Thread Plug Gauge
A thread plug gauge is a precision measuring tool used to inspect the internal threads of a workpiece, ensuring they meet specified tolerances for size and form. It's an essential tool for quality control in manufacturing, ensuring proper fit and function of threaded components.Understanding Thread Plug GaugesThread plug gauges, also known as GO/NO-GO gauges, are designed to quickly and accurately determine if an internal thread is within acceptable limits. They consist of two ends: a GO end and a NO-GO end.The GO EndThe GO end of the thread plug gauge is designed to screw easily and completely into a properly threaded hole. It checks the lower limit of the thread size.The NO-GO EndThe NO-GO end is designed to only enter a short distance into a properly threaded hole (typically no more than two turns). It checks the upper limit of the thread size. If the NO-GO end enters more than the specified distance, the thread is too large.Types of Thread Plug GaugesSeveral types of thread plug gauges are available, each suited for different applications. Here are a few common types: Standard Thread Plug Gauges: These are the most common type and are used for general-purpose thread inspection. Wire Thread Insert (STI) Gauges: Specifically designed for inspecting threads used with wire thread inserts (also known as Heli-Coils). Tapered Thread Plug Gauges: Used for inspecting tapered threads, such as those found in pipe fittings. ACME Thread Plug Gauges: Designed for inspecting ACME threads, commonly used in lead screws and other power transmission applications. Buttress Thread Plug Gauges: Used for inspecting buttress threads, which are designed to withstand high axial loads in one direction.Benefits of Using Thread Plug GaugesUsing thread plug gauges offers several advantages in manufacturing and quality control: Accuracy: Provides a precise and reliable method for inspecting internal threads. Efficiency: Allows for quick and easy inspection, saving time and labor costs. Consistency: Ensures that all threaded parts meet the required specifications, leading to consistent product quality. Cost-effectiveness: Helps prevent costly defects and rework by identifying out-of-tolerance threads early in the manufacturing process.How to Use a Thread Plug GaugeUsing a thread plug gauge is relatively straightforward, but it's important to follow these steps for accurate results: Clean the Thread: Ensure the internal thread being inspected is clean and free of debris. Inspect the Gauge: Check the thread plug gauge for any damage or wear. Insert the GO End: Screw the GO end of the gauge into the thread. It should screw in smoothly and completely with only finger pressure. Insert the NO-GO End: Try to screw the NO-GO end into the thread. It should not enter more than two turns. Interpret the Results: If the GO end goes in and the NO-GO end doesn't go in more than two turns, the thread is within tolerance. If the GO end doesn't go in, the thread is too small. If the NO-GO end goes in more than two turns, the thread is too large.Factors to Consider When Choosing a Thread Plug GaugeSelecting the right thread plug gauge is crucial for accurate and reliable thread inspection. Consider the following factors: Thread Type and Size: Ensure the gauge matches the thread type (e.g., Metric, Unified National) and size being inspected. Tolerance Class: Choose a gauge with the appropriate tolerance class for the application. Material: Select a gauge made from high-quality materials, such as hardened steel, for durability and accuracy. Coating: Consider a gauge with a coating, such as titanium nitride (TiN), for increased wear resistance. Manufacturer: Choose a reputable manufacturer known for producing high-quality gauges. Wayleading Tools offers a wide selection of precision gauges.Troubleshooting Common IssuesSometimes, you may encounter issues when using thread plug gauges. Here are some common problems and their solutions: Gauge Won't Screw In: The thread may be damaged, dirty, or the wrong size. Clean the thread and ensure the gauge is the correct size and type. Gauge Feels Loose: The thread may be worn or oversized. Inspect the thread for damage and consider using a different gauge with a tighter tolerance. Inconsistent Results: Ensure the gauge is clean and in good condition. Also, make sure you're using the gauge correctly and applying only finger pressure.Maintaining Your Thread Plug GaugesProper maintenance is essential for ensuring the accuracy and longevity of your thread plug gauges: Clean Regularly: Clean the gauges after each use with a clean, lint-free cloth. Store Properly: Store the gauges in a protective case or container to prevent damage. Lubricate: Apply a light coat of oil to the gauges to prevent rust. Calibrate Periodically: Have the gauges calibrated periodically to ensure their accuracy.Thread Plug Gauge StandardsSeveral standards govern the design, manufacture, and use of thread plug gauges. Some of the most common standards include: ANSI/ASME B1.2: Standard for Gages and Gaging for Unified Inch Screw Threads. ISO 1502: General purpose metric screw threads -- Gauging. DIN Standards: A series of German standards for various thread types and gauging systems.Where to Buy Thread Plug GaugesThread plug gauges can be purchased from various sources, including: Industrial Supply Stores: Local industrial supply stores often carry a selection of thread plug gauges. Online Retailers: Many online retailers specialize in precision measuring tools and offer a wide variety of gauges. Gauge Manufacturers: Purchasing directly from a gauge manufacturer, such as Wayleading Tools, ensures you get high-quality products and expert support.Example Data Table of Common Thread SizesHere's a simple example of common thread sizes and their corresponding pitch: Thread Size Pitch (mm) M6 x 1.0 1.0 M8 x 1.25 1.25 M10 x 1.5 1./4-20 UNC 1.27 (estimated) Note: Pitch values for UNC threads are typically given in threads per inch (TPI), requiring conversion to millimeters for direct comparison.ConclusionThread plug gauges are essential tools for ensuring the quality and accuracy of internal threads. By understanding the different types of gauges, how to use them properly, and how to maintain them, you can ensure that your threaded components meet the required specifications. Remember to source your thread plug gauges from reputable suppliers like Wayleading Tools to guarantee accuracy and reliability.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
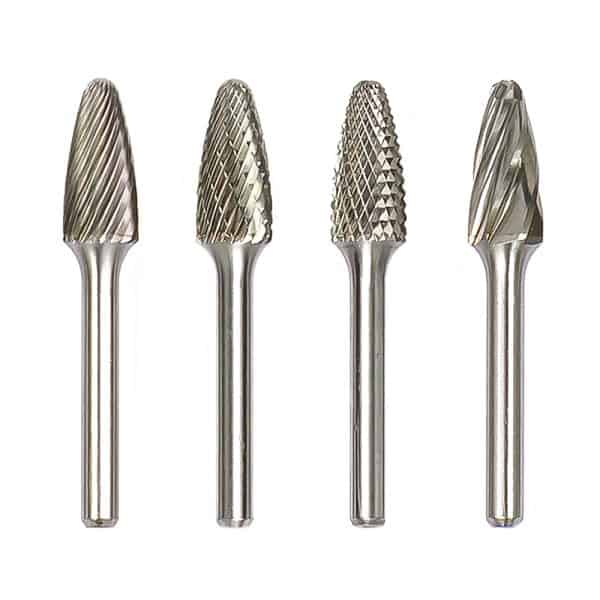
 Type M Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type M Cone Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
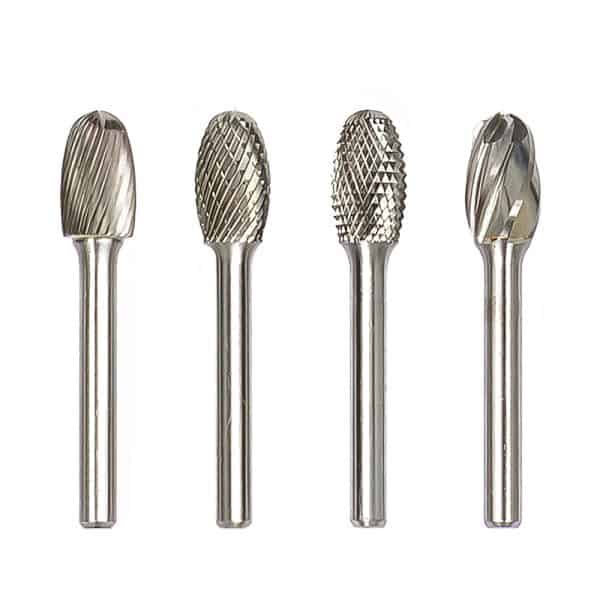 Type E Oval Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type E Oval Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 HSS Metric & Inch Woodruff Keyseat Cutter With Straight Or staggered Teeth
HSS Metric & Inch Woodruff Keyseat Cutter With Straight Or staggered Teeth -
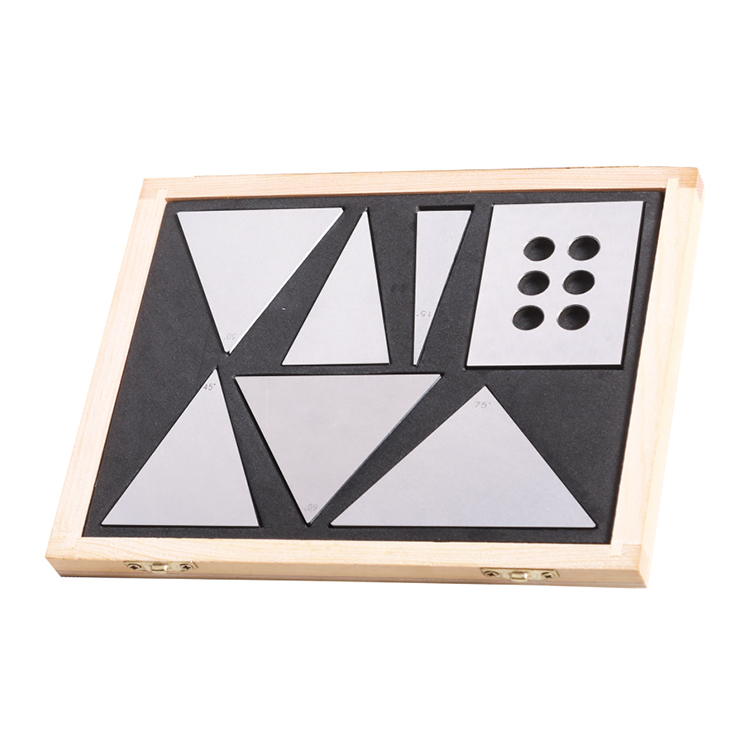 Precision 7pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type
Precision 7pcs Angle Blocks Set With High Quality Type -
 ANSI B94 HSS Jobber Length Drill Bits Fully Ground
ANSI B94 HSS Jobber Length Drill Bits Fully Ground -
 Wedge Type Quick Change Tool Post Set In lathe Machine
Wedge Type Quick Change Tool Post Set In lathe Machine -
 Precision Monoblock Vernier Caliper With Nib Style Jaws Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Monoblock Vernier Caliper With Nib Style Jaws Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 Precision Magnetic Base With Fine Adjustment For Dial Indicator
Precision Magnetic Base With Fine Adjustment For Dial Indicator -
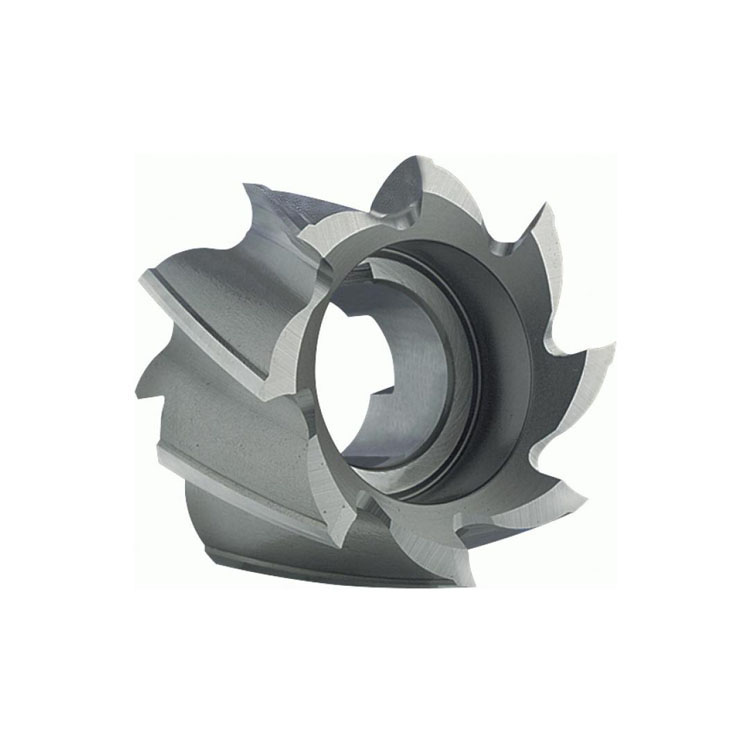 HSS Shell End Mill Cutter With Bright & TiN Or TiAlN Coated
HSS Shell End Mill Cutter With Bright & TiN Or TiAlN Coated -
 Type B Cylinder Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type B Cylinder Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
 Precision V Block And Clamps Set With Heavy Duty
Precision V Block And Clamps Set With Heavy Duty -
 58pcs Clamping Kit With Metric & Inch Size
58pcs Clamping Kit With Metric & Inch Size











