turning tool holder
A turning tool holder is a crucial component in lathe machining, securely holding cutting tools and enabling precise and efficient material removal. Choosing the right holder is vital for achieving desired surface finishes, dimensional accuracy, and tool life. This guide explores different types of turning tool holders, their features, selection criteria, and best practices for optimal performance.Understanding Turning Tool HoldersThe turning tool holder is the interface between the lathe and the cutting tool. Its primary function is to rigidly clamp the cutting tool in a precise position, minimizing vibration and ensuring accurate cutting. The holder's design affects machining performance, tool life, and surface finish. Wayleading Tools offers a wide range of turning tool holders to meet diverse machining needs.Types of Turning Tool HoldersVarious turning tool holder types cater to different machining operations and cutting tools. Here's an overview of common types: External Tool Holders: These holders are designed for external turning, facing, and threading operations. They typically feature a clamp or screw mechanism to secure the cutting tool. Internal Tool Holders (Boring Bars): Used for internal machining operations such as boring, internal threading, and grooving. They are designed with a long, slender shank to reach deep inside the workpiece. Quick Change Tool Holders: Allow for rapid tool changes, reducing setup time and increasing machining efficiency. They typically consist of a master holder and interchangeable tool blocks. Indexable Tool Holders: Designed to hold indexable inserts. These holders allow easy insert replacement, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. Swiss-Type Tool Holders: Specifically designed for Swiss-type lathes, these holders often feature specialized clamping mechanisms and coolant delivery systems.Selecting the Right Turning Tool HolderChoosing the correct turning tool holder requires careful consideration of several factors:Machine Type and SizeEnsure the turning tool holder is compatible with your lathe's spindle size and configuration. The holder's shank diameter must match the lathe's tool post or turret.Cutting Tool Type and SizeSelect a holder that can accommodate the size and type of cutting tool you'll be using. Consider the tool's shank size, cutting edge geometry, and application (e.g., turning, facing, threading).Machining OperationThe specific machining operation dictates the required holder type. External turning requires different holders than internal boring or threading. Choose a holder designed for the intended application.Material Being MachinedThe material's hardness and machinability influence the holder's rigidity and vibration damping requirements. Harder materials may require more rigid holders to minimize vibration and chatter.Coolant DeliveryConsider the coolant delivery system. Some turning tool holders feature internal coolant channels to deliver coolant directly to the cutting edge, improving tool life and chip control. Internal coolant is especially important when machining tougher materials.Accuracy and RigidityHigher accuracy and rigidity are crucial for achieving tight tolerances and fine surface finishes. Look for holders made from high-quality materials with precise machining. Check Wayleading Tools for holders built for precision.Turning Tool Holder Materials and ConstructionThe materials used in turning tool holder construction significantly impact their performance and durability. Common materials include: Alloy Steel: Offers a good balance of strength, toughness, and wear resistance. Often used for general-purpose holders. High-Speed Steel (HSS): Provides excellent wear resistance and toughness, suitable for high-speed machining operations. Carbide: Offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, ideal for machining abrasive materials and high-temperature applications.The holder's construction also affects its rigidity and vibration damping characteristics. Solid holders generally offer higher rigidity than modular holders. Look for holders with a robust design and precise machining.Best Practices for Using Turning Tool HoldersFollowing these best practices will help you maximize the performance and lifespan of your turning tool holder: Proper Clamping: Ensure the cutting tool is securely clamped in the holder. Use the correct torque settings to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening. Regular Inspection: Inspect holders regularly for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Replace worn or damaged holders immediately. Cleanliness: Keep holders clean and free from chips, coolant residue, and other contaminants. Clean holders regularly with a brush and solvent. Proper Storage: Store holders in a clean, dry environment to prevent corrosion and damage. Use a tool cabinet or storage rack to protect holders from impact. Coolant Management: Maintain proper coolant concentration and flow rate to optimize cooling and lubrication. Use a coolant filtration system to remove contaminants.Troubleshooting Common Turning Tool Holder ProblemsHere are some common problems encountered with turning tool holders and their solutions: Vibration and Chatter: May be caused by loose clamping, worn holders, or excessive cutting forces. Try tightening the clamping screws, replacing the holder, or reducing the cutting speed and feed rate. Tool Slippage: Indicates inadequate clamping force. Tighten the clamping screws or replace the holder if the clamping mechanism is damaged. Poor Surface Finish: Can result from worn cutting tools, excessive vibration, or improper coolant delivery. Replace the cutting tool, address vibration issues, and optimize coolant flow.Turning Tool Holder MaintenanceProper maintenance is essential for extending the life of your turning tool holders. This includes regular cleaning, inspection, and lubrication. CleaningRemove chips, coolant, and other debris from the holder after each use. Use a soft brush and a mild solvent to clean the holder thoroughly. InspectionInspect the holder for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Pay close attention to the clamping mechanism and the tool holder body. Replace any worn or damaged parts immediately.LubricationLubricate the clamping mechanism and other moving parts regularly with a light oil or grease. This will help to prevent corrosion and ensure smooth operation. Wayleading Tools recommends specific lubricants based on holder type. See their site at www.wayleading.com.The Future of Turning Tool HoldersThe future of turning tool holders is likely to involve further advancements in materials, design, and functionality. Some potential trends include: Smart Tool Holders: Incorporating sensors to monitor cutting forces, vibration, and temperature. This data can be used to optimize machining parameters and predict tool wear. Additive Manufacturing: Using 3D printing to create custom-designed holders with optimized geometries and internal features. Advanced Materials: Exploring new materials such as ceramics and composites to improve holder stiffness, damping, and thermal stability.ConclusionSelecting the right turning tool holder is crucial for achieving efficient and accurate machining. By understanding the different types of holders, considering the application requirements, and following best practices for usage and maintenance, you can optimize your machining operations and improve your productivity. Remember to visit Wayleading Tools for high-quality turning tool holders.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 32 Blades Feeler Gauge From 0.04-0.88MM
32 Blades Feeler Gauge From 0.04-0.88MM -
 5C Hex Collet With Inch and Metric Size
5C Hex Collet With Inch and Metric Size -
 Precision IP67 Digital Caliper With Data Output For Industrial
Precision IP67 Digital Caliper With Data Output For Industrial -
 Partial profile 60° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type
Partial profile 60° Threading Insert With ER & IR Type -
 Precision V Block And Clamps Set With High Quality Type
Precision V Block And Clamps Set With High Quality Type -
 Precision Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial
Precision Fine-Adjustment Vernier Caliper Of Metric & Imperial For Industrial -
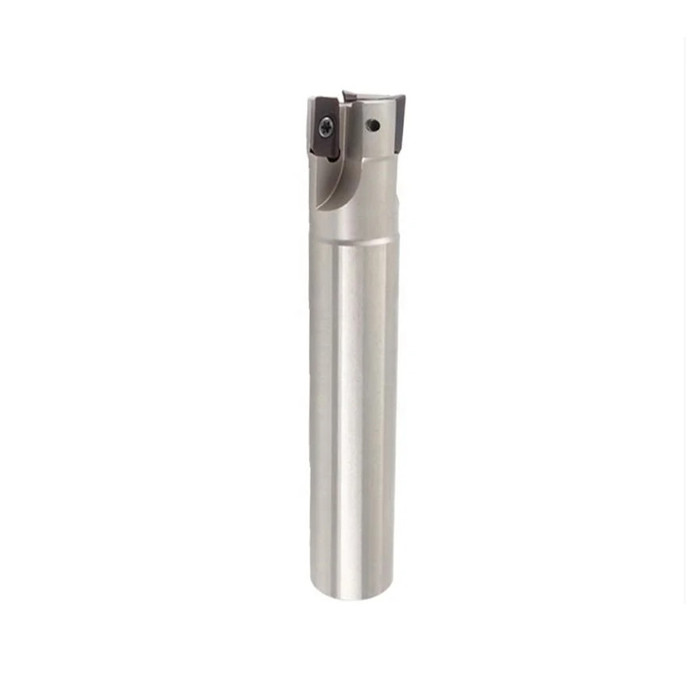 Indexable Square Shoulder End Mill For Industrial
Indexable Square Shoulder End Mill For Industrial -
 High Precision BT-ER Collet Chuck – CNC Tool Holder, Spring Type, ER16–ER40
High Precision BT-ER Collet Chuck – CNC Tool Holder, Spring Type, ER16–ER40 -
 3 Flutes HSS Counterbore Drill Bit With Metric And Inch Size
3 Flutes HSS Counterbore Drill Bit With Metric And Inch Size -
 Type B Cylinder Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr
Type B Cylinder Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burr -
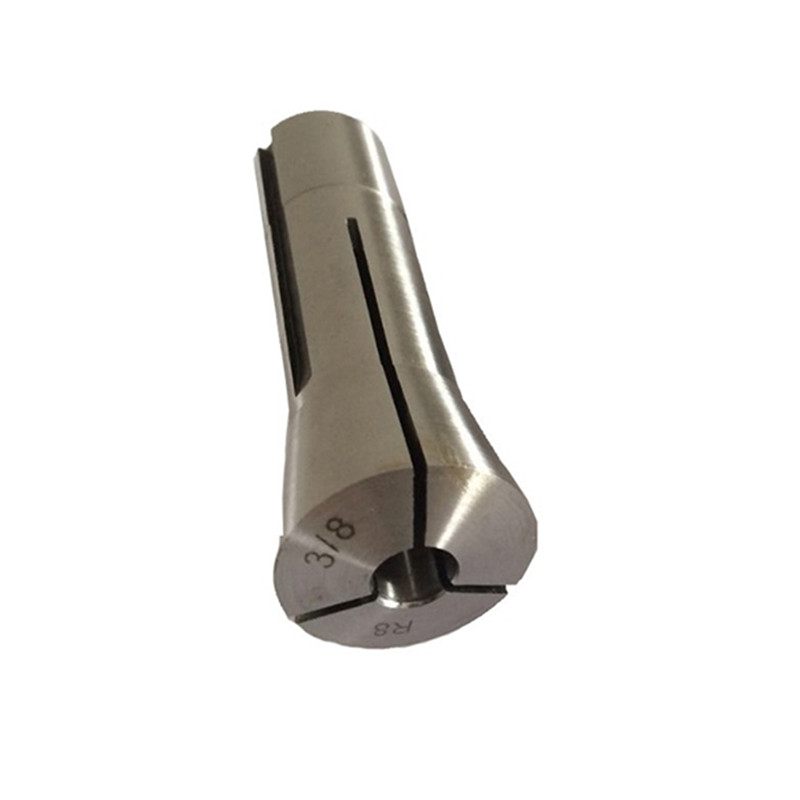 R8 Round Collet With Inch and Metric Size
R8 Round Collet With Inch and Metric Size -
 Key Type Drill Chuck With Heavy Duty Type
Key Type Drill Chuck With Heavy Duty Type