper (BSPT) and British Standard Pipe Parallel (BSPP) threads.Materials Used in Thread Milling InsertsThe choice of insert material is crucial for tool life and machining performance. The most common materials are: Carbide: Provides excellent wear resistance and is suitable for a wide range of materials. It is the most widely used material for thread milling inserts. Coated Carbide: Carbide inserts with coatings such as TiN (Titanium Nitride), TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride), or AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride) offer improved hardness, heat resistance, and lubricity. These coatings extend tool life and allow for higher cutting speeds. Cermet: A composite material of ceramic and metal, offering a good balance of hardness and toughness.Coatings for Thread Milling InsertsCoatings significantly impact the performance of thread milling inserts. Common coatings include: TiN (Titanium Nitride): A general-purpose coating that improves wear resistance and tool life. TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride): Offers higher hardness and wear resistance than TiN, suitable for abrasive materials. AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride): Provides excellent heat resistance and is ideal for high-speed machining and hard materials. CrN (Chromium Nitride): Offers good wear resistance and is particularly effective for machining aluminum and non-ferrous materials. Diamond Coating (CVD/PCD): Extremely hard and wear-resistant, suitable for machining highly abrasive materials such as composites and non-ferrous metals. Note: CVD diamond coatings are chemical vapor deposition, PCD coatings are polycrystalline diamond.Applications of Thread Milling InsertsThread milling with appropriate thread milling inserts is used in various industries and applications: Aerospace: Manufacturing threaded components for aircraft engines and structures. Automotive: Creating threads in engine blocks, cylinder heads, and other automotive parts. Medical: Machining threads on medical implants and instruments. Oil & Gas: Producing threads on pipes, valves, and other oilfield equipment, often requiring NPT or other specialized threads. Mold & Die: Creating threads in mold cavities and die components. General Machining: A versatile solution for threading in a wide range of materials and applications.Selecting the Right Thread Milling InsertChoosing the correct thread milling insert is crucial for achieving optimal results. Consider the following factors: Thread Type and Size: Ensure the insert matches the required thread standard (ISO, UN, NPT, etc.) and pitch. Workpiece Material: Select an insert material and coating suitable for the material being machined (e.g., carbide for steel, coated carbide for stainless steel, diamond coating for aluminum). Machine Setup: Consider the machine's capabilities (speed, feed, rigidity) and choose an insert that can operate within those parameters. Internal vs. External Threading: Select inserts specifically designed for internal or external threading. Number of Flutes: Choose based on desired feed rate and finish.Best Practices for Thread MillingFollowing these best practices will help maximize the performance and lifespan of your thread milling inserts: Proper Tool Holding: Use a rigid and accurate tool holder to minimize vibration and ensure precise thread creation. Wayleading Tools offers a variety of tool holders designed for demanding applications. Correct Cutting Parameters: Use the manufacturer's recommended cutting speeds and feeds for the chosen insert and workpiece material. Adjust as needed based on your specific application and machine. Coolant Application: Apply coolant effectively to dissipate heat and lubricate the cutting zone, extending tool life. Chip Evacuation: Ensure efficient chip removal to prevent chip re-cutting and improve surface finish. Regular Inspection: Inspect thread milling inserts regularly for wear and replace them as needed to maintain thread quality. Threading Strategy: Employ strategies like climb milling to improve surface finish and tool life.Troubleshooting Common IssuesHere are some common problems encountered during thread milling and their potential solutions: Poor Surface Finish: Check cutting parameters, tool wear, and coolant application. Consider using a higher quality insert. Premature Tool Wear: Reduce cutting speeds and feeds, ensure proper coolant application, and consider using a more wear-resistant insert coating. Chipping or Breakage: Reduce cutting speeds and feeds, ensure proper tool holding, and consider using a tougher insert grade. Oversized or Undersized Threads: Calibrate the machine, check the insert dimensions, and adjust the tool path accordingly.Where to Buy Thread Milling InsertsHigh-quality thread milling inserts are available from various suppliers. Consider these factors when choosing a supplier: Reputation and Experience: Choose a supplier with a proven track record and extensive experience in cutting tools. Product Range: Ensure the supplier offers a wide range of inserts to meet your specific needs. Technical Support: Select a supplier that provides technical support and application assistance. Price and Availability: Compare prices and ensure the inserts are readily available.ConclusionThread milling inserts are vital components for efficient and accurate thread production. By understanding the different types of inserts, materials, coatings, and best practices, you can optimize your thread milling operations and achieve superior results. Whether you need ISO metric, UN, or NPT threads, selecting the right thread milling insert is key to success. Contact Wayleading Tools for expert advice and a wide selection of high-quality cutting tools. Our experienced team can help you choose the perfect insert for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and extended tool life. Explore our range of thread milling inserts at www.wayleading.com. Insert Type Material Coating Typical Application Full Profile ISO Metric Carbide TiCN General purpose threading in steel Single Point UN Coated Carbide AlTiN Threading in stainless steel and high-temperature alloys NPT Carbide Uncoated Threading in cast iron and non-ferrous materials References: Sandvik Coromant - Thread Milling Kennametal - Threading Tools Mitsubishi Materials - Threading Tools
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 HSS Metric & Inch T Slot End Mill For Industrial
HSS Metric & Inch T Slot End Mill For Industrial -
 25PCS DIN338 HSS Twist Drill Bit Set From 1-13mm
25PCS DIN338 HSS Twist Drill Bit Set From 1-13mm -
 Partial profile 60° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type
Partial profile 60° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type -
 Type G Arc Pointed Tree Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type G Arc Pointed Tree Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 Precision Straight Shank To Morse Taper Adapter
Precision Straight Shank To Morse Taper Adapter -
 F1 Precision Boring Head With Metric & Inch
F1 Precision Boring Head With Metric & Inch -
 Type N Inverted Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type N Inverted Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 Indexable External Threading Tool Holder – SER / SEL, Metric & Inch
Indexable External Threading Tool Holder – SER / SEL, Metric & Inch -
 HSS Inch Concave Milling Cutter For Industrial
HSS Inch Concave Milling Cutter For Industrial -
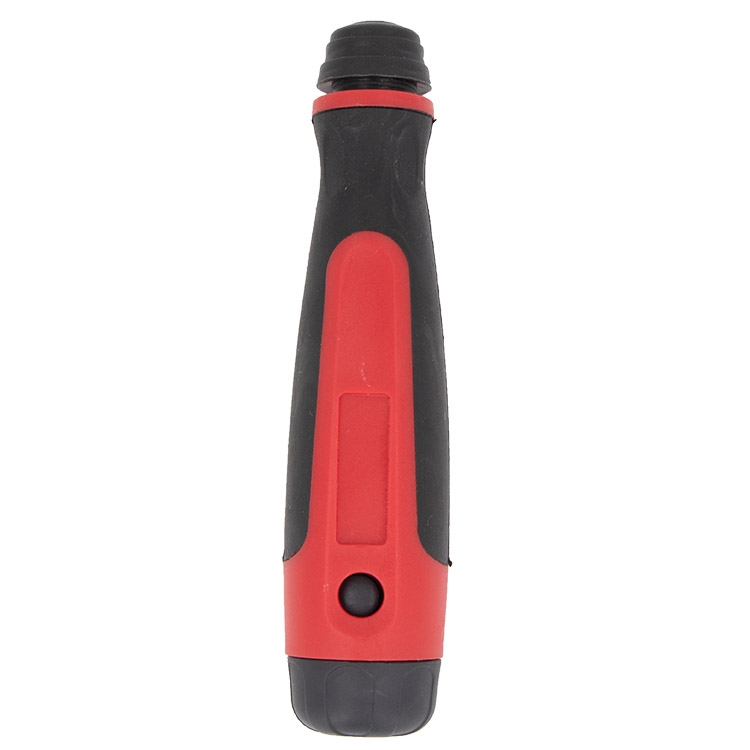 Deburring Tool Holder For The Deburring Tool Blades
Deburring Tool Holder For The Deburring Tool Blades -
 MCLN Indexable Turning Tool Holder – Right- and Left-Hand Types
MCLN Indexable Turning Tool Holder – Right- and Left-Hand Types -
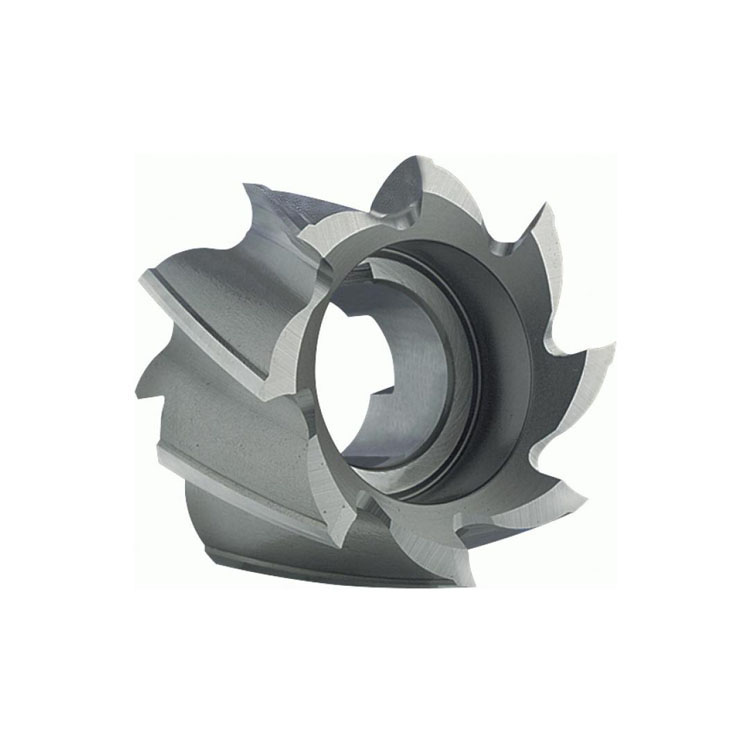 HSS Shell End Mill Cutter With Bright & TiN Or TiAlN Coated
HSS Shell End Mill Cutter With Bright & TiN Or TiAlN Coated
Related search
Related search- end mill adapter Suppliers
- 30pcs indexable boring bar set Factories
- 3pcs mini indexable end mills Factory
- Corner Rounding End Mill set Manufacturers
- SDUC boring bar Factory
- G60 threading insert Manufacturer
- w threading insert
- quick change tool holder Manufacturer
- Deburring Tool Factory
- ER insert Manufacturer








