tubing micrometer
A tubing micrometer is a specialized measuring instrument designed to accurately determine the wall thickness of tubes, pipes, and other cylindrical objects. It differs from a standard micrometer in its frame shape and anvil design, allowing access to narrow spaces and precise measurements on curved surfaces. This guide explores the features, applications, and best practices for using a tubing micrometer.What is a Tubing Micrometer?A tubing micrometer, also known as a pipe micrometer, is a precision tool used for measuring the wall thickness of tubing and pipes. It consists of a frame, spindle, anvil, sleeve, thimble, and ratchet stop. The key difference from a standard micrometer is its extended spindle, which allows it to reach inside tubes and measure their wall thickness. The anvil is usually rounded to better contact the curved surface of the tube.Key Features of a Tubing Micrometer Spindle and Anvil: Specifically designed to measure curved surfaces. The spindle is extended for reaching into tubes, and the anvil is often rounded. Frame: Provides a sturdy base and ensures accuracy by maintaining alignment between the spindle and anvil. Sleeve and Thimble: Marked with precise graduations to provide accurate readings, typically in increments of 0.001 inches or 0.01 mm. Ratchet Stop: Ensures consistent measuring pressure, preventing over-tightening and inaccurate readings. Locking Device: Holds the spindle in place after a measurement is taken, allowing for easy reading.Applications of Tubing MicrometersTubing micrometers are essential in various industries where accurate measurement of tube wall thickness is critical: Manufacturing: Ensuring that tubes and pipes meet specified dimensions and tolerances. Automotive: Measuring brake lines, fuel lines, and exhaust pipes. Aerospace: Verifying the integrity of hydraulic lines and structural tubing. Plumbing and HVAC: Checking the wall thickness of water pipes and refrigerant lines. Medical Device Manufacturing: Measuring the wall thickness of small tubes used in medical devices, a field where Wayleading Tools provides high-quality instruments.How to Use a Tubing MicrometerUsing a tubing micrometer requires careful attention to detail to ensure accurate measurements. Here’s a step-by-step guide: Calibration: Before use, calibrate the micrometer using a gauge block or a known standard to verify its accuracy. Preparation: Clean the tube and the micrometer's measuring surfaces to remove any dirt or debris that could affect the reading. Positioning: Place the tube between the spindle and anvil of the micrometer, ensuring the rounded anvil properly contacts the inner surface of the tube. Adjustment: Rotate the thimble until the spindle gently contacts the tube wall. Use the ratchet stop to apply consistent pressure. Reading: Lock the spindle in place using the locking device. Read the measurement from the sleeve and thimble. Recording: Record the measurement, noting the units (inches or millimeters) and any relevant details.Tips for Accurate Measurements Consistent Pressure: Always use the ratchet stop to apply consistent pressure, which helps avoid over-tightening and inaccurate readings. Proper Alignment: Ensure the tube is properly aligned between the spindle and anvil to avoid skewed measurements. Regular Calibration: Calibrate the micrometer regularly to maintain its accuracy. Cleanliness: Keep the measuring surfaces clean and free of debris. Multiple Measurements: Take multiple measurements at different points around the tube’s circumference to check for variations in wall thickness.Types of Tubing MicrometersWhile the basic principle remains the same, tubing micrometers come in different types to suit various applications: Mechanical Tubing Micrometers: Traditional micrometers with analog scales. Reliable and cost-effective, but require manual reading. Digital Tubing Micrometers: Feature digital displays that provide direct readings, eliminating the need for manual interpretation. Offer enhanced accuracy and convenience. Deep-Reach Tubing Micrometers: Designed with extra-long spindles to reach deep inside tubes and pipes. Pointed Anvil Tubing Micrometers: Feature a pointed anvil for measuring the wall thickness of small-diameter tubes or in hard-to-reach areas.Choosing the Right Tubing MicrometerSelecting the right tubing micrometer depends on your specific needs and application. Consider the following factors: Measurement Range: Ensure the micrometer has a measurement range that accommodates the tube sizes you will be working with. Accuracy: Choose a micrometer with the appropriate accuracy for your application. Digital micrometers generally offer higher accuracy than mechanical models. Resolution: Consider the resolution of the micrometer. Common resolutions are 0.001 inches or 0.01 mm. Type of Display: Decide whether you prefer a traditional analog scale or a digital display. Digital displays offer easier reading and enhanced accuracy. Durability: Look for a micrometer made from high-quality materials that can withstand regular use in your work environment. Features: Consider additional features such as a ratchet stop, locking device, and data output capabilities.Maintenance and CareProper maintenance and care are essential to ensure the longevity and accuracy of your tubing micrometer: Cleaning: Regularly clean the micrometer's measuring surfaces with a soft cloth to remove any dirt or debris. Lubrication: Apply a small amount of oil to the spindle and thimble threads to ensure smooth operation. Storage: Store the micrometer in a protective case to prevent damage. Calibration: Calibrate the micrometer regularly, especially after heavy use or if you suspect it has been damaged. Avoid Dropping: Handle the micrometer with care and avoid dropping it, as this can damage the instrument and affect its accuracy.Tubing Micrometer vs. CaliperWhile both tubing micrometers and calipers are used for measuring dimensions, they have distinct differences. Calipers are versatile and can measure both inside and outside diameters, as well as depths. However, tubing micrometers are specifically designed for measuring wall thickness and offer higher precision for this specific task.Here's a simple comparison: Feature Tubing Micrometer Caliper Primary Use Measuring tube wall thickness Measuring inside diameter, outside diameter, depth Accuracy Higher accuracy for wall thickness Generally lower accuracy than micrometers Versatility Limited to measuring wall thickness More versatile, can measure various dimensions ConclusionA tubing micrometer is an indispensable tool for accurately measuring the wall thickness of tubes and pipes. By understanding its features, applications, and best practices for use, you can ensure precise measurements and maintain the integrity of your projects. Whether you are in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, or any other industry that relies on accurate tube measurements, a tubing micrometer is a valuable investment.For high-quality measuring tools, consider exploring the offerings at Wayleading Tools. We are committed to providing precision instruments for various industrial applications.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 HSS Metric Taper Shank Twist Drills for High-Precision Metal Cutting
HSS Metric Taper Shank Twist Drills for High-Precision Metal Cutting -
 ISO Metric Hexagon Die With Right Hand
ISO Metric Hexagon Die With Right Hand -
 SCFC Indexable Boring Bar
SCFC Indexable Boring Bar -
 High Precision BT-ER Collet Chuck – CNC Tool Holder, Spring Type, ER16–ER40
High Precision BT-ER Collet Chuck – CNC Tool Holder, Spring Type, ER16–ER40 -
 Boring Head Shank For Boring Head With Industrial Type
Boring Head Shank For Boring Head With Industrial Type -
 Precision Digital Bore Guage From 6-450mm Range
Precision Digital Bore Guage From 6-450mm Range -
 Wedge Type Quick Change Tool Post Set In lathe Machine
Wedge Type Quick Change Tool Post Set In lathe Machine -
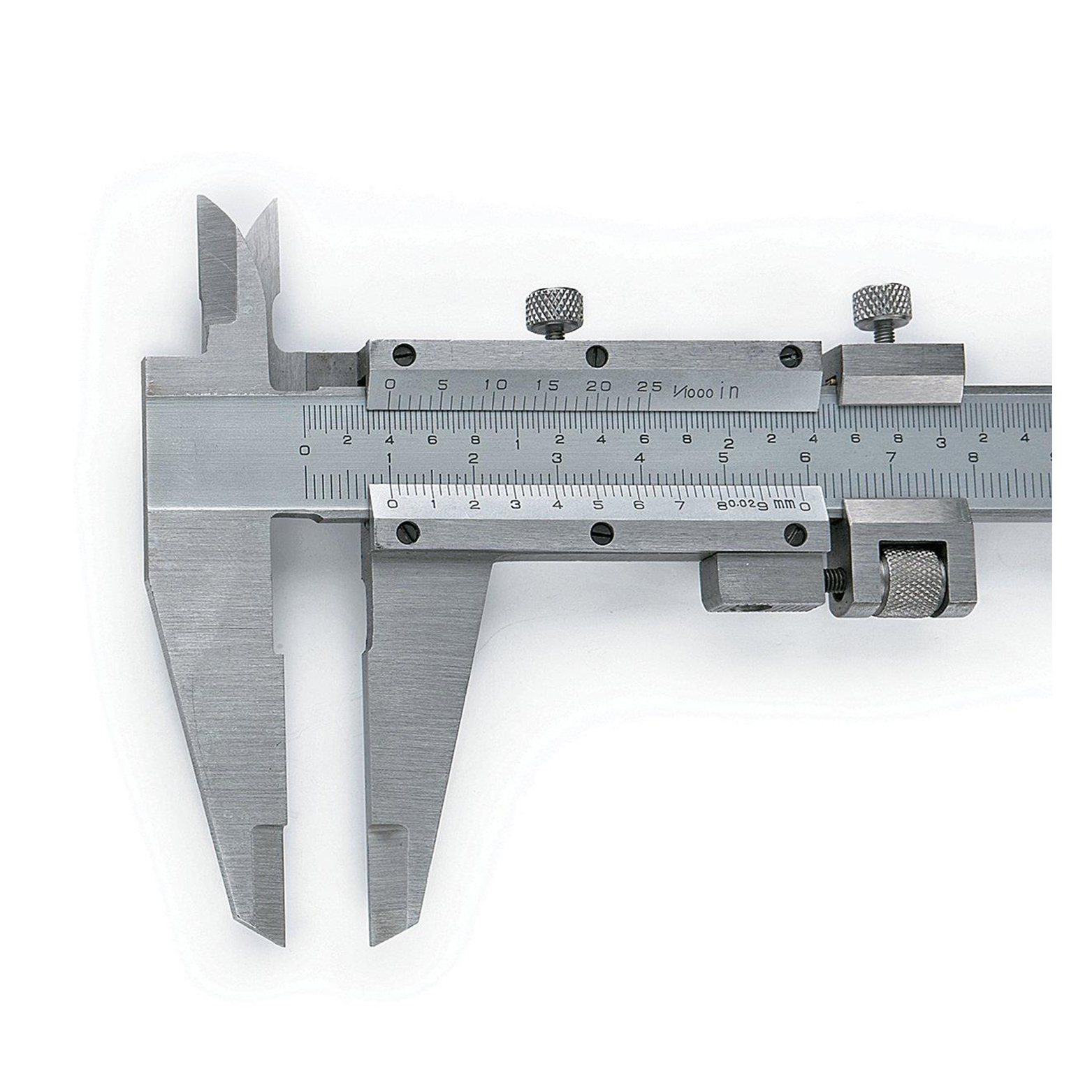 Precision Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
 Outside Micrometer Set Of Inch & Metric For Industrial
Outside Micrometer Set Of Inch & Metric For Industrial -
 Precision V Block Set With Industrial Type
Precision V Block Set With Industrial Type -
 Precision Magnetic Base With Fine Adjustment For Dial Indicator
Precision Magnetic Base With Fine Adjustment For Dial Indicator -
 Type E Heavy Duty Deburring Tool Set With Deburring Holder And Deburring Blade
Type E Heavy Duty Deburring Tool Set With Deburring Holder And Deburring Blade











